
How would you calculate the formal charge of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: For calculating the formal charge of an atom which is present inside the molecule then we have to know about the total number of valence electrons present in the atom, electrons which are not involved in the bonding and electrons which takes part in the formation of bond.
Complete answer:
Formal charge is that charge of the atom which explains the excess or low number of electrons present to that atom for the completion of eight electrons in the outermost shell.
Formal charge of an atom which is present inside the molecule is calculated as follow:
‘Formal charge = Number of valence electrons present on the atom – Non bonded electrons – Number of bonds’
In ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule, nitrogen is bonded with three hydrogen atom in the following manner:
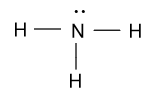
-Formal charge (F.C.) on nitrogen atom is calculated by using above given equation as follow:
F.C. on Nitrogen atom = Number of valence electrons present on nitrogen – Non bonded electrons on nitrogen – Number of bonds formed by nitrogen
F.C. on Nitrogen = $5 - 2 - 3 = 0$
-Formal charge (F.C.) on each hydrogen atom is calculated by using above given equation as follow:
F.C. on Hydrogen atom = Number of valence electrons present on hydrogen – Non bonded electrons on hydrogen – Number of bonds formed by hydrogen
F.C. on Hydrogen = $1 - 0 - 1 = 0$
-Now for calculating the formal charge of the whole molecule we have to add the formal charge of each atom present in that, so we get zero by adding the formal charge of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
Hence, the formal charge of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is zero.
Note:
In this question some of you may do wrong calculation if you are not familiar with the atomic number as well as with the electronic configuration of the atoms present in the molecule.
Complete answer:
Formal charge is that charge of the atom which explains the excess or low number of electrons present to that atom for the completion of eight electrons in the outermost shell.
Formal charge of an atom which is present inside the molecule is calculated as follow:
‘Formal charge = Number of valence electrons present on the atom – Non bonded electrons – Number of bonds’
In ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule, nitrogen is bonded with three hydrogen atom in the following manner:

-Formal charge (F.C.) on nitrogen atom is calculated by using above given equation as follow:
F.C. on Nitrogen atom = Number of valence electrons present on nitrogen – Non bonded electrons on nitrogen – Number of bonds formed by nitrogen
F.C. on Nitrogen = $5 - 2 - 3 = 0$
-Formal charge (F.C.) on each hydrogen atom is calculated by using above given equation as follow:
F.C. on Hydrogen atom = Number of valence electrons present on hydrogen – Non bonded electrons on hydrogen – Number of bonds formed by hydrogen
F.C. on Hydrogen = $1 - 0 - 1 = 0$
-Now for calculating the formal charge of the whole molecule we have to add the formal charge of each atom present in that, so we get zero by adding the formal charge of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
Hence, the formal charge of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is zero.
Note:
In this question some of you may do wrong calculation if you are not familiar with the atomic number as well as with the electronic configuration of the atoms present in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




