
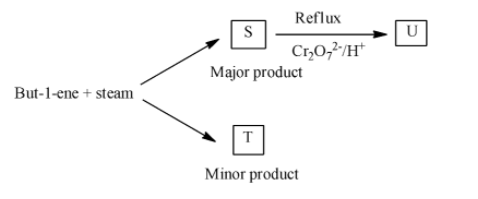
But-1-ene reacts with steam as shown to form a mixture of two structural isomers, S and T.

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: But-1-ene contains a double bond at carbon-1. Whenever but-1-ene reacts with steam it produces two different products (alcohols) in different percentages due to the asymmetrical nature of the but-1-ene.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that But-1-ene reacts with steam and produces the products S (major amount0 and product T (minor amount).
- We have to identify the products S and T in the given reaction.
- The chemical reaction of but-1-ene with steam is as follows.
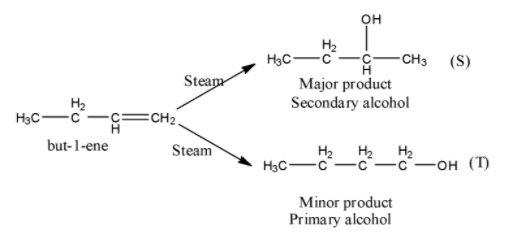
- In the above chemical reaction but-1-ene reacts with steam and forms two types of products.
- The two products are secondary alcohol (major amount) and primary alcohol (minor amount).
- The reason behind the formation of the secondary alcohol in major amounts is the formation of secondary carbocation as an intermediate during the reaction of but-1-ene with steam.
- Secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation.
- The formed product S (secondary alcohol) further undergoes reaction with potassium dichromate (oxidizing reagent) and forms a ketone as the product.
- The chemical reaction of product S with potassium dichromate is as follows.
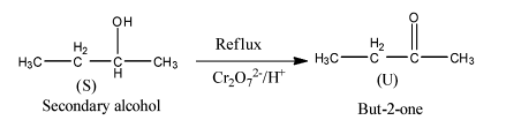
- Therefore the product formed when compound ‘S’ is going to react with potassium dichromate is But-2-one (U).
Note: Whenever secondary alcohols react with potassium dichromate ketones are going to form as the product. While primary alcohols react with potassium dichromate and forms aldehyde as the product under reflux conditions.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that But-1-ene reacts with steam and produces the products S (major amount0 and product T (minor amount).
- We have to identify the products S and T in the given reaction.
- The chemical reaction of but-1-ene with steam is as follows.

- In the above chemical reaction but-1-ene reacts with steam and forms two types of products.
- The two products are secondary alcohol (major amount) and primary alcohol (minor amount).
- The reason behind the formation of the secondary alcohol in major amounts is the formation of secondary carbocation as an intermediate during the reaction of but-1-ene with steam.
- Secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation.
- The formed product S (secondary alcohol) further undergoes reaction with potassium dichromate (oxidizing reagent) and forms a ketone as the product.
- The chemical reaction of product S with potassium dichromate is as follows.

- Therefore the product formed when compound ‘S’ is going to react with potassium dichromate is But-2-one (U).
Note: Whenever secondary alcohols react with potassium dichromate ketones are going to form as the product. While primary alcohols react with potassium dichromate and forms aldehyde as the product under reflux conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




