
What causes a Deletion Mutation?
Answer
489.3k+ views
Hint: Mutation was first introduced by Hugo de Vries. This term was used by him for large spontaneous inheritable changes which occur suddenly in a naturally reproducing population. Based on mutation theory there are two types of mutations- Somatic and Germinal mutation. Somatic mutation occurs in somatic cells and germinal mutation takes place in gametes.
Complete answer-
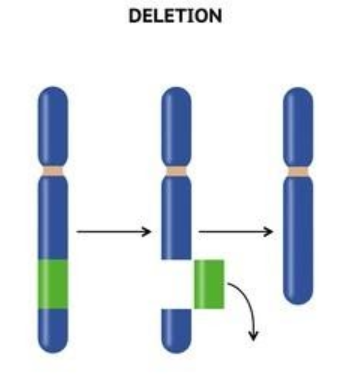
Mutation based on genes and chromosomes are categorized into the involvement of depending on the number of gene loci. Deletion mutation is a type of chromosomal mutation which shows visible changes in the structure of chromosomes involving changes either in the total number of genes or gene loci in a chromosome or chromosomal arrangements.
Deletion mutations arise from breaks in chromosomes and they are also known as chromosomal derangements. Deletion mutation is the deficiency of chromosome segments resulting in the loss of segments. Depending upon loss of gene segments the genes vary from single gene to block containing many genes.
Deletion mutation is categorized into two subtypes Terminal Deletion and Intercalary deletion where the cause for terminal deletion is the loss of segment from one or another end of chromosomes. Terminal acentric part of chromosomes is unable to survive. The terminal deletion is caused by breaking or a single break in the chromosome.
Intercalary deletion is the involvement of loss of segment from intercalary of the chromosome with the reunion of terminal segments. Therefore, the intercalary deletion is caused by two breaks from the middle and the reunion of terminal parts.
Note:
The function of mutations is to bring undesirable changes and sudden changes in the organism. The mutation part is controlled by genes. Some mutations can be beneficial which occur in bacteria for the survival of antibiotic drugs which leads to development of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
Complete answer-
Mutation based on genes and chromosomes are categorized into the involvement of depending on the number of gene loci. Deletion mutation is a type of chromosomal mutation which shows visible changes in the structure of chromosomes involving changes either in the total number of genes or gene loci in a chromosome or chromosomal arrangements.
Deletion mutations arise from breaks in chromosomes and they are also known as chromosomal derangements. Deletion mutation is the deficiency of chromosome segments resulting in the loss of segments. Depending upon loss of gene segments the genes vary from single gene to block containing many genes.
Deletion mutation is categorized into two subtypes Terminal Deletion and Intercalary deletion where the cause for terminal deletion is the loss of segment from one or another end of chromosomes. Terminal acentric part of chromosomes is unable to survive. The terminal deletion is caused by breaking or a single break in the chromosome.
Intercalary deletion is the involvement of loss of segment from intercalary of the chromosome with the reunion of terminal segments. Therefore, the intercalary deletion is caused by two breaks from the middle and the reunion of terminal parts.

Note:
The function of mutations is to bring undesirable changes and sudden changes in the organism. The mutation part is controlled by genes. Some mutations can be beneficial which occur in bacteria for the survival of antibiotic drugs which leads to development of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




