
How will you bring the following conversion?
Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol.
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: It is the conversion of ketone to alcohol. This process is just the reverse of the formation of ketone from alcohol but the reagent used will be different. Alcohol is oxidized to ketone in presence of oxidizing agents.
Complete answer:
The ketone is readily reduced to alcohol with hydride reagents like $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ and $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. Firstly let's understand reduction and reducing agent, Reduction is the process of gaining of electrons from any element or atom is known as reduction process. This reduction is accompanied by reducing agents. The reducing agents are elements that can lose electrons so that other compounds or molecules may get reduced. In these processes if we observe the reducing agent it gets oxidized itself and reduces others. Here the reducing agents are $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ and $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. Now, let's see $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$. It is a strong reducing agent which is unselective for polar double bonds. It is the main source of ${{H}^{-}}$. It can reduce carboxylic acids, ketone, aldehyde, amides, ester and carboxylate salt to alcohol. so, $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ over $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. The conversion of ketone to alcohol is conversion of Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol: Butan-2-one is readily reduced in presence of $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ to butan-2-ol.

-Let's see the mechanism for better understanding.
-Mechanism: Firstly, the nucleophilic addition by the hydride anion that is the hydride anion attacks the carbonyl carbon due to which there is accumulation of negative charge of oxygen. Li ion gets attached to the oxygen atom.
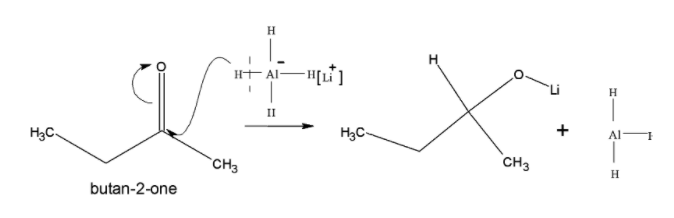
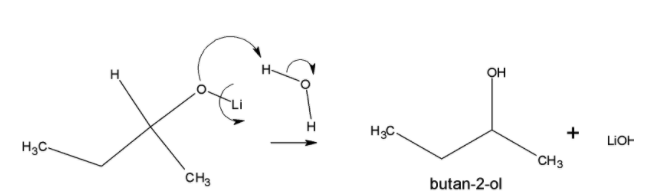
Followed by the protonation of alkoxide formed gives butan-2-ol and LiOH as the product.
Note: The anion in $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ will not be present during the course of this reaction. This reagent basically serves as a source of hydride due to presence of metal-hydrogen bond which will be polar in nature. Because of this polar nature, the $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ is a good reducing agent. It is preferred over $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. $NaB{{H}_{4}}$ can be used to ketone and aldehyde only. In case of reducing amide it is not feasible.
Complete answer:
The ketone is readily reduced to alcohol with hydride reagents like $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ and $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. Firstly let's understand reduction and reducing agent, Reduction is the process of gaining of electrons from any element or atom is known as reduction process. This reduction is accompanied by reducing agents. The reducing agents are elements that can lose electrons so that other compounds or molecules may get reduced. In these processes if we observe the reducing agent it gets oxidized itself and reduces others. Here the reducing agents are $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ and $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. Now, let's see $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$. It is a strong reducing agent which is unselective for polar double bonds. It is the main source of ${{H}^{-}}$. It can reduce carboxylic acids, ketone, aldehyde, amides, ester and carboxylate salt to alcohol. so, $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ over $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. The conversion of ketone to alcohol is conversion of Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol: Butan-2-one is readily reduced in presence of $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ to butan-2-ol.

-Let's see the mechanism for better understanding.
-Mechanism: Firstly, the nucleophilic addition by the hydride anion that is the hydride anion attacks the carbonyl carbon due to which there is accumulation of negative charge of oxygen. Li ion gets attached to the oxygen atom.

Followed by the protonation of alkoxide formed gives butan-2-ol and LiOH as the product.

Note: The anion in $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ will not be present during the course of this reaction. This reagent basically serves as a source of hydride due to presence of metal-hydrogen bond which will be polar in nature. Because of this polar nature, the $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ is a good reducing agent. It is preferred over $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. $NaB{{H}_{4}}$ can be used to ketone and aldehyde only. In case of reducing amide it is not feasible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




