
Cellulose is a polymer of
A ) glucose
B ) fructose
C ) ribose
D ) sucrose
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The monomer of cellulose is an aldohexose. An aldohexose is a sugar containing 6 Carbon atoms and an aldehydic group.
Complete step by step answer:
Cellulose is an important component of the cell walls in plants. It is present as microfibrils of plant cell wall. Thus, it is the structural component of plant cell wall and primitive fungi. Cellulose is also used for the production of papers. Cellulose is non reducing sugar as aldehyde group is not free. Aldehyde group is involved in glycosidic bond formation.
Cellulose is a fibrous, straight chain polymer. It is a polysaccharide consisting of several glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. The glycosidic linkage is between C-1 of one glucose unit and C-4 of other glucose unit. Cellulose is also called glucosan homopolysaccharide. One linear chain of cellulose contains around 6000 to 10000 glucose units. Cellulose is also called hexosan polysaccharide because the monomer glucose is a hexose sugar.
The structure of glucose is as shown below:
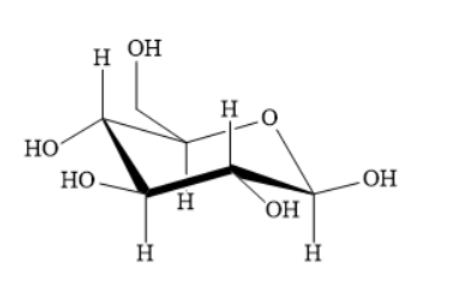
The structure of cellulose is as shown below:
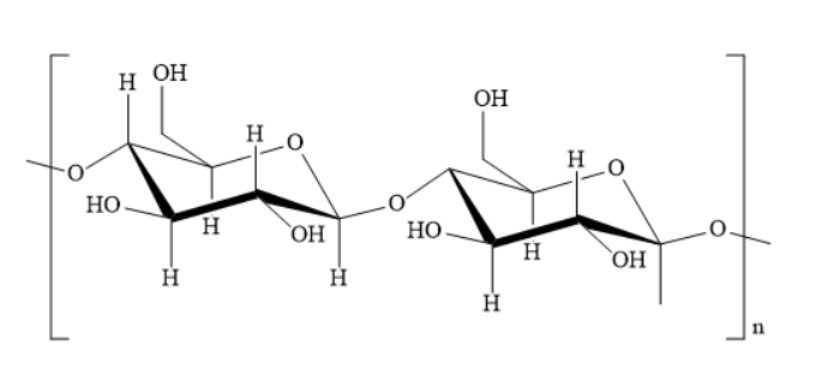
Hence, the option A ) glucose is the correct answer.
Note:
Sucrose is a disaccharide which gives glucose and fructose on hydrolysis. Cellulose is a polymer of a monosaccharide.
Complete step by step answer:
Cellulose is an important component of the cell walls in plants. It is present as microfibrils of plant cell wall. Thus, it is the structural component of plant cell wall and primitive fungi. Cellulose is also used for the production of papers. Cellulose is non reducing sugar as aldehyde group is not free. Aldehyde group is involved in glycosidic bond formation.
Cellulose is a fibrous, straight chain polymer. It is a polysaccharide consisting of several glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. The glycosidic linkage is between C-1 of one glucose unit and C-4 of other glucose unit. Cellulose is also called glucosan homopolysaccharide. One linear chain of cellulose contains around 6000 to 10000 glucose units. Cellulose is also called hexosan polysaccharide because the monomer glucose is a hexose sugar.
The structure of glucose is as shown below:

The structure of cellulose is as shown below:

Hence, the option A ) glucose is the correct answer.
Note:
Sucrose is a disaccharide which gives glucose and fructose on hydrolysis. Cellulose is a polymer of a monosaccharide.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




