
Carbonyl compounds react with ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$forming oximes which represent syn-anti geometrical isomerism. Which carbonyl compound forms oxime but does not show syn-anti geometrical isomerism.
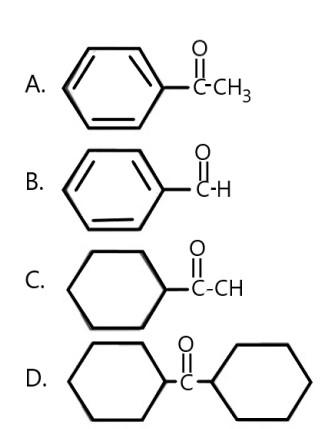

Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: Carbonyl compounds have \[CO\]/ \[( - C = O)\] groups in them. And syn-anti isomerism is just another name for cis-trans geometrical isomerism. In cis-isomerism similar groups (atoms/molecules), are on the same side, and in trans-isomerism, similar groups are at opposite sides (${180^ \circ }$apart).
Complete step-by-step answer:
Following the given hint we get the basic idea about the cis-trans isomerism. Now to get our answer we have to draw the corresponding oxime for each case and look for the syn-anti isomerism. The reaction in each case is similar as we are using the same reagent that is ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ and every reactant has the same functional group i.e., \[( - C = O)\] (the functional group governs the chemical property of any compound it is attached to). Therefore, in each case ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$molecules will release.
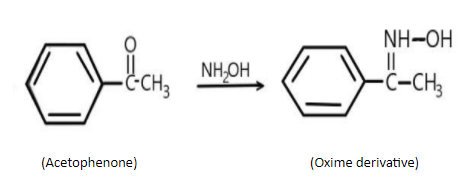
A) In the first case, acetophenone is reacting with oxime and is being released, the product form is:
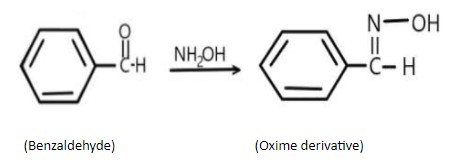
B) In 2nd reaction, we have, benzaldehyde reacting with oxime, and forming the corresponding oxime derivative, the reaction can be written as;
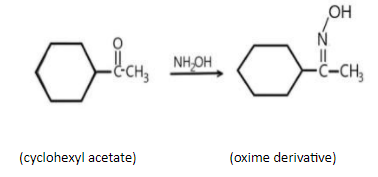
C) In 3rd reaction, we have cyclohexyl acetone reacting with oxime, its oxime derivatives can be written as,
D) In the 4th reaction we have di- cyclohexyl ketone reacting with oxime, the oxime derivative can be written as;
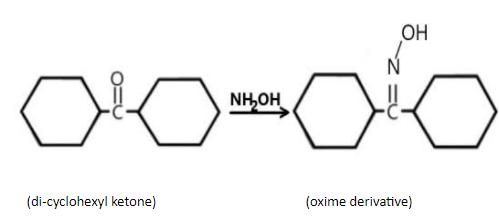
By looking at the oxime derivative of all the given compounds we can conclude that option (D) will not form the syn-anti isomerism, because ketones having the same acyl group bonded with the carbonyl (\[( - C = O)\]) group does not show syn-anti isomerism.
Hence, the correct answer is option (D) i.e., the di-cyclohexyl ketone.
Additional information:
We can sum up cis-trans isomerism in the following three requirements.
i) The first condition is that rotation must not be allowed in a compound. We know that any compound is present in a 3-dimension state in the ‘real world’, therefore it can so happen that the compound will undergo rotation and change its orientation. Hence to get a stable cis-trans isomer the rotation of the compound must be prohibited, that’s why we look for double bonds in a compound.
ii) However, having a double bond only restricts the rotation, it does not confirm cis-trans isomerism.
iii) The second condition is that there must be at least two non-identical groups on both sides of the double bond.
iv) If all groups are different in a compound (say A, B, C, D) then, by keeping the position of one group (say, fixing the position of the group ‘A’), we can assign one of the conformations as cis(assuming A and B, on one side as cis) and the other as trans (A and B on different sides).
Note: We just saw that syn-anti isomerism can be called as cis- trans isomerism, but cis-trans isomers can also be written as Z-E isomers, respectively. That is why it is important to keep a note of all the other terms related to an isomer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Following the given hint we get the basic idea about the cis-trans isomerism. Now to get our answer we have to draw the corresponding oxime for each case and look for the syn-anti isomerism. The reaction in each case is similar as we are using the same reagent that is ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ and every reactant has the same functional group i.e., \[( - C = O)\] (the functional group governs the chemical property of any compound it is attached to). Therefore, in each case ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$molecules will release.
A) In the first case, acetophenone is reacting with oxime and is being released, the product form is:

B) In 2nd reaction, we have, benzaldehyde reacting with oxime, and forming the corresponding oxime derivative, the reaction can be written as;

C) In 3rd reaction, we have cyclohexyl acetone reacting with oxime, its oxime derivatives can be written as,

D) In the 4th reaction we have di- cyclohexyl ketone reacting with oxime, the oxime derivative can be written as;

By looking at the oxime derivative of all the given compounds we can conclude that option (D) will not form the syn-anti isomerism, because ketones having the same acyl group bonded with the carbonyl (\[( - C = O)\]) group does not show syn-anti isomerism.
Hence, the correct answer is option (D) i.e., the di-cyclohexyl ketone.
Additional information:
We can sum up cis-trans isomerism in the following three requirements.
i) The first condition is that rotation must not be allowed in a compound. We know that any compound is present in a 3-dimension state in the ‘real world’, therefore it can so happen that the compound will undergo rotation and change its orientation. Hence to get a stable cis-trans isomer the rotation of the compound must be prohibited, that’s why we look for double bonds in a compound.
ii) However, having a double bond only restricts the rotation, it does not confirm cis-trans isomerism.
iii) The second condition is that there must be at least two non-identical groups on both sides of the double bond.
iv) If all groups are different in a compound (say A, B, C, D) then, by keeping the position of one group (say, fixing the position of the group ‘A’), we can assign one of the conformations as cis(assuming A and B, on one side as cis) and the other as trans (A and B on different sides).
Note: We just saw that syn-anti isomerism can be called as cis- trans isomerism, but cis-trans isomers can also be written as Z-E isomers, respectively. That is why it is important to keep a note of all the other terms related to an isomer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




