
Body of Euspongia is mainly composed of
(a) Calcareous spicules
(b) Spongin fibers
(c) Siliceous spicules
(d) Mesoglea
Answer
523.5k+ views
Hint: A modified type of protein present in the phylum Porifera to give them structural support. The openings in sponges are surrounded by fibers.
Complete answer:
Euspongia also is known as Spongia is the variety of sponges commonly known as a bath sponge. It is used commercially. The individuals grow on large lobes having small openings which are formed by the interwoven network of primary and secondary spongin fibers.
Additional information :
1. Euspongia is found throughout the Mediterranean Sea to rocky surfaces.
2. They have small openings that are elevated and have cone-shaped gaps called conules.
3. A small mouth-like opening called oscula is present at the tip of the lobes.
4. Their ectosomal skeleton has primary and secondary spongin fibers together form the conulose openings.
5. They also have a choanosomal skeleton having a dark mesh of secondary fibers from which primary fibers arise.
6. These primary fibers are made up of spongin and have other particles like sand grains and spicules.
7. The secondary fibers are made up of only spongin and no other particles present.
8. The primary fibers are 50-100 nanometres in diameter while secondary fibers are 20-36 nanometres in diameter.
So, the correct answer is ‘Spongin fibers’.
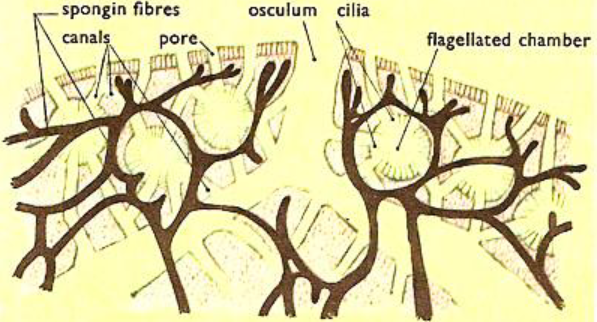
Note: Spongin fibers are the modified collagen proteins that form the fibrous skeleton of most of the organisms of phylum Porifera (sponges). They are secreted by sponge cells called spongocytes. Spongin fibers give flexibility to the sponges and help in connecting siliceous spicules. Siliceous spicules are made up of silicon dioxide which gives rough and porous texture to the shells. Calcareous spicules are made up of mainly calcium carbonate which gives the shell hardness and stiffness. The mesoglea is the innermost layer of the tissue which is the characteristic feature of the jellyfish.
Complete answer:
Euspongia also is known as Spongia is the variety of sponges commonly known as a bath sponge. It is used commercially. The individuals grow on large lobes having small openings which are formed by the interwoven network of primary and secondary spongin fibers.
Additional information :
1. Euspongia is found throughout the Mediterranean Sea to rocky surfaces.
2. They have small openings that are elevated and have cone-shaped gaps called conules.
3. A small mouth-like opening called oscula is present at the tip of the lobes.
4. Their ectosomal skeleton has primary and secondary spongin fibers together form the conulose openings.
5. They also have a choanosomal skeleton having a dark mesh of secondary fibers from which primary fibers arise.
6. These primary fibers are made up of spongin and have other particles like sand grains and spicules.
7. The secondary fibers are made up of only spongin and no other particles present.
8. The primary fibers are 50-100 nanometres in diameter while secondary fibers are 20-36 nanometres in diameter.
So, the correct answer is ‘Spongin fibers’.

Note: Spongin fibers are the modified collagen proteins that form the fibrous skeleton of most of the organisms of phylum Porifera (sponges). They are secreted by sponge cells called spongocytes. Spongin fibers give flexibility to the sponges and help in connecting siliceous spicules. Siliceous spicules are made up of silicon dioxide which gives rough and porous texture to the shells. Calcareous spicules are made up of mainly calcium carbonate which gives the shell hardness and stiffness. The mesoglea is the innermost layer of the tissue which is the characteristic feature of the jellyfish.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




