
Blessy has two bags containing numbered counters.
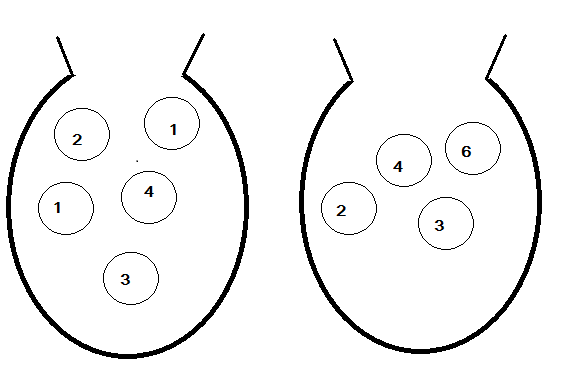
She takes one counter at random from bag A and another counter at random from Bag B. She adds the numbers on her two counters. Find the probability that Blessy’s answer is more than 6.

Answer
585k+ views
Hint: n this question, we need to determine the probability that Blessy’s answer was more than 6 when she had drawn 2 balls at random from the bags A and B. For this, we will use the basic formula of probability which is given as $P(E) = \dfrac{{n(F)}}{{n(A)}}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A total number of events of drawing counters from bag A and bag B having 5 counters and 4 counters respectively is the product of the total counters in the bags.
Let the total number of events be $n(A)$.
So, the total number of events is given as: $n(A) = 5 \times 4 = 20 - - - - (i)$
Now, a favourable number of events are the events satisfying the given condition in the question. Here, the condition is that the total sum of the counters should be more than 6.
So, the favourable number of outcomes is given as:
\[n(F) = \left\{ {\left( {1,6} \right);\left( {2,6} \right);\left( {3,4} \right);\left( {3,6} \right);\left( {4,3} \right);\left( {1,6} \right);\left( {4,4} \right);\left( {4,6} \right)} \right\} = 8 - - - - (ii)\]
Now, the ratio of the favourable number of outcomes to the total number of outcomes results in the probability of satisfying the favourable outcomes. Mathematically $P(E) = \dfrac{{n(F)}}{{n(A)}}$. Here, a favourable number of outcomes is 8, and the total number of outcomes is 20.
So, substitute $n(F) = 8{\text{ and }}n(A) = 20$ in the formula $P(E) = \dfrac{{n(F)}}{{n(A)}}$ to determine the probability that Blessy’s have more than 6 as the sum of the counters.
\[
P(E) = \dfrac{{n(F)}}{{n(A)}} \\
= \dfrac{8}{{20}} \\
= \dfrac{2}{5} \\
= 0.4 \\
\]
Hence, the probability that Bleesy has the sum of the counters in her hand is 0.4.
Note: Students must be careful while estimating the total number of favourable outcomes as if even one favourable outcome has not been counted then, it will lead to the wrong answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A total number of events of drawing counters from bag A and bag B having 5 counters and 4 counters respectively is the product of the total counters in the bags.
Let the total number of events be $n(A)$.
So, the total number of events is given as: $n(A) = 5 \times 4 = 20 - - - - (i)$
Now, a favourable number of events are the events satisfying the given condition in the question. Here, the condition is that the total sum of the counters should be more than 6.
So, the favourable number of outcomes is given as:
\[n(F) = \left\{ {\left( {1,6} \right);\left( {2,6} \right);\left( {3,4} \right);\left( {3,6} \right);\left( {4,3} \right);\left( {1,6} \right);\left( {4,4} \right);\left( {4,6} \right)} \right\} = 8 - - - - (ii)\]
Now, the ratio of the favourable number of outcomes to the total number of outcomes results in the probability of satisfying the favourable outcomes. Mathematically $P(E) = \dfrac{{n(F)}}{{n(A)}}$. Here, a favourable number of outcomes is 8, and the total number of outcomes is 20.
So, substitute $n(F) = 8{\text{ and }}n(A) = 20$ in the formula $P(E) = \dfrac{{n(F)}}{{n(A)}}$ to determine the probability that Blessy’s have more than 6 as the sum of the counters.
\[
P(E) = \dfrac{{n(F)}}{{n(A)}} \\
= \dfrac{8}{{20}} \\
= \dfrac{2}{5} \\
= 0.4 \\
\]
Hence, the probability that Bleesy has the sum of the counters in her hand is 0.4.
Note: Students must be careful while estimating the total number of favourable outcomes as if even one favourable outcome has not been counted then, it will lead to the wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




