
Cambium of the root is the example of
(a) Apical meristem
(b) Intercalary meristem
(c) Primary meristem
(d) Secondary meristem
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The vascular cambium consists of both the interfascicular cambium (within the vascular bundle) and the interfascicular (between the vascular bundles). The vascular cambium along with cork cambium help in the secondary growth in dicot root and stem.
Complete answer:
The primary meristems are derived from the embryonic cells.
- Primary meristem gives rise to the primary plant body. The cells produced by the primary meristem become permanent later in the life of the plant producing permanent tissues.
- The vascular (fascicular) cambium and the cork cambium are examples of lateral meristematic tissue. - These lateral tissues are secondary in origin as they are formed from the permanent tissues. When the cells of the permanent tissues under the influence of hormones and other physiological factors start dedifferentiating into actively dividing meristematic cells, lateral meristems are formed.
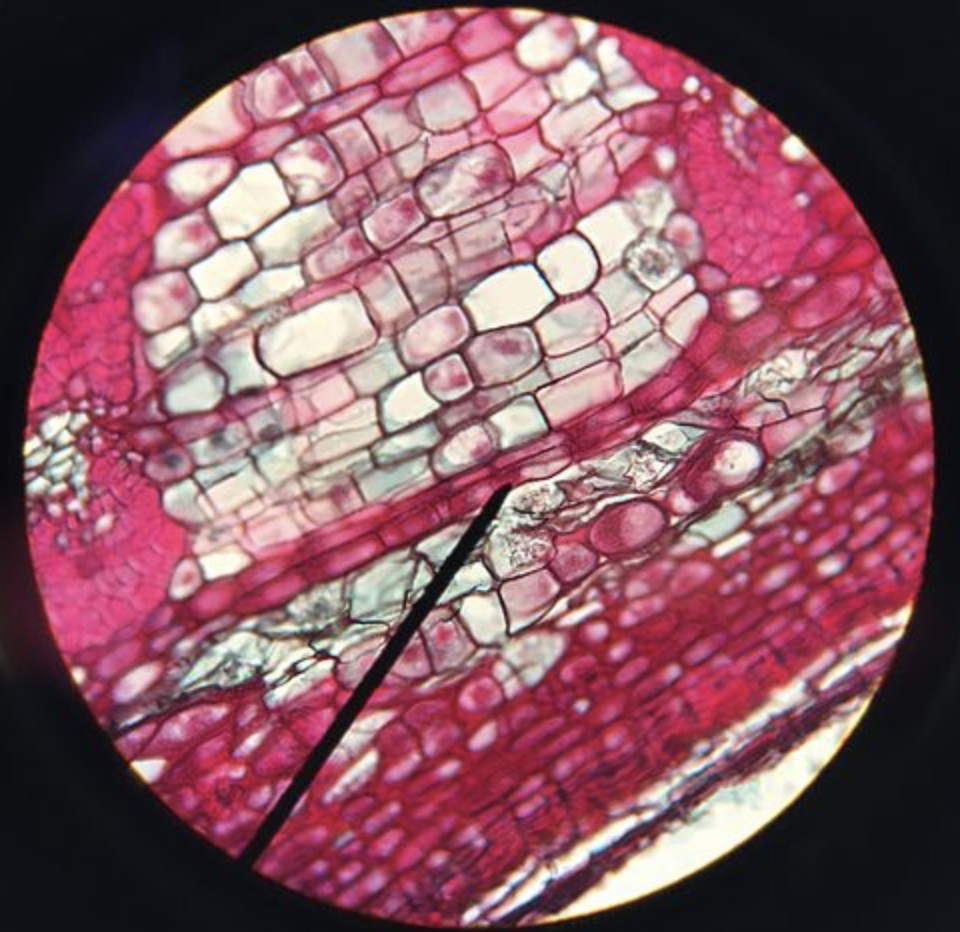
- The cambium is a strip of meristematic tissue undergoing active division when activated.
- The intrafascicular cambium is present in between the xylem tissue and phloem tissue of the vascular bundle of dicots.
Additional information:
- The lateral meristems occur on the lateral side of the stem and root of a plant. These meristems help in lateral growth (increase in girth) of the plant.
- The interfascicular meristem is present between the adjacent vascular bundles of the dicot root or stem.
- The intra and interfascicular meristem together form the fascicular meristem. During, spring season fascicular cambium is highly active and thus starts producing secondary xylem and phloem tissues.
- This causes an increase in the girth of the stem and root of dicots plants which is visible in the form of a cambium ring via a transverse section of the stem or root. A similar cork cambium also produces secondary tissues below the epidermis in the cortex region.
So, the correct answer is ‘Secondary meristem’.
Note:
- Intercalary meristem is the meristematic tissue present in the internode region of the stem which causes the internode elongation in various monocots like grasses.
- It helps in the vertical growth of the plant.
Complete answer:
The primary meristems are derived from the embryonic cells.
- Primary meristem gives rise to the primary plant body. The cells produced by the primary meristem become permanent later in the life of the plant producing permanent tissues.
- The vascular (fascicular) cambium and the cork cambium are examples of lateral meristematic tissue. - These lateral tissues are secondary in origin as they are formed from the permanent tissues. When the cells of the permanent tissues under the influence of hormones and other physiological factors start dedifferentiating into actively dividing meristematic cells, lateral meristems are formed.

- The cambium is a strip of meristematic tissue undergoing active division when activated.
- The intrafascicular cambium is present in between the xylem tissue and phloem tissue of the vascular bundle of dicots.
Additional information:
- The lateral meristems occur on the lateral side of the stem and root of a plant. These meristems help in lateral growth (increase in girth) of the plant.
- The interfascicular meristem is present between the adjacent vascular bundles of the dicot root or stem.
- The intra and interfascicular meristem together form the fascicular meristem. During, spring season fascicular cambium is highly active and thus starts producing secondary xylem and phloem tissues.
- This causes an increase in the girth of the stem and root of dicots plants which is visible in the form of a cambium ring via a transverse section of the stem or root. A similar cork cambium also produces secondary tissues below the epidermis in the cortex region.
So, the correct answer is ‘Secondary meristem’.
Note:
- Intercalary meristem is the meristematic tissue present in the internode region of the stem which causes the internode elongation in various monocots like grasses.
- It helps in the vertical growth of the plant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




