
Centripetal xylem is present in
(a) Dicot root
(b) Dicot stem
(c) Monocot stem
(d) Branches of stem
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: In the portion of the plant that aids in the absorption of water and organic compounds, centripetal xylem is present. Their function is to anchor the body of the plant to the soil and store food and nutrients. They have got two cotyledons.
Complete step by step answer:
Centripetal xylem is the formulation of xylem from the periphery to the middle. The growth of Xylem in the roots is in the inward direction from the outer regions and is known as centripetal. A centrifugal direction that means towards the outside is the growth of xylem in shoots. The growth of phloem in roots and shoots is in the centripetal direction. Given are the anatomy of dicot root and the exarch and endarch diagrams.
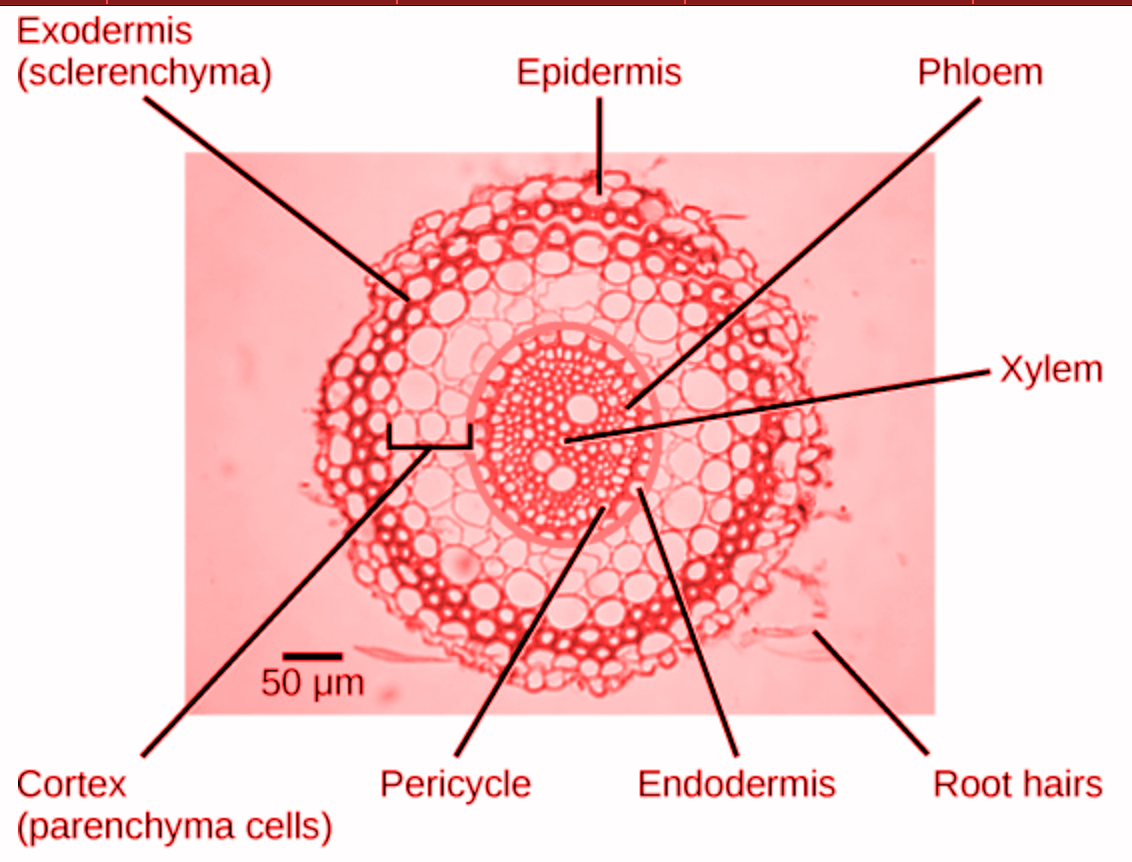
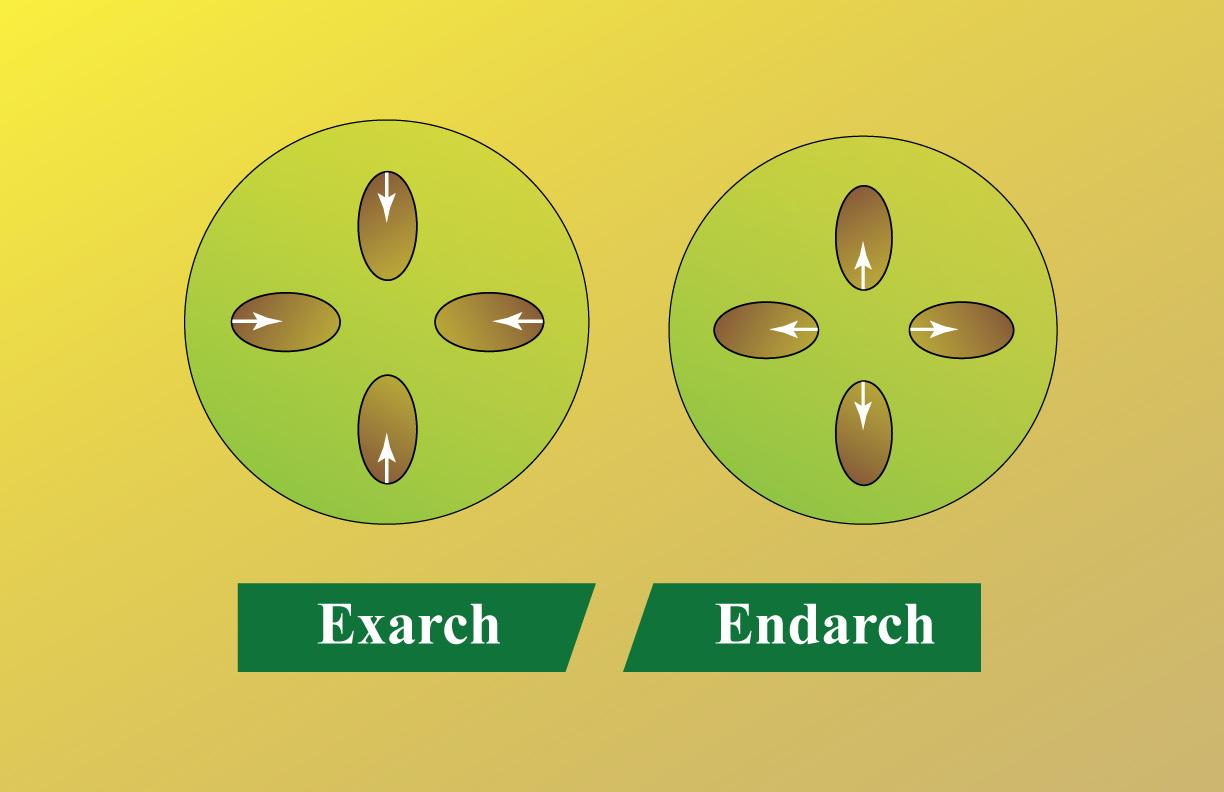
In dicotyledonous roots, xylem plates typically join to form a solid core at the end. The stele is thus classified as a protostele. Due to the centripetal mode of separation from the procambium, xylem is always exac, so protoxylem occurs towards the circumference and metaxylem towards the middle.
Exarch is used when there is more than one strand of primary xylem in the root or stem, and centripetal xylem grows from outside to within, while endarch is used when there is more than one strand of primary xylem in the root or stem, and centrifugal xylem grows from inside to outside.
The dicot roots do not have a central pith area, in the region where the vascular structures of the dicot root are located, parenchyma serves as connective tissue.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Dicot root’.
Note: The xylem and phloem arrangement is different in dicots than in monocots. In the center of the dicot root, the xylem is all placed and bundles of phloem are arranged around it, separated by vascular cambium from it. They differentiate into secondary growth xylem and phloem as cells of the vascular cambium divide, which increases the girth of dicot roots and stems.
Complete step by step answer:
Centripetal xylem is the formulation of xylem from the periphery to the middle. The growth of Xylem in the roots is in the inward direction from the outer regions and is known as centripetal. A centrifugal direction that means towards the outside is the growth of xylem in shoots. The growth of phloem in roots and shoots is in the centripetal direction. Given are the anatomy of dicot root and the exarch and endarch diagrams.


In dicotyledonous roots, xylem plates typically join to form a solid core at the end. The stele is thus classified as a protostele. Due to the centripetal mode of separation from the procambium, xylem is always exac, so protoxylem occurs towards the circumference and metaxylem towards the middle.
Exarch is used when there is more than one strand of primary xylem in the root or stem, and centripetal xylem grows from outside to within, while endarch is used when there is more than one strand of primary xylem in the root or stem, and centrifugal xylem grows from inside to outside.
The dicot roots do not have a central pith area, in the region where the vascular structures of the dicot root are located, parenchyma serves as connective tissue.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Dicot root’.
Note: The xylem and phloem arrangement is different in dicots than in monocots. In the center of the dicot root, the xylem is all placed and bundles of phloem are arranged around it, separated by vascular cambium from it. They differentiate into secondary growth xylem and phloem as cells of the vascular cambium divide, which increases the girth of dicot roots and stems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




