
What is black body radiation? Explain the characteristics of it.
Answer
500.4k+ views
Hint: A black body is an idealized object that absorbs all electromagnetic radiation it comes in contact with. It then emits the absorbed radiation as thermal radiation in a continuous spectrum according to its temperature. It follows certain laws when it emits thermal radiation.
Formula used:
${j^*} = \sigma {T^4}$ where ${j^*}$ is the black body radiant emittance, $\sigma $ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant and $T$ is the thermodynamic temperature .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The radiation emitted by a black body is called black body radiation. The distribution of energy of a black body radiation $I$ at different temperatures $T$ , with its wavelength $\lambda $ is as shown in the figure
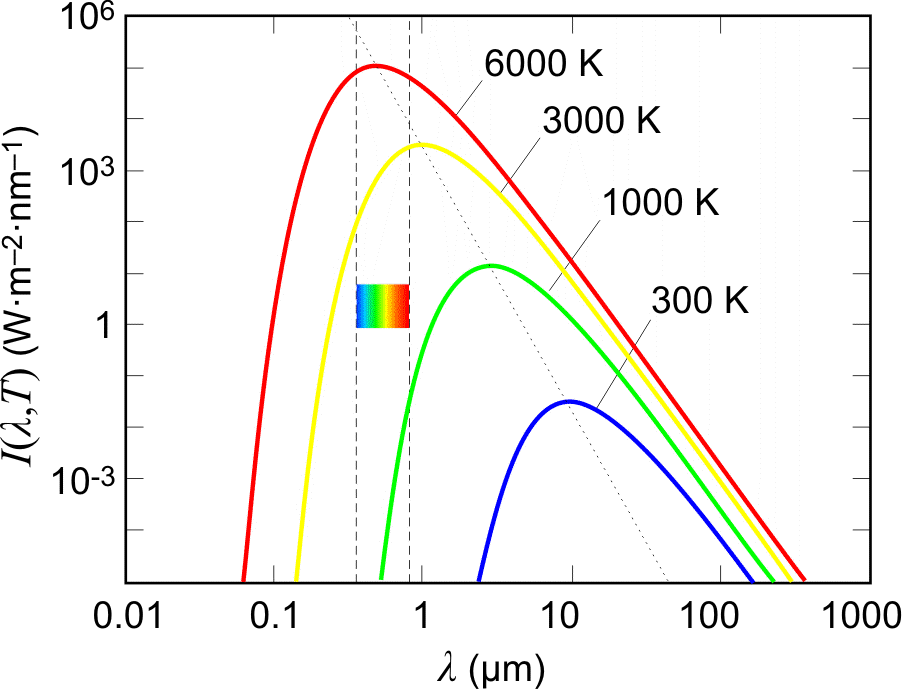
Characteristics of a blackbody radiation spectra are:
(1) The emissive power of a blackbody $I$ , for every wavelength $\lambda $ , increases with increasing temperature.
(2) Each curve has a characteristic form with a maximum for $I$ at a certain wavelength ${\lambda _m}$
(3) ${\lambda _m}$ depends only on the absolute temperature of the blackbody and, with increasing temperature, shifts towards shorter wavelength (i.e. towards the U.V. end of the light spectrum).
(4) The area under each curve gives the total radiant power per unit area $I$ of a blackbody at that temperature and total radiation emitted is directly proportional to ${T^4}$ according to Stefan's law.
Note: The Stefan-Boltzmann constant, $\sigma $ , is derived from other known physical constants in use. The value of the constant has been widely accepted as \[\sigma = \dfrac{{2{\pi ^2}{k^4}}}{{15{c^2}{h^3}}}\] where $k$ is the Boltzmann constant $h$ is Planck’s constant and $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum.
Formula used:
${j^*} = \sigma {T^4}$ where ${j^*}$ is the black body radiant emittance, $\sigma $ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant and $T$ is the thermodynamic temperature .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The radiation emitted by a black body is called black body radiation. The distribution of energy of a black body radiation $I$ at different temperatures $T$ , with its wavelength $\lambda $ is as shown in the figure

Characteristics of a blackbody radiation spectra are:
(1) The emissive power of a blackbody $I$ , for every wavelength $\lambda $ , increases with increasing temperature.
(2) Each curve has a characteristic form with a maximum for $I$ at a certain wavelength ${\lambda _m}$
(3) ${\lambda _m}$ depends only on the absolute temperature of the blackbody and, with increasing temperature, shifts towards shorter wavelength (i.e. towards the U.V. end of the light spectrum).
(4) The area under each curve gives the total radiant power per unit area $I$ of a blackbody at that temperature and total radiation emitted is directly proportional to ${T^4}$ according to Stefan's law.
Note: The Stefan-Boltzmann constant, $\sigma $ , is derived from other known physical constants in use. The value of the constant has been widely accepted as \[\sigma = \dfrac{{2{\pi ^2}{k^4}}}{{15{c^2}{h^3}}}\] where $k$ is the Boltzmann constant $h$ is Planck’s constant and $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




