
Calculate the number of unpaired electrons in the following gaseous state ions: $ M{n^{3 + }} $ , $ C{r^{3 + }} $ , $ {V^{3 + }} $ and $ F{e^{2 + }} $ . Which one of these is the most stable in aqueous solutions? (Atomic number of $ V = 23 $ , $ Cr = 24 $ , $ Mn = 25 $ and $ Fe = 26 $ ).
Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint :The number of electrons lost or gained by an atom while forming a chemical bond is known as its oxidation state. When the electrons of an atom are present in the lowest possible energy, then it is known as the ground state of an atom whereas when the element is represented with its oxidation state, then it is known as gaseous state or excited state of an ion.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To calculate the number of unpaired electrons in each gaseous state ion, we need to write the electronic configuration of each element at gaseous state as well as at excited state.
Manganese (Mn):
Atomic number $ = 25 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^5}4{s^2} $
At the $ + 3 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ M{n^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ M{n^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^4}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ M{n^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
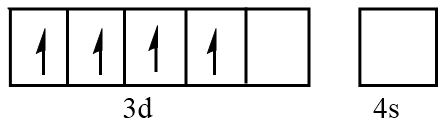
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ M{n^{3 + }} = 4 $
Chromium (Cr):
Atomic number $ = 24 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^5}4{s^1} $
At the $ + 3 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ C{r^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ C{r^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^3}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ C{r^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
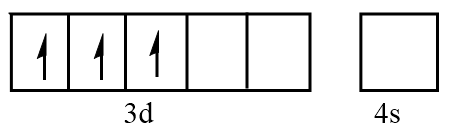
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ C{r^{3 + }} = 3 $
Vanadium (V):
Atomic number $ = 23 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^3}4{s^2} $
At the $ + 3 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ {V^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ {V^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^2}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ {V^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
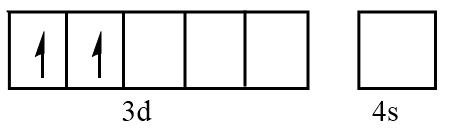
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ {V^{3 + }} = 2 $
Iron (Fe):
Atomic number $ = 26 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^6}4{s^2} $
At the $ + 2 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ F{e^{2 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ F{e^{2 + }} = [Ar]3{d^6}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ F{e^{2 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
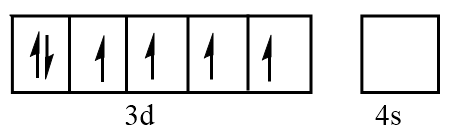
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ F{e^{2 + }} = 4 $
Now, among the given gaseous state ions the most stable ion in aqueous solution will be $ C{r^{3 + }} $ ion because it has three unpaired electrons and on splitting of d-orbital, the $ {t_{2g}} $ orbital will be half-filled which leads to increase the stability of the ion.
Note :
It is important to note that when electrons of ligands reach the d-orbital of metals, the d-orbitals closer to the ligands will have comparatively higher energy than those which are further away. So, due to electronic repulsions the splitting of d-orbital takes place. Also, half-filled and completely filled orbitals are more stable than partially filled d-orbitals.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To calculate the number of unpaired electrons in each gaseous state ion, we need to write the electronic configuration of each element at gaseous state as well as at excited state.
Manganese (Mn):
Atomic number $ = 25 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^5}4{s^2} $
At the $ + 3 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ M{n^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ M{n^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^4}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ M{n^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:

Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ M{n^{3 + }} = 4 $
Chromium (Cr):
Atomic number $ = 24 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^5}4{s^1} $
At the $ + 3 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ C{r^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ C{r^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^3}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ C{r^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:

Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ C{r^{3 + }} = 3 $
Vanadium (V):
Atomic number $ = 23 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^3}4{s^2} $
At the $ + 3 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ {V^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ {V^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^2}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ {V^{3 + }} $ ion will be as follows:

Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ {V^{3 + }} = 2 $
Iron (Fe):
Atomic number $ = 26 $
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom $ = [Ar]3{d^6}4{s^2} $
At the $ + 2 $ oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of $ F{e^{2 + }} $ ion will be as follows:
$ F{e^{2 + }} = [Ar]3{d^6}4{s^0} $
Orbital representation for electrons of $ F{e^{2 + }} $ ion will be as follows:

Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in $ F{e^{2 + }} = 4 $
Now, among the given gaseous state ions the most stable ion in aqueous solution will be $ C{r^{3 + }} $ ion because it has three unpaired electrons and on splitting of d-orbital, the $ {t_{2g}} $ orbital will be half-filled which leads to increase the stability of the ion.
Note :
It is important to note that when electrons of ligands reach the d-orbital of metals, the d-orbitals closer to the ligands will have comparatively higher energy than those which are further away. So, due to electronic repulsions the splitting of d-orbital takes place. Also, half-filled and completely filled orbitals are more stable than partially filled d-orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




