
Bond order of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 0
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: According to the molecular orbital theory, the bond order is defined as the number of covalent bonds in a molecule. Bond order is equal to half of the difference between the number of electrons in bonding (\[{{N}_{b}}\]) and antibonding molecular orbitals (\[{{N}_{a}}\]).
Complete Solution :
\[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule will be formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals of two beryllium atoms.
A Be atom has four electrons. It has two valence electrons and its electronic configuration is \[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}\]. Therefore, \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule has eight electrons which are to be filled in four molecular orbitals.
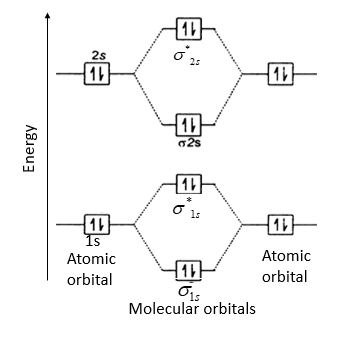
Thus, electronic configuration of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] is \[{{\left( \sigma 1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( \sigma 2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}2s \right)}^{2}}\]
Here, bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{b}}\] = 4 and anti-bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{a}}\]= 4
Therefore, bond order (B.O.) of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule is
\[\begin{align}
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\frac{1}{2}({{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}) \\
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.}=\frac{1}{2}(4-4)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
- Zero value of bond order corresponds to non-existence of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The bond order of a molecule conveys the following information:
1. The stability of a molecule can also be expressed in terms of bond order. Higher the bond order, more stable is the molecule.
2. Bond length: Bond order and bond length are inversely related. Thus, higher the bond order, shorter is the bond length and vice-versa.
3. Bond dissociation energy: Bond order in a molecule is directly proportional to its bond dissociation energy. Greater the bond order, more will be the value of bond dissociation energy.
Complete Solution :
\[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule will be formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals of two beryllium atoms.
A Be atom has four electrons. It has two valence electrons and its electronic configuration is \[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}\]. Therefore, \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule has eight electrons which are to be filled in four molecular orbitals.

Thus, electronic configuration of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] is \[{{\left( \sigma 1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( \sigma 2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}2s \right)}^{2}}\]
Here, bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{b}}\] = 4 and anti-bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{a}}\]= 4
Therefore, bond order (B.O.) of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule is
\[\begin{align}
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\frac{1}{2}({{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}) \\
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.}=\frac{1}{2}(4-4)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
- Zero value of bond order corresponds to non-existence of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The bond order of a molecule conveys the following information:
1. The stability of a molecule can also be expressed in terms of bond order. Higher the bond order, more stable is the molecule.
2. Bond length: Bond order and bond length are inversely related. Thus, higher the bond order, shorter is the bond length and vice-versa.
3. Bond dissociation energy: Bond order in a molecule is directly proportional to its bond dissociation energy. Greater the bond order, more will be the value of bond dissociation energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




