
How do you carry out the following conversion?
Aniline to p-bromoaniline.
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Aniline is an aromatic amine has the chemical formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ and p-bromo aniline is the substituted aniline that has the chemical formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br}}$. The conversion of Aniline to p-bromoaniline is done in 3 steps.
Complete step by step answer:
Following are the three steps involved in the conversion of aniline to p-bromoaniline:
Step 1: Conversion of aniline to N-phenyl acetamide
In this step aniline undergoes acetylation when treated with acetic anhydride in the presence of pyridine.
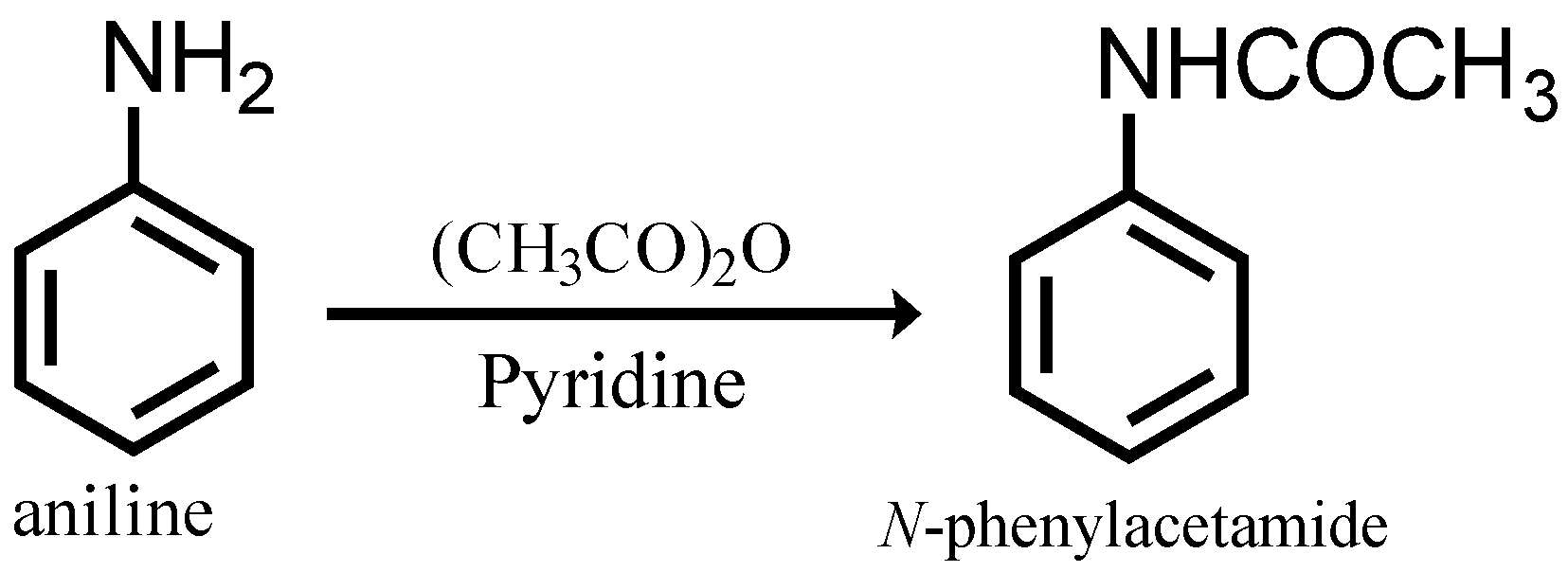
Step 2: Conversion of N-phenyl acetamide to 4-bromo-N-phenyl acetamide
The second step is the bromination. Bromine atoms being an ortho-para directing group may substitute at ortho and even para position in order to avoid the substitution at ortho position we need to block the ortho position. The first step is crucial in order to block the ortho positions so that in the next step while performing bromination, bromine attacks the para position rather than ortho position. The reason behind this is steric hindrance at the ortho position. Thus, bromination of N-phenyl acetamide gives para brominated products as the major product.
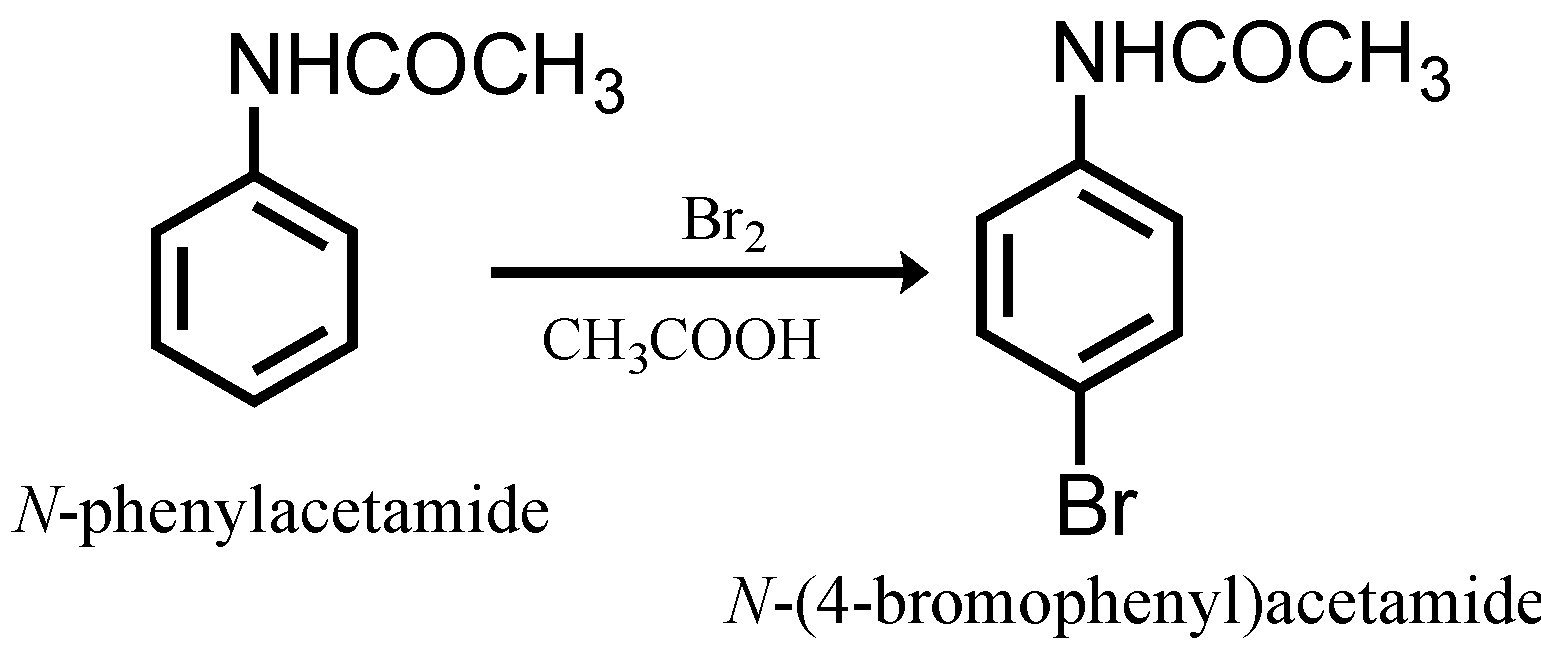
Step 3: Conversion of 4-bromo-N-phenyl acetamide to p-bromoaniline
Deacetylation is done through acid or basic hydrolysis to yield the desired p-bromoaniline.
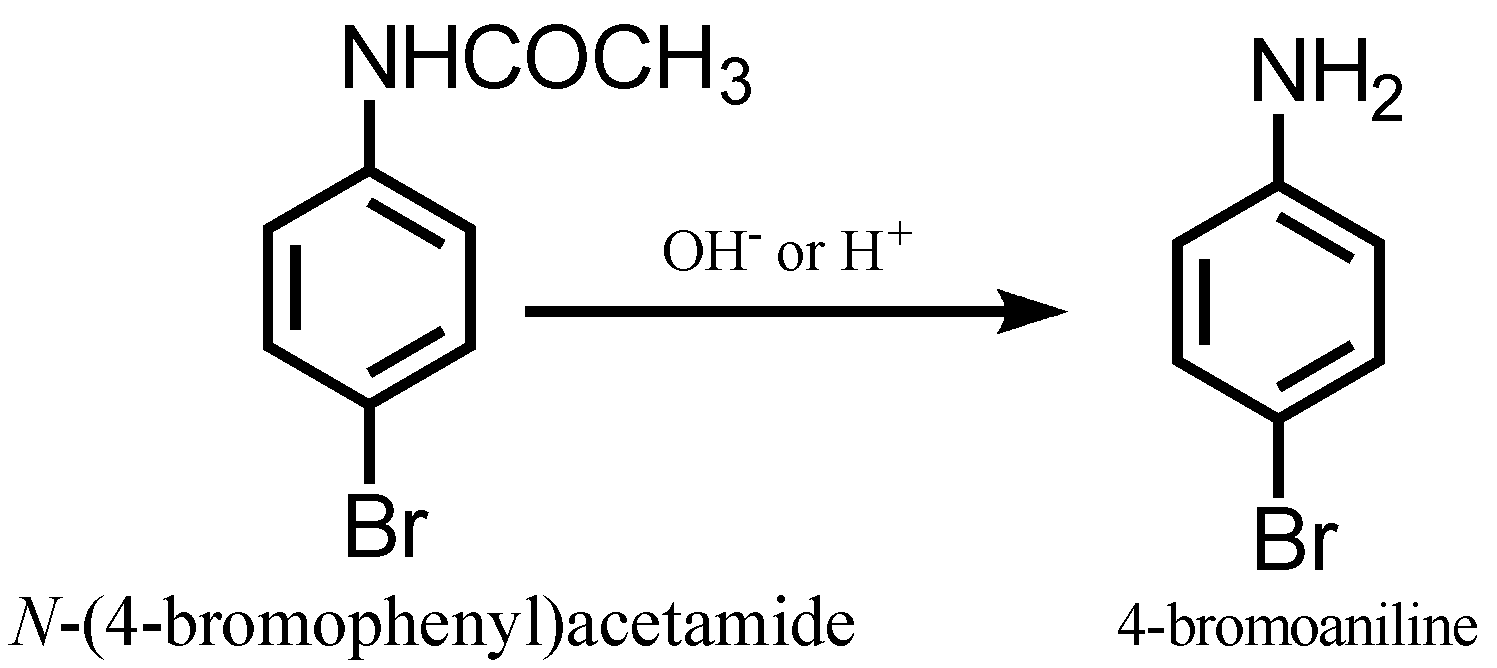
Note:
Direct bromination of aniline will also yield p-bromo aniline but along with o-bromoaniline. In order to avoid major and minor products the first step to block the ortho position is necessary.

Complete step by step answer:
Following are the three steps involved in the conversion of aniline to p-bromoaniline:
Step 1: Conversion of aniline to N-phenyl acetamide
In this step aniline undergoes acetylation when treated with acetic anhydride in the presence of pyridine.

Step 2: Conversion of N-phenyl acetamide to 4-bromo-N-phenyl acetamide
The second step is the bromination. Bromine atoms being an ortho-para directing group may substitute at ortho and even para position in order to avoid the substitution at ortho position we need to block the ortho position. The first step is crucial in order to block the ortho positions so that in the next step while performing bromination, bromine attacks the para position rather than ortho position. The reason behind this is steric hindrance at the ortho position. Thus, bromination of N-phenyl acetamide gives para brominated products as the major product.

Step 3: Conversion of 4-bromo-N-phenyl acetamide to p-bromoaniline
Deacetylation is done through acid or basic hydrolysis to yield the desired p-bromoaniline.

Note:
Direct bromination of aniline will also yield p-bromo aniline but along with o-bromoaniline. In order to avoid major and minor products the first step to block the ortho position is necessary.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




