
Calculate the dynamic viscosity of oil which is used for lubrication between a square plate of size $0.8m\times 0.8m$ and an inclined plane with an angle of inclination ${{30}^{o}}$ as shown. The mass of the square plate is $30kg$ and it slides down the inclined plane with a velocity of $0.3m{{s}^{-1}}$. The thickness of the oil film is $1.5mm$.
(A). $\mu =9.5poise$
(B). $\mu =11.7poise$
(C). $\mu =12.2poise$
(D). $\mu =13.2poise$

Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint: Oil is used for lubrication between block and an inclined plane. According to Newton's second law, the block is moving due to the forces acting on it. Using the FBD diagram, we can resolve the forces. Drag will resist the motion of the block; hence it will act opposite to the force. The dynamic viscosity is related to velocity of the block, thickness of film and area of cross section.
Formulas used:
$mg\sin \theta =drag(viscous\,force)$
$F=\mu \dfrac{v}{t}A$
Complete step-by-step solution:
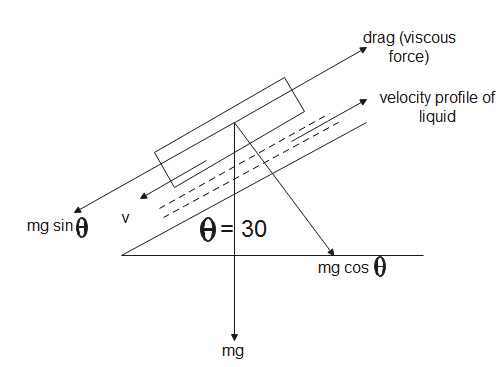
The above given figure is the FBD diagram for the block on the inclined plane. From the above figure we can see that,
$mg\sin \theta =drag(viscous\,force)$
The dynamic viscosity is the internal resistance provided by the fluid in the direction of flow. It is a constant quantity and the SI unit is Pascal-second ($P-s$).
Drag is the frictional force acting between a fluid and a surface moving through the fluid. It is the force acting on a body opposite to its motion relative to the fluid Its SI unit is Newton ($N$). It is given by-
$F=\mu \dfrac{v}{t}A$
Here, $\mu $ is the coefficient of viscosity
$v$ is the velocity of the body
$t$ is the thickness of fluid film
$A$ is the area of cross section
We substitute the given values in above equation to get,
$\begin{align}
& F=\mu \dfrac{v}{t}A \\
& \Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =\mu \dfrac{0.3\times {{10}^{-2}}}{1.5\times {{10}^{-1}}cm}0.8\times 0.8\times {{10}^{-4}}c{{m}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{30\times {{10}^{-3}}gm\times 10\times 1.5\times {{10}^{5}}}{2\times 0.3\times 0.8\times 0.8}=\mu \\
& \therefore \mu =11.7poise \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the value of dynamic viscosity of the fluid is $11.7poise$.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Dynamic viscosity is also known as the coefficient of viscosity. The dynamic viscosity acts between the layers of the fluid when they slide over each other. The drag is the frictional force acting on the block hence it is negative. We converted all units into CGS to calculate poise which is a CGS unit of dynamic viscosity.
Formulas used:
$mg\sin \theta =drag(viscous\,force)$
$F=\mu \dfrac{v}{t}A$
Complete step-by-step solution:

The above given figure is the FBD diagram for the block on the inclined plane. From the above figure we can see that,
$mg\sin \theta =drag(viscous\,force)$
The dynamic viscosity is the internal resistance provided by the fluid in the direction of flow. It is a constant quantity and the SI unit is Pascal-second ($P-s$).
Drag is the frictional force acting between a fluid and a surface moving through the fluid. It is the force acting on a body opposite to its motion relative to the fluid Its SI unit is Newton ($N$). It is given by-
$F=\mu \dfrac{v}{t}A$
Here, $\mu $ is the coefficient of viscosity
$v$ is the velocity of the body
$t$ is the thickness of fluid film
$A$ is the area of cross section
We substitute the given values in above equation to get,
$\begin{align}
& F=\mu \dfrac{v}{t}A \\
& \Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =\mu \dfrac{0.3\times {{10}^{-2}}}{1.5\times {{10}^{-1}}cm}0.8\times 0.8\times {{10}^{-4}}c{{m}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{30\times {{10}^{-3}}gm\times 10\times 1.5\times {{10}^{5}}}{2\times 0.3\times 0.8\times 0.8}=\mu \\
& \therefore \mu =11.7poise \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the value of dynamic viscosity of the fluid is $11.7poise$.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Dynamic viscosity is also known as the coefficient of viscosity. The dynamic viscosity acts between the layers of the fluid when they slide over each other. The drag is the frictional force acting on the block hence it is negative. We converted all units into CGS to calculate poise which is a CGS unit of dynamic viscosity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




