
What is the cause of hyperpolarization?
a. due to excess K+ outfit
b. due to influx of Cl- ions
c. after releasing of GABA
d. all the above
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Hyperpolarization takes place when the cell membrane's potential becomes more negative than the resting potential i.e., -70mV. It is the opposite of Depolarization.
Complete answer:
When at rest, a neuron has a resting potential of -70 mV. This indicates that the interior of the cell is negatively charged as compared to the outside of the cell. When a signal is to be transmitted through neurons, it requires the development of an Action potential (+30 mV). On the other hand, to prevent any stimulus that is already sent up through the axon, from triggering an action potential in a subsequent neuron, Hyperpolarization is required.
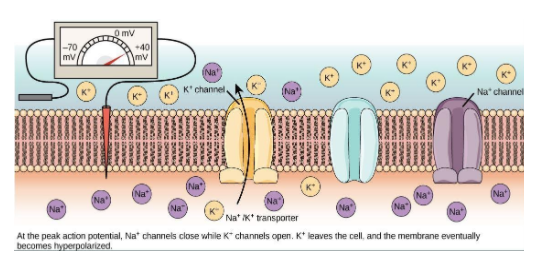
To make the membrane potential more negative resulting in hyperpolarization, it will require either of the following ways:
1. The opening of channels leads to the flow of positive charge out of the membrane. Eg.: Opening of channels that let K+ out of the cell.
2. The opening of channels leads to the flow of negative charge into the cell membrane. Eg.: Influx of Cl- into the cell.
3. Release of an Inhibitory neurotransmitter like GABA forms the presynaptic neuronal membrane that makes the resting potential more negative. Such a hyperpolarization is referred to as Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP).
Therefore, hyperpolarization can be caused due to excess K+ outfit, the influx of Cl- ions or after releasing GABA.
The correct option is D. All of the above.
Note: Resting membrane potential of a neuron is about -70mV which means that the inside of the neuron is 70mV less than the outside. The membrane is said to be Depolarized when this resting potential becomes more positive and hyperpolarized when the resting potential becomes more negative.
Complete answer:
When at rest, a neuron has a resting potential of -70 mV. This indicates that the interior of the cell is negatively charged as compared to the outside of the cell. When a signal is to be transmitted through neurons, it requires the development of an Action potential (+30 mV). On the other hand, to prevent any stimulus that is already sent up through the axon, from triggering an action potential in a subsequent neuron, Hyperpolarization is required.

To make the membrane potential more negative resulting in hyperpolarization, it will require either of the following ways:
1. The opening of channels leads to the flow of positive charge out of the membrane. Eg.: Opening of channels that let K+ out of the cell.
2. The opening of channels leads to the flow of negative charge into the cell membrane. Eg.: Influx of Cl- into the cell.
3. Release of an Inhibitory neurotransmitter like GABA forms the presynaptic neuronal membrane that makes the resting potential more negative. Such a hyperpolarization is referred to as Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP).
Therefore, hyperpolarization can be caused due to excess K+ outfit, the influx of Cl- ions or after releasing GABA.
The correct option is D. All of the above.
Note: Resting membrane potential of a neuron is about -70mV which means that the inside of the neuron is 70mV less than the outside. The membrane is said to be Depolarized when this resting potential becomes more positive and hyperpolarized when the resting potential becomes more negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




