
\[B{F_3}\] does not obey octet rule. State the given statement is True or False
Answer
501k+ views
Hint: We must remember that the octet rule states that atoms below atomic number $20$ tend to combine so that they each have eight electrons in their valence shells, which gives them the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rule is applicable to the main- group elements, especially carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens, but also to metals such as sodium and magnesium.
Complete answer:
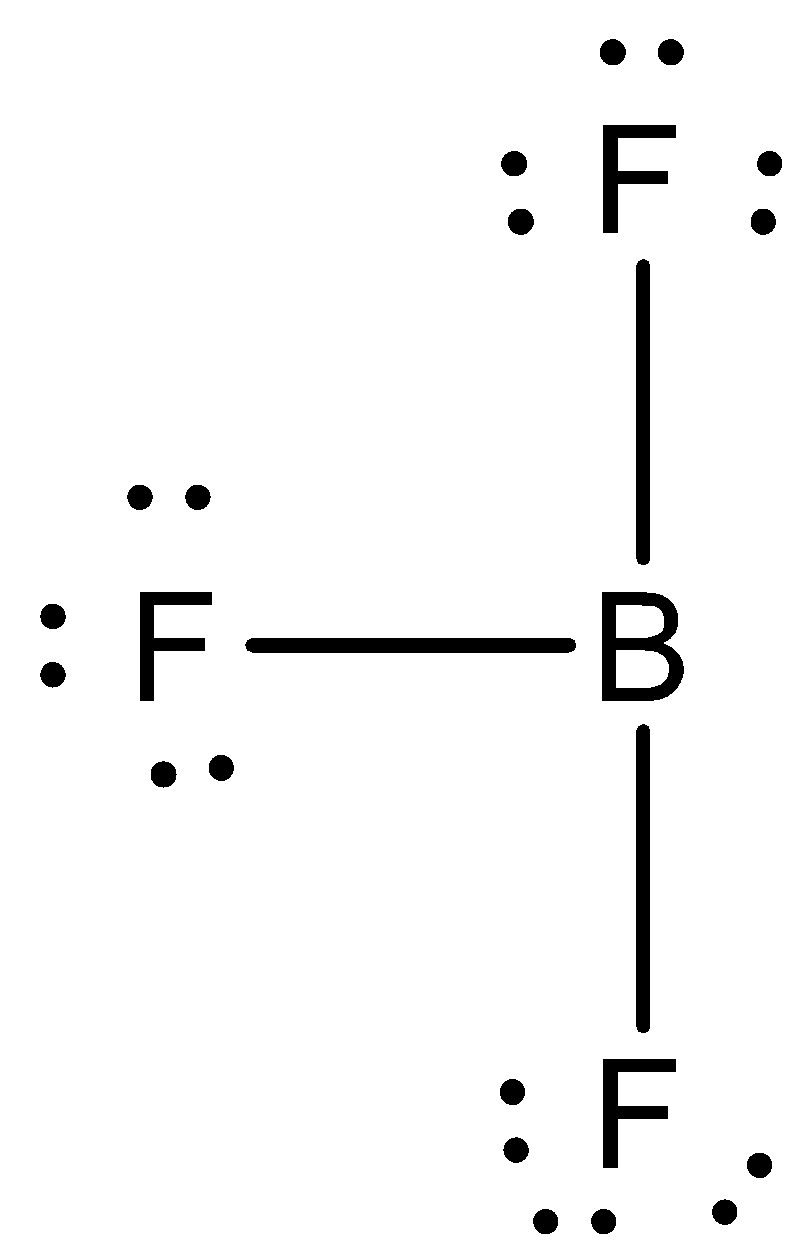
We need to know that the octet rule states that atoms with an atomic number below $20$ tend to combine so that they each have eight electrons in their valence shells, which give them the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The two elements that most commonly fail to complete an octet are boron and aluminum; they both readily form compounds in which they have six valence electrons, rather than the usual eight predicted by the octet rule. When we talk of \[B{F_3}\] molecule, $F$ completes its octet by sharing one electron from 'Boron' While 'Boron' shares three electron from three $'F'$ atom and has only $6$ electrons in outermost cell thus it has an incomplete octet.
In boron trifluoride (\[B{F_3}\]),the bonding is relatively simple to model with a Lewis structure if we allow each valence level electron in the boron atom to be shared in a covalent bond with each fluorine atom. In this compound, the boron atom only has six valence shell electrons, but the octet rule is satisfied by the fluorine atoms.
Note:
Less common than hypervalent compounds, but by no means rare, are species in which an atom does not achieve an octet of electrons. Such compounds are called incomplete-octet compounds. The rule is applicable to the main- group elements, especially carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens, but also to metals such as sodium and magnesium.
Complete answer:
We need to know that the octet rule states that atoms with an atomic number below $20$ tend to combine so that they each have eight electrons in their valence shells, which give them the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The two elements that most commonly fail to complete an octet are boron and aluminum; they both readily form compounds in which they have six valence electrons, rather than the usual eight predicted by the octet rule. When we talk of \[B{F_3}\] molecule, $F$ completes its octet by sharing one electron from 'Boron' While 'Boron' shares three electron from three $'F'$ atom and has only $6$ electrons in outermost cell thus it has an incomplete octet.
In boron trifluoride (\[B{F_3}\]),the bonding is relatively simple to model with a Lewis structure if we allow each valence level electron in the boron atom to be shared in a covalent bond with each fluorine atom. In this compound, the boron atom only has six valence shell electrons, but the octet rule is satisfied by the fluorine atoms.

Note:
Less common than hypervalent compounds, but by no means rare, are species in which an atom does not achieve an octet of electrons. Such compounds are called incomplete-octet compounds. The rule is applicable to the main- group elements, especially carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens, but also to metals such as sodium and magnesium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




