
Briefly explain the structure of pollen grains.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Pollen grains represent the male gametophyte . When the anther undergoes maturation and anther dehydrates , the microspores dissociate from each other and develop into pollen grains. Inside each and single microsporangium , several thousands which are very large in number of microspores or pollen grains are formed that are released with the dehiscence of anther. Pollen grains are usually male gametes.
Complete answer:
The pollen grains represent the male gametophytes
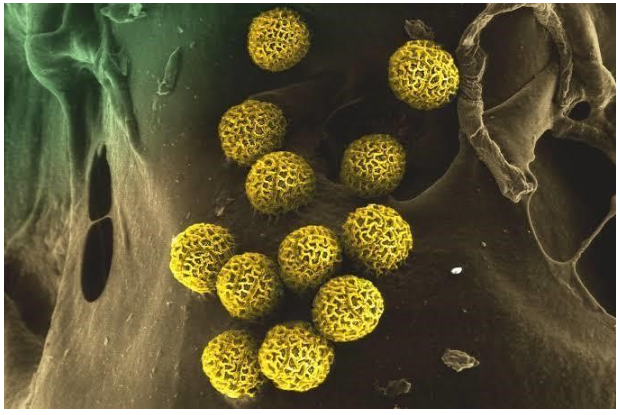
These are generally spherical structures measuring about 25-50 micrometre in diameter.
The cell wall of pollen grain is called sporoderm which consists of two layers., i.e., exine and intine.
Exine: It is a hard outer layer made up of sporopollenin (one of the most resistant organic materials known). The layer exane is protective as it can withstand high temperature, strong acids and alkali. No enzyme that degrades sporopollenin is so far known.
This also helps in fossilization. Pollen grains can be preserved and can be studied as fossils because of the presence of sporopollenin.
It is hard so that the pollen grains remain protected and sealed from hazardous environments when they are pollinated by biotic/abiotic agents; it exhibits a fascinating array of patterns and designs which is of taxonomic significance.
It has prominent apertures called germ-pores where sporopollenin is absent.
Intine: It is the inner wall which is thin and continuous and made up of cellulose and pectin.
Cytoplasm of pollen grain is surrounded by plasma membrane.
Note: Pollen grains of many species (especially anemophilous plants) cause severe allergies and bronchial afflictions in some people often leading to chronic respiratory disorders like asthma and bronchitis. Pollen grains are rich in nutrients. They increase performance of athletes .
Complete answer:
The pollen grains represent the male gametophytes

These are generally spherical structures measuring about 25-50 micrometre in diameter.
The cell wall of pollen grain is called sporoderm which consists of two layers., i.e., exine and intine.
Exine: It is a hard outer layer made up of sporopollenin (one of the most resistant organic materials known). The layer exane is protective as it can withstand high temperature, strong acids and alkali. No enzyme that degrades sporopollenin is so far known.
This also helps in fossilization. Pollen grains can be preserved and can be studied as fossils because of the presence of sporopollenin.
It is hard so that the pollen grains remain protected and sealed from hazardous environments when they are pollinated by biotic/abiotic agents; it exhibits a fascinating array of patterns and designs which is of taxonomic significance.
It has prominent apertures called germ-pores where sporopollenin is absent.
Intine: It is the inner wall which is thin and continuous and made up of cellulose and pectin.
Cytoplasm of pollen grain is surrounded by plasma membrane.
Note: Pollen grains of many species (especially anemophilous plants) cause severe allergies and bronchial afflictions in some people often leading to chronic respiratory disorders like asthma and bronchitis. Pollen grains are rich in nutrients. They increase performance of athletes .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




