
Catalytic hydrogenation of Benzene give
A) Xylene
B) Cyclohexane
C) Benzoic acid
D) Toluene
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: Since benzene is highly unsaturated so in most of the reactions unsaturation of the benzene ring is retained. Under extreme conditions, high pressure, and temperature benzene gives cyclohexane on treatment with a nickel catalyst. This reaction is an example of an addition reaction.
Complete answer:
First, we will define what the catalytic hydrogenation reaction is- it is adding hydrogen on double and triple bonds in the presence of a catalyst such as Ni, Pd, Pt.
Benzene is a stable aromatic compound and it has a high unsaturated ring. We know that most of the organic reactions of unsaturation of benzene are retained. But under extreme conditions like high pressure and high temperature and in the presence of nickel catalyst hydrogenation of benzene gives cyclohexane. The catalytic hydrogenation of benzene has been performed as a model reaction for raising hydrogenated cyclic compounds from aromatic substances. Nickel shows the best activity for benzene conversion reaction.
Catalytic hydrogenation of benzene:
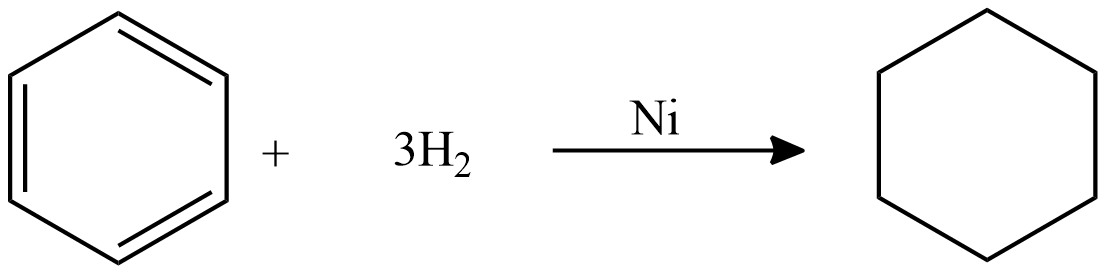
To saturate benzene 3 moles of hydrogen is required. Because we have three double bonds each mole of hydrogen saturates one double bond. The reaction is carried out at high pressure and temperature. This reaction is carried out in the vapor phase as well as in the liquid phase. The yield of this reaction is $99\% $ .
Cyclohexane is not naturally available so it is produced industrially from benzene.
Benzene is naturally occurring as well as can be prepared by a human. Naturally, benzene occurs in crude oil, gasoline, smoke and volcanoes, and forest fires.
Hence option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
Cyclohexane may also be obtained from naphtha fractionation and by isomerization of methyl cyclopentane. By the hydrogenation reaction substituted benzene rings may also reduce in the same manner. Nickel/ palladium on carbon is used as catalysts for this purpose.
Complete answer:
First, we will define what the catalytic hydrogenation reaction is- it is adding hydrogen on double and triple bonds in the presence of a catalyst such as Ni, Pd, Pt.
Benzene is a stable aromatic compound and it has a high unsaturated ring. We know that most of the organic reactions of unsaturation of benzene are retained. But under extreme conditions like high pressure and high temperature and in the presence of nickel catalyst hydrogenation of benzene gives cyclohexane. The catalytic hydrogenation of benzene has been performed as a model reaction for raising hydrogenated cyclic compounds from aromatic substances. Nickel shows the best activity for benzene conversion reaction.
Catalytic hydrogenation of benzene:
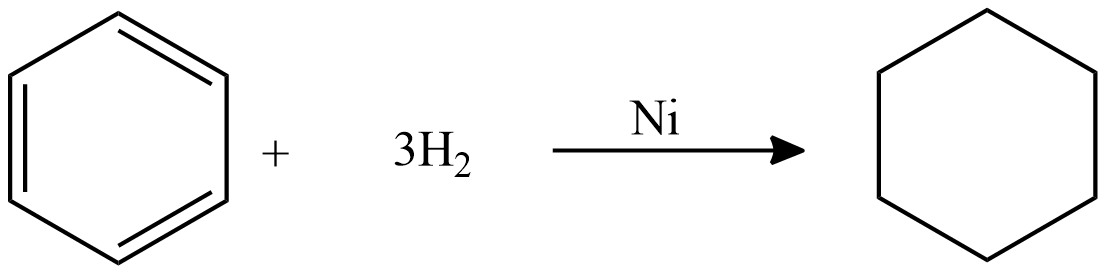
To saturate benzene 3 moles of hydrogen is required. Because we have three double bonds each mole of hydrogen saturates one double bond. The reaction is carried out at high pressure and temperature. This reaction is carried out in the vapor phase as well as in the liquid phase. The yield of this reaction is $99\% $ .
Cyclohexane is not naturally available so it is produced industrially from benzene.
Benzene is naturally occurring as well as can be prepared by a human. Naturally, benzene occurs in crude oil, gasoline, smoke and volcanoes, and forest fires.
Hence option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
Cyclohexane may also be obtained from naphtha fractionation and by isomerization of methyl cyclopentane. By the hydrogenation reaction substituted benzene rings may also reduce in the same manner. Nickel/ palladium on carbon is used as catalysts for this purpose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




