
\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}O\] is the molecular formula for two compounds A and B. They have a different structural formula.
A. What is this phenomenon known as?
B. Give the structural formula of A and B.
C. Write down their common and IUPAC names.
D. Mention the functional groups of A and B.
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: Sometimes there is more than one way to connect a given group of atoms into a molecular structure. They have the same formula but different structures which gives them their unique properties.
Complete step by step solution:
A. This is called isomerism. Isomers are the molecules which have the same molecular formula, but have a different arrangement of the atoms. They have the same empirical formula but they do not necessarily share similar physical and chemical properties.
B. The structural formula of A (\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\]) is
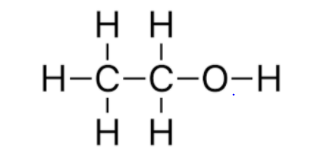
The structural formula of B (\[C{{H}_{3}}OC{{H}_{3}}\]) is
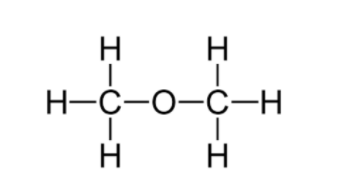
C. Common name: Ethyl alcohol
IUPAC name: Ethanol
Common name: Dimethyl ether
IUPAC name: Methoxymethane
D. The functional group of A is alcohol.
The functional group of B is ether.
Additional Information:
At room temperature, dimethyl ether is a gas whereas ethanol is a liquid.
The dominant intermolecular attraction between ethanol molecules is hydrogen bonding whereas in dimethyl ether the major intermolecular attraction involves regular dipole moments.
Dimethyl ether has a melting point of -138°C and boiling -25°C while ethanol has a melting point of -117°C and boiling 78°C.
Note: These two compounds are functional isomers. There are even more types of isomers, mainly classified as chain isomers, position isomers, and functional group isomers.
Complete step by step solution:
A. This is called isomerism. Isomers are the molecules which have the same molecular formula, but have a different arrangement of the atoms. They have the same empirical formula but they do not necessarily share similar physical and chemical properties.
B. The structural formula of A (\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\]) is

The structural formula of B (\[C{{H}_{3}}OC{{H}_{3}}\]) is

C. Common name: Ethyl alcohol
IUPAC name: Ethanol
Common name: Dimethyl ether
IUPAC name: Methoxymethane
D. The functional group of A is alcohol.
The functional group of B is ether.
Additional Information:
At room temperature, dimethyl ether is a gas whereas ethanol is a liquid.
The dominant intermolecular attraction between ethanol molecules is hydrogen bonding whereas in dimethyl ether the major intermolecular attraction involves regular dipole moments.
Dimethyl ether has a melting point of -138°C and boiling -25°C while ethanol has a melting point of -117°C and boiling 78°C.
Note: These two compounds are functional isomers. There are even more types of isomers, mainly classified as chain isomers, position isomers, and functional group isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




