
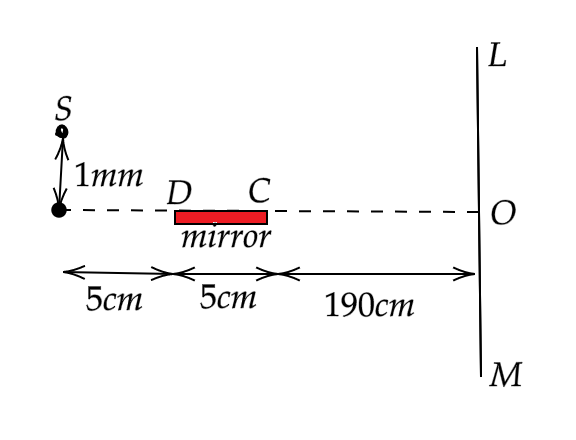
Calculate the number of fringes in

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint:The given question is an application of Young’s double-slit experiment. The fringes are seen due to the interference pattern caused as a result of overlapping light waves from the two slits.
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given fig,
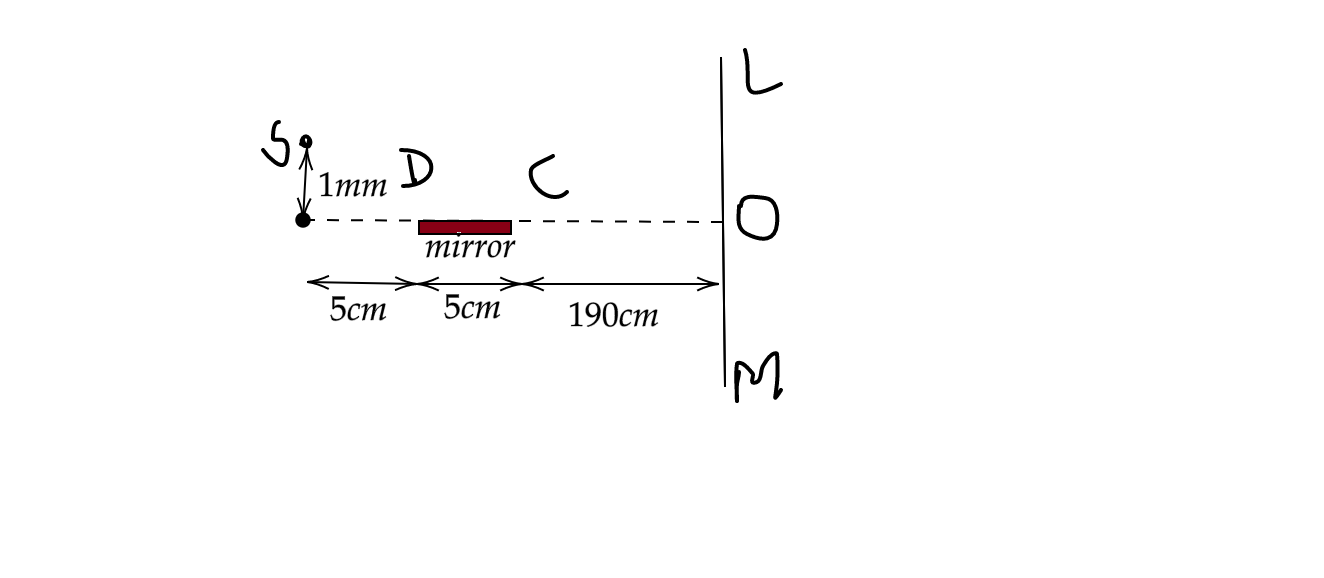
S is a point source of light
DC is the mirror
The rays from S get reflected on the mirror at points D and C and reach the screen at L and N
Thus, LN is the region in which fringes are visible.
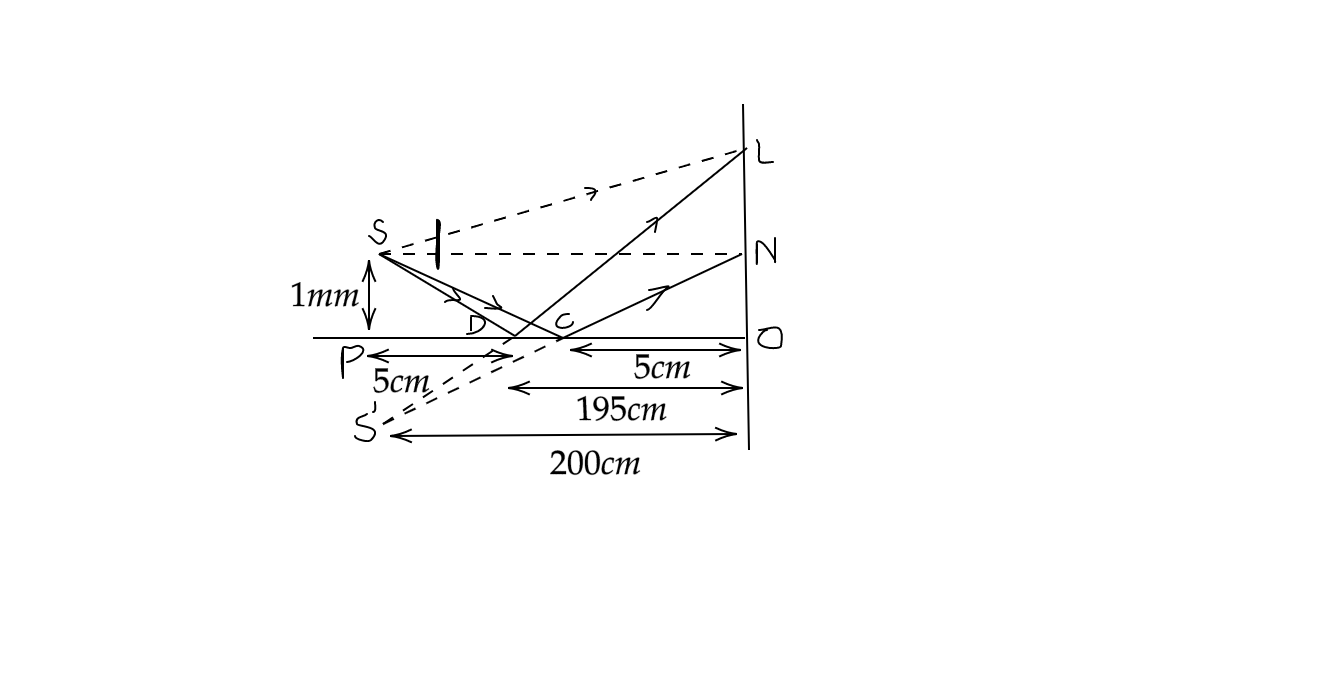
From the triangles SDP and LDO, using properties of similar triangles, we can state that
\[{{y}_{2}}=39mm\]
Now, from the triangles SCP and NCO, using properties of similar triangles, we can say that
\[{{y}_{1}}=19mm\]
Thus, the width of fringe visibility is LN, as stated above,
LN \[={{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}=20mm=2cm\]
The width of the fringe \[\beta =0.05cm\]
Hence, we can also conclude that in interference, fringe width is constant for all fringes.
Now, the number of fringes can be seen by us is given as the ratio of the width of fringe visibility (which is nothing but the effective screen width) to the width of a single fringe, that is,
\[\begin{align}
& N=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{\beta } \\
& \Rightarrow N=\dfrac{2}{0.05} \\
& \Rightarrow N=40 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the number of fringes observed in the given setup will be \[40\].
Note:- Interference is a phenomenon that supports the wave nature of light since only waves can overlap to produce a wave of greater, lower or the same amplitude. One other phenomenon that supports the wave nature of light is diffraction which is the bending of a light wave around the corners of an aperture.
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given fig,

S is a point source of light
DC is the mirror
The rays from S get reflected on the mirror at points D and C and reach the screen at L and N
Thus, LN is the region in which fringes are visible.

From the triangles SDP and LDO, using properties of similar triangles, we can state that
\[{{y}_{2}}=39mm\]
Now, from the triangles SCP and NCO, using properties of similar triangles, we can say that
\[{{y}_{1}}=19mm\]
Thus, the width of fringe visibility is LN, as stated above,
LN \[={{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}=20mm=2cm\]
The width of the fringe \[\beta =0.05cm\]
Hence, we can also conclude that in interference, fringe width is constant for all fringes.
Now, the number of fringes can be seen by us is given as the ratio of the width of fringe visibility (which is nothing but the effective screen width) to the width of a single fringe, that is,
\[\begin{align}
& N=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{\beta } \\
& \Rightarrow N=\dfrac{2}{0.05} \\
& \Rightarrow N=40 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the number of fringes observed in the given setup will be \[40\].
Note:- Interference is a phenomenon that supports the wave nature of light since only waves can overlap to produce a wave of greater, lower or the same amplitude. One other phenomenon that supports the wave nature of light is diffraction which is the bending of a light wave around the corners of an aperture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




