
What is cell division and why is it necessary?
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Cells are the structural and functional unit of life. Cells are living entities and undergo biochemical processes that cause wear and tear mechanisms. Organisms that reproduce sexually arise from a single cell called the zygote, while asexual organisms clone themselves to produce offsprings. These processes cause the cell to divide several times in its life.
Complete answer:
Cell division is the process by which cells divide and increase in number to produce new cells. The cell that divides is termed as the parent cell and the new cells that are formed are known as daughter cells.
A cell comprises organelles and the genetic material – the chromosome. The main aim of a cell, when it divides, is to maintain its genome. Therefore, before division begins, the chromosomes of the parent cell are duplicated and equal numbers of chromosomes are passed onto the daughter cells.
Cell division is a part of the cyclical process called cell cycle, where a cell undergoes genome duplication and the subsequent division in repeated cycles controlled by various checkpoints that detect damages in chromosome duplication and segregation and arrest the process until the defects are repaired.
Cell division in eukaryotes can be Mitotic or Meiotic. When a parent cell divides to form a clone of itself, the process is called Mitosis. In this process, the parent cell divides once and forms two daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes. However, in Meiosis the parent cell divides twice to produce four daughter cells, each of which have half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Typically, mitosis and meiosis occur in eukaryotes only. All cells of the body are produced by mitosis except the gametes, which arise by meiosis.
A cell division has four stages – Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
Prokaryotic organisms under a simple cell division called binary fission, where the parent cell simply divided into two daughter cells. The genetic material which is duplicated beforehand, is segregated equally in the two daughter cells.
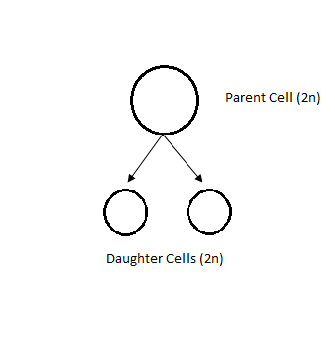
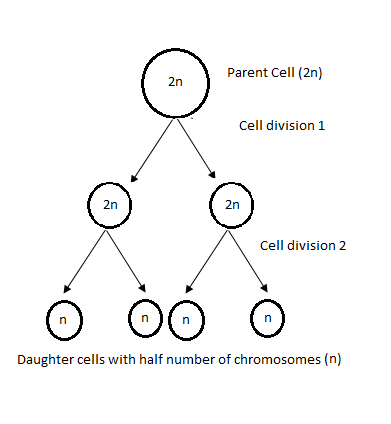
Figure: Schematic representation of Mitosis (left) and Meiosis (right)
Therefore, in other words, the key to life is cell division. A cell divides for various reasons – some of which are listed below:
-Cells divide to replace or repair damaged cells.
-It is responsible for maintaining the cell’s genome.
-Producing gametes – sperm and egg.
-Serves as a means of reproduction in prokaryotes.
-Cell division introduces genetic variation.
-It causes growth of organisms.
Note: Cell division is the process by which cells divide to increase in number. It can be of two types – Mitosis and Meiosis. Mitosis is called equational division because it maintains the cell’s genetic material. Meiosis, on the other hand, is known as reduction division since the chromosome number in daughter cells is half of the parent cell. Cells divide to repair damaged cells, produce gametes and maintain the chromosome number in cells.
Complete answer:
Cell division is the process by which cells divide and increase in number to produce new cells. The cell that divides is termed as the parent cell and the new cells that are formed are known as daughter cells.
A cell comprises organelles and the genetic material – the chromosome. The main aim of a cell, when it divides, is to maintain its genome. Therefore, before division begins, the chromosomes of the parent cell are duplicated and equal numbers of chromosomes are passed onto the daughter cells.
Cell division is a part of the cyclical process called cell cycle, where a cell undergoes genome duplication and the subsequent division in repeated cycles controlled by various checkpoints that detect damages in chromosome duplication and segregation and arrest the process until the defects are repaired.
Cell division in eukaryotes can be Mitotic or Meiotic. When a parent cell divides to form a clone of itself, the process is called Mitosis. In this process, the parent cell divides once and forms two daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes. However, in Meiosis the parent cell divides twice to produce four daughter cells, each of which have half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Typically, mitosis and meiosis occur in eukaryotes only. All cells of the body are produced by mitosis except the gametes, which arise by meiosis.
A cell division has four stages – Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
Prokaryotic organisms under a simple cell division called binary fission, where the parent cell simply divided into two daughter cells. The genetic material which is duplicated beforehand, is segregated equally in the two daughter cells.


Figure: Schematic representation of Mitosis (left) and Meiosis (right)
Therefore, in other words, the key to life is cell division. A cell divides for various reasons – some of which are listed below:
-Cells divide to replace or repair damaged cells.
-It is responsible for maintaining the cell’s genome.
-Producing gametes – sperm and egg.
-Serves as a means of reproduction in prokaryotes.
-Cell division introduces genetic variation.
-It causes growth of organisms.
Note: Cell division is the process by which cells divide to increase in number. It can be of two types – Mitosis and Meiosis. Mitosis is called equational division because it maintains the cell’s genetic material. Meiosis, on the other hand, is known as reduction division since the chromosome number in daughter cells is half of the parent cell. Cells divide to repair damaged cells, produce gametes and maintain the chromosome number in cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




