
By writing molecular orbital configuration for \[NO,CO\] and \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] molecules calculate the bond order and also determine whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
Answer
495.9k+ views
Hint: The bond order is a measure of the number of bonds that exist between two atoms and can be calculated by multiplying the difference of number of electrons present in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals by half.
Complete answer:
The placement of electrons in bonding or antibonding molecular orbitals can be determined by drawing the molecular orbital diagram of the molecule. This diagram is the virtual representation of the linear combination of atomic orbitals that combine to give molecular orbitals. The molecular orbital configuration can be written with the help of the following diagrams.
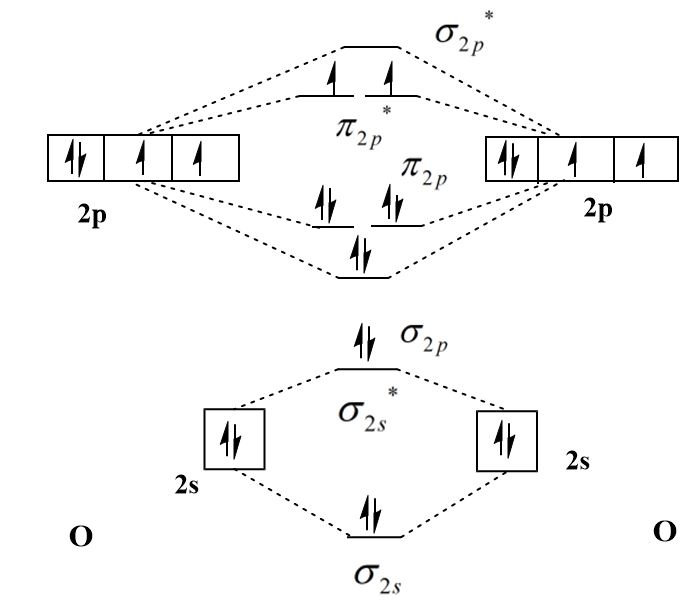
The molecular orbital diagram of oxygen molecule \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] is:
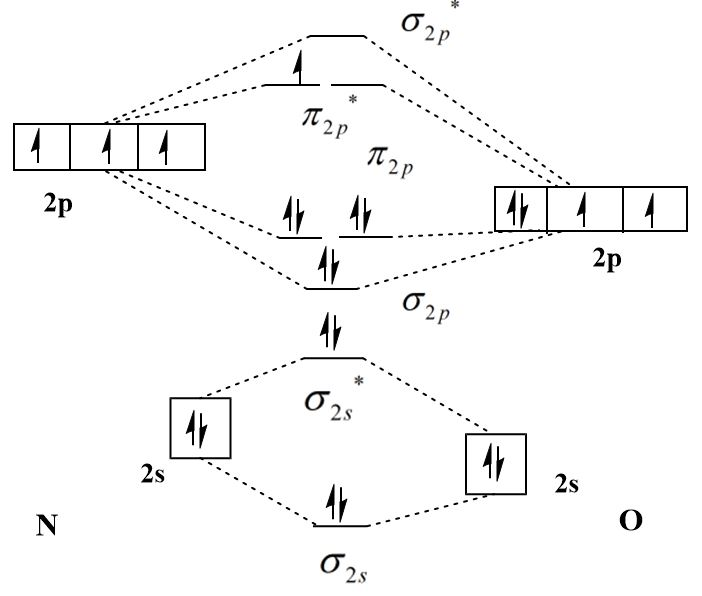
The molecular orbital diagram of \[NO\] is:
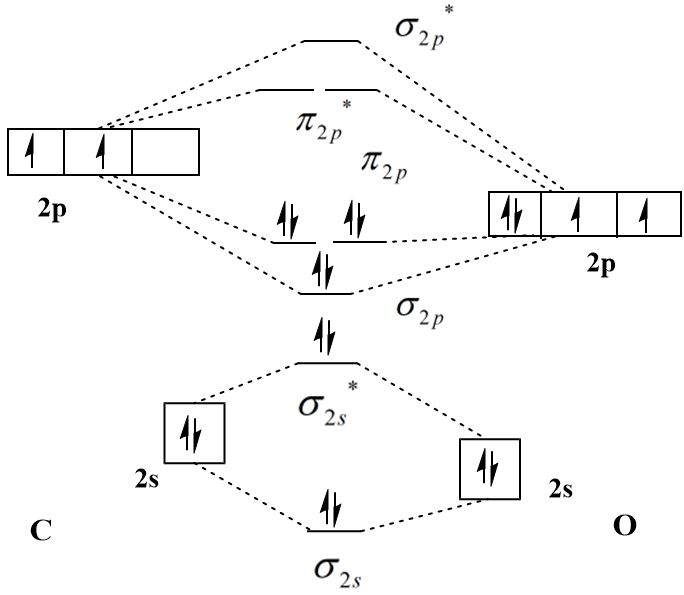
The molecular orbital diagram of \[CO\] is:
The molecular orbital configuration of oxygen molecule \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] is:
\[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma _{2s}}^{*2}{\sigma _{2p}}^2{\pi _{2p}}^4{\pi _{2p}}^{*2}\]
The molecular orbital configuration of \[NO\] is:
\[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma _{2s}}^{*2}{\sigma _{2p}}^2{\pi _{2p}}^4{\pi _{2p}}^{*1}\]
The molecular orbital configuration of \[CO\] is:
\[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma _{2s}}^{*2}{\sigma _{2p}}^2{\pi _{2p}}^4\]
The following formula can be used to calculate the bond order:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{{\text{bonding electrons}} - anti{\text{ - }}bonding{\text{ electrons}}}}{2}\]
The number of bonding electrons in oxygen molecule is eight and the number of antibonding electrons is four therefore the bond of oxygen molecule is:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{8 - 4}}{2} = 2\]
There are eight bonding electron in nitrogen monoxide and three antibonding electrons therefore the bond order of nitrogen monoxide molecule is:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{8 - 3}}{2} = 2.5\]
The number of bonding electrons in carbon monoxide is eight and that of antibonding electrons is two and therefore the bond order is:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{8 - 2}}{2} = 3\]
The presence of an unpaired electron in the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) of \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] and \[NO\] makes them paramagnetic and the absence of unpaired electrons in \[CO\] makes it diamagnetic.
\[ \Rightarrow \] Hence, the bond order for \[NO\] , \[CO\] and \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] are \[2.5,3\] and \[2\] respectively. Oxygen and nitrogen monoxide are paramagnetic and carbon monoxide is diamagnetic.
Note:
The atomic orbitals are not placed along the same horizontal axis if the atoms involved have an electronegativity difference. The atomic orbitals of oxygen atoms always occupy relatively lower positions due to its higher electronegativity as compared to carbon and nitrogen atoms.
Complete answer:
The placement of electrons in bonding or antibonding molecular orbitals can be determined by drawing the molecular orbital diagram of the molecule. This diagram is the virtual representation of the linear combination of atomic orbitals that combine to give molecular orbitals. The molecular orbital configuration can be written with the help of the following diagrams.
The molecular orbital diagram of oxygen molecule \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] is:

The molecular orbital diagram of \[NO\] is:

The molecular orbital diagram of \[CO\] is:

The molecular orbital configuration of oxygen molecule \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] is:
\[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma _{2s}}^{*2}{\sigma _{2p}}^2{\pi _{2p}}^4{\pi _{2p}}^{*2}\]
The molecular orbital configuration of \[NO\] is:
\[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma _{2s}}^{*2}{\sigma _{2p}}^2{\pi _{2p}}^4{\pi _{2p}}^{*1}\]
The molecular orbital configuration of \[CO\] is:
\[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma _{2s}}^{*2}{\sigma _{2p}}^2{\pi _{2p}}^4\]
The following formula can be used to calculate the bond order:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{{\text{bonding electrons}} - anti{\text{ - }}bonding{\text{ electrons}}}}{2}\]
The number of bonding electrons in oxygen molecule is eight and the number of antibonding electrons is four therefore the bond of oxygen molecule is:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{8 - 4}}{2} = 2\]
There are eight bonding electron in nitrogen monoxide and three antibonding electrons therefore the bond order of nitrogen monoxide molecule is:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{8 - 3}}{2} = 2.5\]
The number of bonding electrons in carbon monoxide is eight and that of antibonding electrons is two and therefore the bond order is:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{8 - 2}}{2} = 3\]
The presence of an unpaired electron in the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) of \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] and \[NO\] makes them paramagnetic and the absence of unpaired electrons in \[CO\] makes it diamagnetic.
\[ \Rightarrow \] Hence, the bond order for \[NO\] , \[CO\] and \[{{\text{O}}_2}\] are \[2.5,3\] and \[2\] respectively. Oxygen and nitrogen monoxide are paramagnetic and carbon monoxide is diamagnetic.
Note:
The atomic orbitals are not placed along the same horizontal axis if the atoms involved have an electronegativity difference. The atomic orbitals of oxygen atoms always occupy relatively lower positions due to its higher electronegativity as compared to carbon and nitrogen atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




