
Can you draw a triangle, which has exactly two lines of symmetry? Sketch a rough figure.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to draw a triangle, which has exactly two lines of symmetry. For this, we will draw three types of triangles based on sides, which are the scalene triangle, isosceles triangle, and equilateral triangle. After that, we will try to draw lines of symmetry of these triangles and check if any of them have exactly two lines of symmetry.
Complete step-by-step solution
Here, we have to draw a triangle, which has exactly two lines of symmetry.
Let us first understand what a line of symmetry is.
A line of symmetry is a line that cuts a shape exactly in half. If we place a mirror along the line, the shape will remain unchanged.
Based on this, we can draw three triangles based on their sides which are the scalene triangle, isosceles triangle, and equilateral triangle.
Now, let us draw these triangles and their possible lines of symmetry.
Scalene triangle: It is a triangle, which has all three sides different.
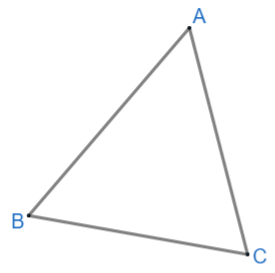
As we can see, the scalene triangle has no line of symmetry. No line can cut this triangle into exactly two identical parts. So this is not our required triangle.
Isosceles triangle: It is a triangle, which has two sides equal. (AB = AD in triangle ABC).
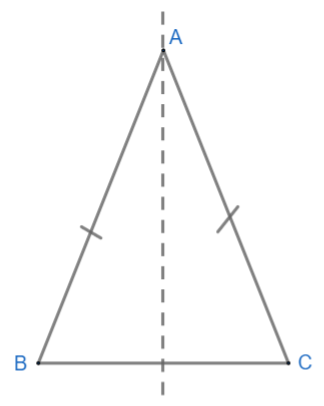
As we can see, this triangle has only one line of symmetry. So, this is not our required triangle.
Equilateral triangle: It is a triangle which has all sides equal. (AB = AC = BC in triangle ABC).
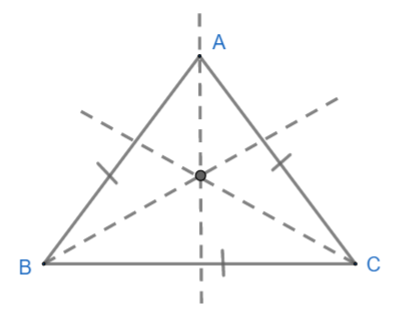
As we can see, this triangle has exactly three lines of symmetry. So this is not our required triangle.
Hence, there exists no triangle with exactly two lines of symmetry.
Note: Students should take care that the line of symmetry creates two shapes which are mirror images of each other. We are not talking about the area here. If we had to draw any shape having exactly two lines of symmetry then the rectangle is our required shape. Students should note that we classify only three types of triangles based on sides.
Complete step-by-step solution
Here, we have to draw a triangle, which has exactly two lines of symmetry.
Let us first understand what a line of symmetry is.
A line of symmetry is a line that cuts a shape exactly in half. If we place a mirror along the line, the shape will remain unchanged.
Based on this, we can draw three triangles based on their sides which are the scalene triangle, isosceles triangle, and equilateral triangle.
Now, let us draw these triangles and their possible lines of symmetry.
Scalene triangle: It is a triangle, which has all three sides different.

As we can see, the scalene triangle has no line of symmetry. No line can cut this triangle into exactly two identical parts. So this is not our required triangle.
Isosceles triangle: It is a triangle, which has two sides equal. (AB = AD in triangle ABC).

As we can see, this triangle has only one line of symmetry. So, this is not our required triangle.
Equilateral triangle: It is a triangle which has all sides equal. (AB = AC = BC in triangle ABC).

As we can see, this triangle has exactly three lines of symmetry. So this is not our required triangle.
Hence, there exists no triangle with exactly two lines of symmetry.
Note: Students should take care that the line of symmetry creates two shapes which are mirror images of each other. We are not talking about the area here. If we had to draw any shape having exactly two lines of symmetry then the rectangle is our required shape. Students should note that we classify only three types of triangles based on sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE





