
Butanone is a four-carbon compound with functional group:
A.Carboxylic acid
B.Aldehyde
C.Ketone
D.Alcohol
Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint:We need to remember that the butanone, otherwise called methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is a natural compound with the equation \[C{H_3}COC{H_2}C{H_3}\] . This boring fluid ketone has a sharp, sweet smell suggestive of \[{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}CO\] . We can produce it by oxidation of 2-butanol.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the structure of butanone as,
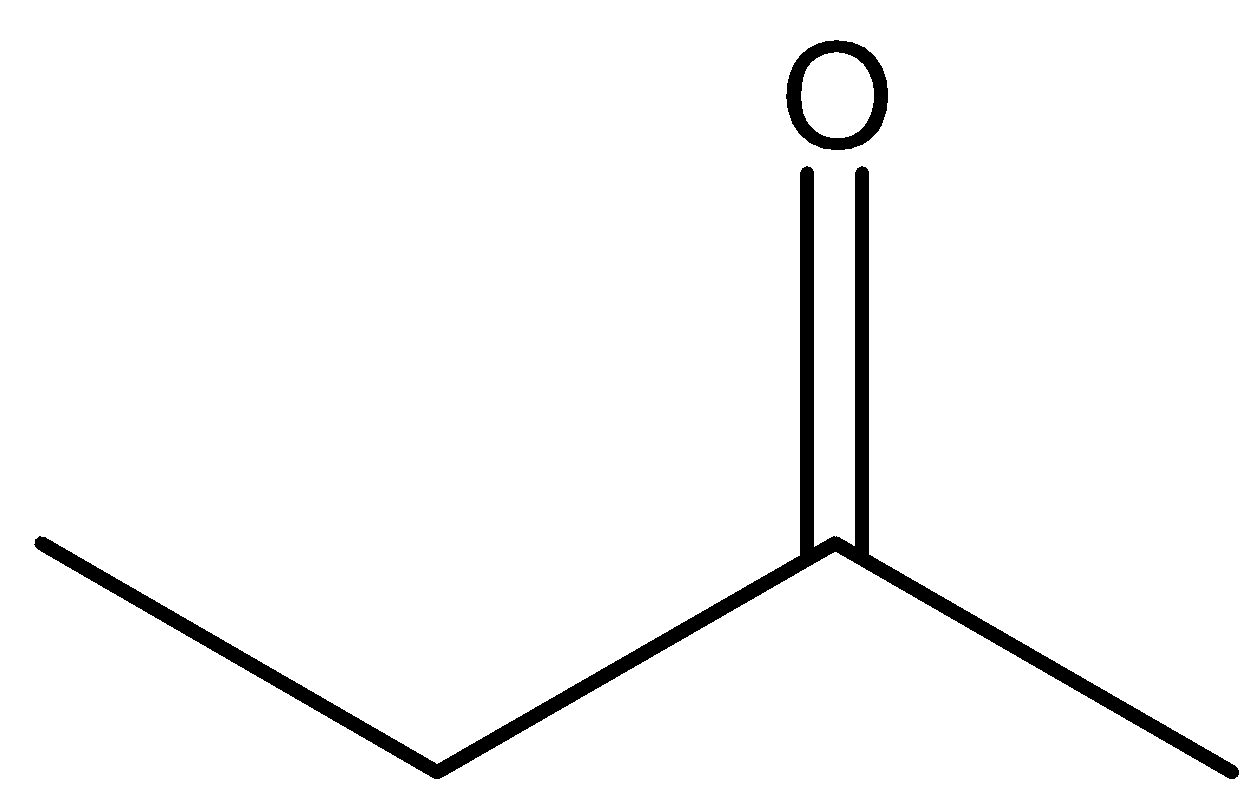
From the presence of the $ - COOH$ functional group present in the compound, we can say that the compound contains a carboxylic acid functional group.
The carbonyl group in aldehydes is attached at the end of the hydrocarbon chain. The carbonyl carbon is bonded to minimum one hydrogen. Aldehydes have a general formula of \[\left( {R - CHO} \right)\] . Here, R is the alkyl group.
From the presence of carbonyl carbon attached with double bonded oxygen, we can say the compound contains a ketone functional group.
An organic compound that comprises a hydroxyl group that is covalently linked to a carbon atom is alcohol. The general formula of alcohol is $R - OH$. Here, R is the alkyl group.
From the structure of butanone, we can see that carbonyl carbon is linked to double-bonded oxygen, so the functional group present in butanone is a ketone.
And hence option (C) is correct.
Note:
We know that hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are made up of carbon and hydrogen. We can say in IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, a number of suffixes, prefixes, and infixes are used to explain the position and type of the functional groups present in the compound. The various kinds of functional groups in organic compounds are alcohols, alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, amines, amides, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the structure of butanone as,

From the presence of the $ - COOH$ functional group present in the compound, we can say that the compound contains a carboxylic acid functional group.
The carbonyl group in aldehydes is attached at the end of the hydrocarbon chain. The carbonyl carbon is bonded to minimum one hydrogen. Aldehydes have a general formula of \[\left( {R - CHO} \right)\] . Here, R is the alkyl group.
From the presence of carbonyl carbon attached with double bonded oxygen, we can say the compound contains a ketone functional group.
An organic compound that comprises a hydroxyl group that is covalently linked to a carbon atom is alcohol. The general formula of alcohol is $R - OH$. Here, R is the alkyl group.
From the structure of butanone, we can see that carbonyl carbon is linked to double-bonded oxygen, so the functional group present in butanone is a ketone.
And hence option (C) is correct.
Note:
We know that hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are made up of carbon and hydrogen. We can say in IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, a number of suffixes, prefixes, and infixes are used to explain the position and type of the functional groups present in the compound. The various kinds of functional groups in organic compounds are alcohols, alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, amines, amides, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




