
Bordered pits occur in
(a) Secondary phloem
(b) Protoxylem
(c) Metaxylem
(d) Bark
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: Vascular tissue in plants are organized into discrete strands called vascular bundles, each of them contains xylem and phloem.
Bordered pits occur in Metaxylem in their lignified walls. The vascular system of stems consists of discrete vascular bundles while in the roots, it is organized within a single central vascular cylinder. The xylem is responsible for conducting water and minerals within the primary plant body and the phloem conducts the food.
Complete answer: Protoxylem is the first part of the primary xylem which later matures and these cells are usually smaller in size than the metaxylem. While metaxylem is the part of the primary xylem that differentiates after protoxylem and these cells are usually larger than the protoxylem.
The functioning of the xylem network depends to a large degree on bordered pits. They connect adjacent conduits and the finely porous pit membranes that prevent the movement of gas and pathogens between conduits. Thus it is said that the bordered pits act as safety valves in the hydraulic system of plants.
The center of the bordered pit is occupied by 'torus' which is made up of the primary cell wall material. The structure of pits varies greatly across species, with large differences evident in their porosity and thickness of pit membranes.
So, the correct answer is ‘Metaxylem’.
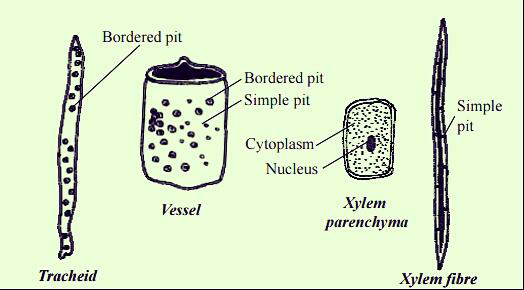
Note: Primary xylem consists of lignified tracheary elements (tracheids and vessel elements), which die at maturity (as they lose their protoplasts). The end walls of adjacent tracheids contain paired, small, rimmed, non-perforated pores; these are the bordered pits.
The maximum number of bordered pits is present in the gymnosperms followed by the angiosperms.
Bordered pits occur in Metaxylem in their lignified walls. The vascular system of stems consists of discrete vascular bundles while in the roots, it is organized within a single central vascular cylinder. The xylem is responsible for conducting water and minerals within the primary plant body and the phloem conducts the food.
Complete answer: Protoxylem is the first part of the primary xylem which later matures and these cells are usually smaller in size than the metaxylem. While metaxylem is the part of the primary xylem that differentiates after protoxylem and these cells are usually larger than the protoxylem.
The functioning of the xylem network depends to a large degree on bordered pits. They connect adjacent conduits and the finely porous pit membranes that prevent the movement of gas and pathogens between conduits. Thus it is said that the bordered pits act as safety valves in the hydraulic system of plants.
The center of the bordered pit is occupied by 'torus' which is made up of the primary cell wall material. The structure of pits varies greatly across species, with large differences evident in their porosity and thickness of pit membranes.
So, the correct answer is ‘Metaxylem’.

Note: Primary xylem consists of lignified tracheary elements (tracheids and vessel elements), which die at maturity (as they lose their protoplasts). The end walls of adjacent tracheids contain paired, small, rimmed, non-perforated pores; these are the bordered pits.
The maximum number of bordered pits is present in the gymnosperms followed by the angiosperms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




