
Brain sugar is
A) Lactose
B) Glucose
C) Fructose
D) Galactose
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Brain sugar shows benefits towards supporting the brain development of babies and children. This sugar is essential during the early developmental stages of mammalian infants, when they are exclusively dependent on milk.
Complete answer:
Brain sugar is Galactose. Even though a diversity of monosaccharide is found in living organisms, three hexoses are specifically ample D-glucose, D-galactose and D-fructose. D-galactose does not occur in nature in the absolute form. It is formed when lactose, a disaccharide present in milk, gets hydrolyzed. The galactose required by the human body is derived by the metabolic conversion of D-glucose to D-galactose. It is a chief component of the glycolipids that takes place in the brain and the myelin sheath of nerve cells. For this reason it is also known as brain sugar.
Additional information
-Galactose is an optical isomer of glucose.
-It is an aldohexose and exists naturally in the D-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides and mucoproteins.
This is the molecular structure of D-galactose.
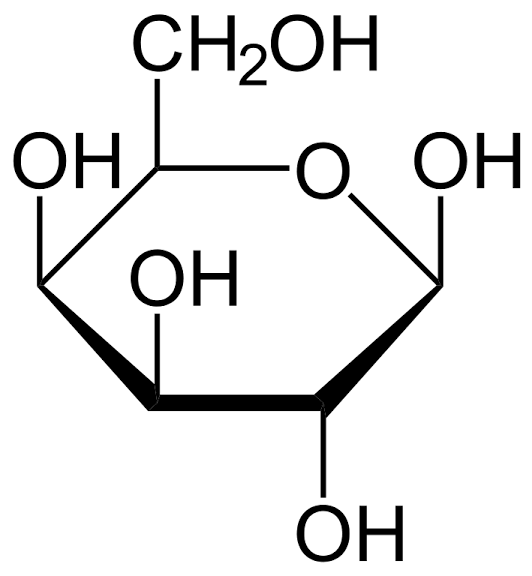
-Inadequacy of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase begins a fallacy in galactose metabolism which is known as galactosemia. It results in elevations of galactose levels in the blood.
-Galactose is a variety of sugar which is present in dairy products, in sugar beets, etc.
-It is also synthesized by the body, where it forms a part of glycolipids and glycoproteins in several tissues.
So, the correct answer is ‘Galactose’.
Note: Galactose is a simple sugar that is normally transformed in the liver before being used up as energy. This sugar is plentiful in human diets. It helps in a variety of functions. It has been helpful in the controlling of a number of diseases, especially those affecting brain functions.
Complete answer:
Brain sugar is Galactose. Even though a diversity of monosaccharide is found in living organisms, three hexoses are specifically ample D-glucose, D-galactose and D-fructose. D-galactose does not occur in nature in the absolute form. It is formed when lactose, a disaccharide present in milk, gets hydrolyzed. The galactose required by the human body is derived by the metabolic conversion of D-glucose to D-galactose. It is a chief component of the glycolipids that takes place in the brain and the myelin sheath of nerve cells. For this reason it is also known as brain sugar.
Additional information
-Galactose is an optical isomer of glucose.
-It is an aldohexose and exists naturally in the D-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides and mucoproteins.
This is the molecular structure of D-galactose.

-Inadequacy of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase begins a fallacy in galactose metabolism which is known as galactosemia. It results in elevations of galactose levels in the blood.
-Galactose is a variety of sugar which is present in dairy products, in sugar beets, etc.
-It is also synthesized by the body, where it forms a part of glycolipids and glycoproteins in several tissues.
So, the correct answer is ‘Galactose’.
Note: Galactose is a simple sugar that is normally transformed in the liver before being used up as energy. This sugar is plentiful in human diets. It helps in a variety of functions. It has been helpful in the controlling of a number of diseases, especially those affecting brain functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




