
How many chambers present in the stomach of ruminating mammals?
(a)Four
(b)Five
(c)Three
(d)Two
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Ruminant animals like cattle, sheep, goat, etc. are herbivores in nature which make diets rich in cellulose thus, they produce cellulase enzyme within their stomach by the help of bacteria.
Complete answer:
Ruminant animals have a four-compartments stomach that is: rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum. Their stomach occupies three- fourth of the abdominal cavity. As these animals' food contain a lot of cellulose thus, they have cellulose enzymes which are absent in mammals.
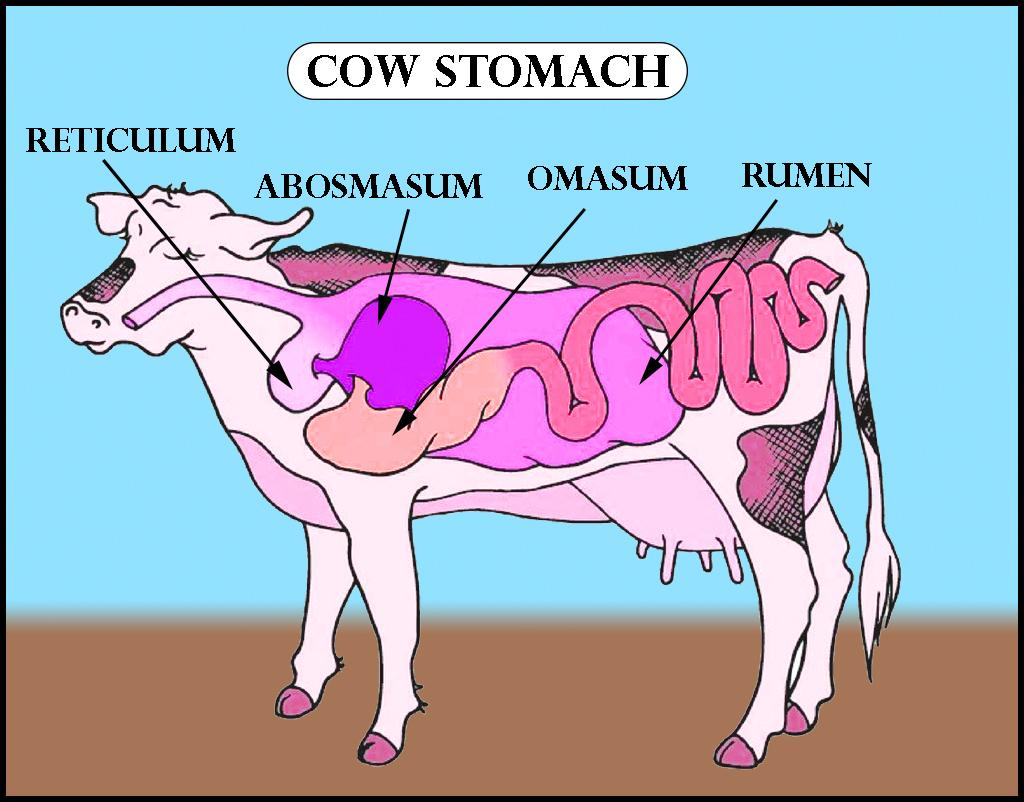
Additional Information: -Rumen
-The first compartment of ruminant animals.
-Most feed collects here after being swallowed.
-Cellulose is broken down here with the help of rumen microbes present there.
-It is the largest part of the stomach.
-This part of the stomach absorbs nutrients and requires a lot of water.
-Reticulum
-The second part of the stomach.
-There are many folds present in the reticulum and thus its nickname is a honeycomb.
-It is known as a hardware stomach.
-It traps foreign material that the material may pick up and it is very thick thus, harder to damage.
-Store foreign particles are eaten by animals so that damaging items do not go through the digestive tract.
-Omasum
-It is the third chamber of the stomach.
-It is also known as many piles as it looks like pages of a book.
-It helps in absorbing nutrients.
-Abomasum
-The fourth compartment of the stomach.
-This is the part where true digestion occurs.
-In this part, enzyme activity breaks down feed.
So, the correct answer is, ‘four.’
Note:
-The rumen contains a large number of bacteria which produces cellulase enzymes.
-The bacteria and the ruminant both are present in mutualism relationships.
-Herbivorous ruminant animals quickly engulf grass and stores in rumen where they temporarily store and partially digested, come back to mouth in small lumps.
Complete answer:
Ruminant animals have a four-compartments stomach that is: rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum. Their stomach occupies three- fourth of the abdominal cavity. As these animals' food contain a lot of cellulose thus, they have cellulose enzymes which are absent in mammals.

Additional Information: -Rumen
-The first compartment of ruminant animals.
-Most feed collects here after being swallowed.
-Cellulose is broken down here with the help of rumen microbes present there.
-It is the largest part of the stomach.
-This part of the stomach absorbs nutrients and requires a lot of water.
-Reticulum
-The second part of the stomach.
-There are many folds present in the reticulum and thus its nickname is a honeycomb.
-It is known as a hardware stomach.
-It traps foreign material that the material may pick up and it is very thick thus, harder to damage.
-Store foreign particles are eaten by animals so that damaging items do not go through the digestive tract.
-Omasum
-It is the third chamber of the stomach.
-It is also known as many piles as it looks like pages of a book.
-It helps in absorbing nutrients.
-Abomasum
-The fourth compartment of the stomach.
-This is the part where true digestion occurs.
-In this part, enzyme activity breaks down feed.
So, the correct answer is, ‘four.’
Note:
-The rumen contains a large number of bacteria which produces cellulase enzymes.
-The bacteria and the ruminant both are present in mutualism relationships.
-Herbivorous ruminant animals quickly engulf grass and stores in rumen where they temporarily store and partially digested, come back to mouth in small lumps.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




