
What is cell division? Write two types of cell division.
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: It was first discovered by German botanist Hugo Von Mohl under a microscope in 1835 when he was working over green alga cladophora glomerata. It is very much important for the growth and development of an organism.
Complete answer:
A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known organisms. Cell division may be a process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It occurs as a part of a large cell cycle. The cell cycle involves the stages through which the cell passes to allow them to divide and produce new cells. The stages are- two gap phases (G1 and G2), an S phase (duplication of genetic material), and an M phase (mitosis). There are mainly two types of cell division that occurs in living organisms-
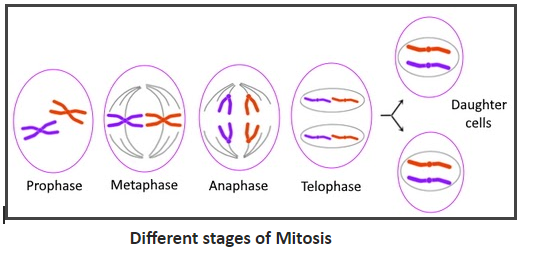
1. Mitosis: where a parent cell divides into two daughter cells each of which is genetically identical to the parent cell. Mitosis is also known as vegetative cell division. It occurs in several stages, they are-
(a) Prophase- chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes. The nuclear membrane breaks down and spindles form at opposite poles of the cell.
(b) Metaphase- the spindle reaches maturity and chromosomes align at the equator.
(c) Anaphase- paired chromosomes separate and begin moving to poles. Spindle fibers are not connected to chromatids. At the end of the anaphase, each pole contains a complete compilation of chromosomes.
(d) Telophase- The chromosomes begin to condense Two new nuclei form, one for each set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis- Cytokinesis is a type of division of the cell's cytoplasm. It begins before the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophase/mitosis. At the end of cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. These are diploid cells, with each cell containing a complement of chromosomes.
2. Meiosis: It is the division of a cell in two stages that results in four daughter cells, each with half the chromosomes of the original cell. Meiosis is also known as reproductive cell division. Meiosis I and Meiosis II are two stages of meiosis. Meiosis I involves-
(a) Prophase I- Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs.
(b) Metaphase I- Spindle fibers from opposing centrosomes connect to bivalents (at centromeres) and align them along the middle of the cell.
(c)Anaphase I- Spindle fibers contract and split the bivalent, homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell.
(d) Telophase I- Chromosomes condense, the nuclear membrane may reform, the cell divides (cytokinesis) to form two haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis II involves-
(a) Prophase II- Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrosomes move to opposite poles.
(b) Metaphase II- Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrosomes move to opposite poles.
(c) Anaphase II- Spindle fibers contract and separate the sister chromatids, chromatids (now called chromosomes) move to opposite poles.
(d) Telophase II- Chromosomes de condense, nuclear membrane reforms, cells divide (cytokinesis) to form four haploid daughter cells.
Note:
-The cell was discovered by Mr. Robert Hooke in 1665. It consists of a cytoplasm that contains proteins and nucleic acid and is enclosed within a membrane called the cell membrane.
-Meiosis I include crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs.
-Meiosis II starts with two haploid parent cells and ends with four haploid daughter cells, maintaining the number of chromosomes in each cell.
Complete answer:
A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known organisms. Cell division may be a process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It occurs as a part of a large cell cycle. The cell cycle involves the stages through which the cell passes to allow them to divide and produce new cells. The stages are- two gap phases (G1 and G2), an S phase (duplication of genetic material), and an M phase (mitosis). There are mainly two types of cell division that occurs in living organisms-
1. Mitosis: where a parent cell divides into two daughter cells each of which is genetically identical to the parent cell. Mitosis is also known as vegetative cell division. It occurs in several stages, they are-
(a) Prophase- chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes. The nuclear membrane breaks down and spindles form at opposite poles of the cell.
(b) Metaphase- the spindle reaches maturity and chromosomes align at the equator.
(c) Anaphase- paired chromosomes separate and begin moving to poles. Spindle fibers are not connected to chromatids. At the end of the anaphase, each pole contains a complete compilation of chromosomes.
(d) Telophase- The chromosomes begin to condense Two new nuclei form, one for each set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis- Cytokinesis is a type of division of the cell's cytoplasm. It begins before the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophase/mitosis. At the end of cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. These are diploid cells, with each cell containing a complement of chromosomes.

2. Meiosis: It is the division of a cell in two stages that results in four daughter cells, each with half the chromosomes of the original cell. Meiosis is also known as reproductive cell division. Meiosis I and Meiosis II are two stages of meiosis. Meiosis I involves-
(a) Prophase I- Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs.
(b) Metaphase I- Spindle fibers from opposing centrosomes connect to bivalents (at centromeres) and align them along the middle of the cell.
(c)Anaphase I- Spindle fibers contract and split the bivalent, homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell.
(d) Telophase I- Chromosomes condense, the nuclear membrane may reform, the cell divides (cytokinesis) to form two haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis II involves-
(a) Prophase II- Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrosomes move to opposite poles.
(b) Metaphase II- Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrosomes move to opposite poles.
(c) Anaphase II- Spindle fibers contract and separate the sister chromatids, chromatids (now called chromosomes) move to opposite poles.
(d) Telophase II- Chromosomes de condense, nuclear membrane reforms, cells divide (cytokinesis) to form four haploid daughter cells.
Note:
-The cell was discovered by Mr. Robert Hooke in 1665. It consists of a cytoplasm that contains proteins and nucleic acid and is enclosed within a membrane called the cell membrane.
-Meiosis I include crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs.
-Meiosis II starts with two haploid parent cells and ends with four haploid daughter cells, maintaining the number of chromosomes in each cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




