
Car and petrol are example of __________
A.Competitive goods
B.Substitute goods
C.Gillen goods
D.Complementary goods
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: Complementarity may be influenced by psychological processes in which the consumption of one product (for example, cola) drives desire for its complementary goods (e.g., a cheeseburger). When a person consumes a meal or beverage, they are motivated to try its complements, which are items that they feel taste better together. Cola boosts people's willingness to spend more for a cheeseburger. This impact appears to be dependent on how these connections are perceived by consumers rather than their sensory characteristics.
Complete answer:
In economics, a complementary good is one whose appeal grows when its counterpart grows in popularity. It has a negative cross elasticity of demand, which means that demand for it rises when the price of another product falls. If A is a complement to B, a rise in the price of A will induce a downward movement along A's demand curve and a shift inward of B's demand curve, resulting in less of each product being sought. A reduction in the price of A, on the other hand, will produce a positive shift in the demand curve of A and a shift outward in the demand curve of B, resulting in more of each product being wanted.
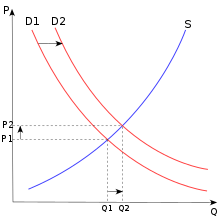
The desire for automobiles and gasoline is one illustration of this. The picture on the right depicts the supply and demand for automobiles, with D1 representing the initial demand. Assume that P1 represents the beginning price of automobiles, and Q1 represents the quantity demanded. If the price of gasoline were to drop by a certain amount, the demand for automobiles would increase. The demand curve would move rightward to a new point D2 as a result of the larger amount required. Assuming a steady supply curve S for automobiles, the new increased quantity required will occur at Q2, with a new higher price P2. Automobiles and petrol, mobile phones and cellular service, and printers and cartridges are among more examples.
Note:
A great complement is anything that has to be consumed with something else. As seen in the picture, the indifference curve of a perfect complement has a right angle. A Leontief utility function can be used to describe such preferences. Only a few products work well together. A left shoe and a right shoe, for example, are naturally sold in pairs, and the ratio of left to right shoe sales will never change much from 1:1.
Complete answer:
In economics, a complementary good is one whose appeal grows when its counterpart grows in popularity. It has a negative cross elasticity of demand, which means that demand for it rises when the price of another product falls. If A is a complement to B, a rise in the price of A will induce a downward movement along A's demand curve and a shift inward of B's demand curve, resulting in less of each product being sought. A reduction in the price of A, on the other hand, will produce a positive shift in the demand curve of A and a shift outward in the demand curve of B, resulting in more of each product being wanted.
The desire for automobiles and gasoline is one illustration of this. The picture on the right depicts the supply and demand for automobiles, with D1 representing the initial demand. Assume that P1 represents the beginning price of automobiles, and Q1 represents the quantity demanded. If the price of gasoline were to drop by a certain amount, the demand for automobiles would increase. The demand curve would move rightward to a new point D2 as a result of the larger amount required. Assuming a steady supply curve S for automobiles, the new increased quantity required will occur at Q2, with a new higher price P2. Automobiles and petrol, mobile phones and cellular service, and printers and cartridges are among more examples.

Note:
A great complement is anything that has to be consumed with something else. As seen in the picture, the indifference curve of a perfect complement has a right angle. A Leontief utility function can be used to describe such preferences. Only a few products work well together. A left shoe and a right shoe, for example, are naturally sold in pairs, and the ratio of left to right shoe sales will never change much from 1:1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




