
Chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. Give reason
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: If one of the hydrogen is replaced with chlorine in the methyl group of acetic acid then it is known as chloro acetic acid. Chlorine being a strong electron withdrawing group uses inductive effect to pull the negative charge towards itself , resulting in reduced negative charge density on the oxygen atom, hence stabilizing the conjugate base of chloroacetic acid.
Complete step by step solution:
Chlorine being -I imparting group shift electrons towards itself from carbonyl carbon and as a consequence of which Carbonyl carbon will acquire delta + charge and to compensate, it will attract electron from hydrogen thereby making it easy for hydrogen to leave - that’s what acidity is, how easily hydrogen atom leaves a compound.
More the number of -I imparting, easier will be for carbonyl carbon to lose hydrogen. In other words, Chloroacetic acid has a chlorine atom attached to its beta carbon. Due to the inductive effect of the chlorine atom the electron density is reduced over the already weakened O-H bond in the carboxylic moiety (due to the presence of alpha carbonyl group) which in turn make it a stronger acid than acetic acid as the ease of releasing the hydrogen to the base is increased.
Let us elaborate on the Inductive effect more, the Polarisation of sigma bond due to electron withdrawing or electron donating effect of adjacent groups of atoms is called inductive effect.
$\delta \delta \delta \delta +\quad \delta \delta \delta +\quad \delta \delta +\quad \delta +\quad \delta -\\ { CH }_{ 3 }{ \twoheadrightarrow CH }_{ 2 }\twoheadrightarrow { CH }_{ 2 }{ \twoheadrightarrow CH }_{ 2 }\twoheadrightarrow Cl$
Types of inductive effect
Negative inductive effect(-I): the electron withdrawing nature of groups of atoms is called negative inductive effect. It is denoted by -I.
Following are the example of groups in the decreasing order of their -I effect:
${ NH }_{ 3 }^{ + }{ >NO }_{ 2 }{ >CN }{ >SO }_{ 3 }{ H }>{ CHO }>{ CO> }{ COOH }>{ COCl }>{ CONH }_{ 2 }>{ F }>{ Cl> }{ Br }>I>{ OH> }{ OR> }{ NH }{ C(CH }_{ 3 })_{ 3 }{ >CH(CH }_{ 3 })_{ 2 }{ >CH }_{ 2 }{ CH }_{ 3 }{ >CH }_{ 3 }>H$
Positive inductive effect (+I): the electron releasing nature of a group of atoms is called positive inductive effect. It is denoted by +I.
The decreasing order of +I effect of some electron releasing groups is as follows:-
Tertiary methyl > secondary methyl > primary methyl > hydrogen.
The relative stability of the conjugate bases is responsible for the strength of their respective acids. In case of chloro acetic acid, due to —I effect of chlorine atom, the conjugate base of chloro acetic acid gets stability. On the other hand, in case of acetic acid, the stability of acetate anion that is the conjugate base of acetic acid becomes less stable due to+ I effect of methyl group. Hence chloro acetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.
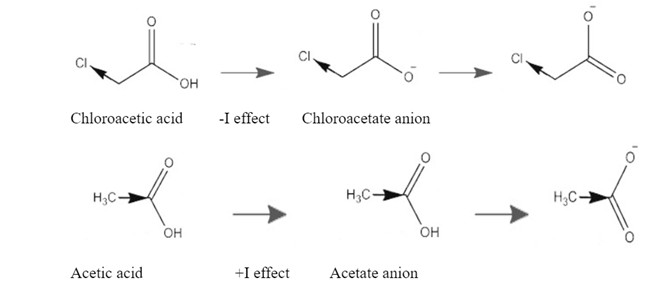
This diagram shows inductive effects in both acetic acid and chloroacetic acid.
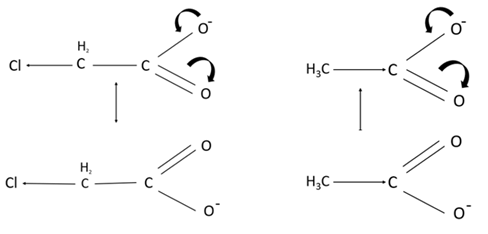
This diagram depicts that the conjugate base of chloroacetic acid is more stable than acetic acid.
Note: The strength of an acid depends on the extent of its ionization to give protons. The carboxylate anion is formed on deprotonation of carboxylic acids. The anion is stabilized by resonance (i.e. the charge spreads over both oxygen atoms) but can also be stabilized by the R group if this has -I effect.
Complete step by step solution:
Chlorine being -I imparting group shift electrons towards itself from carbonyl carbon and as a consequence of which Carbonyl carbon will acquire delta + charge and to compensate, it will attract electron from hydrogen thereby making it easy for hydrogen to leave - that’s what acidity is, how easily hydrogen atom leaves a compound.
More the number of -I imparting, easier will be for carbonyl carbon to lose hydrogen. In other words, Chloroacetic acid has a chlorine atom attached to its beta carbon. Due to the inductive effect of the chlorine atom the electron density is reduced over the already weakened O-H bond in the carboxylic moiety (due to the presence of alpha carbonyl group) which in turn make it a stronger acid than acetic acid as the ease of releasing the hydrogen to the base is increased.
Let us elaborate on the Inductive effect more, the Polarisation of sigma bond due to electron withdrawing or electron donating effect of adjacent groups of atoms is called inductive effect.
$\delta \delta \delta \delta +\quad \delta \delta \delta +\quad \delta \delta +\quad \delta +\quad \delta -\\ { CH }_{ 3 }{ \twoheadrightarrow CH }_{ 2 }\twoheadrightarrow { CH }_{ 2 }{ \twoheadrightarrow CH }_{ 2 }\twoheadrightarrow Cl$
Types of inductive effect
Negative inductive effect(-I): the electron withdrawing nature of groups of atoms is called negative inductive effect. It is denoted by -I.
Following are the example of groups in the decreasing order of their -I effect:
${ NH }_{ 3 }^{ + }{ >NO }_{ 2 }{ >CN }{ >SO }_{ 3 }{ H }>{ CHO }>{ CO> }{ COOH }>{ COCl }>{ CONH }_{ 2 }>{ F }>{ Cl> }{ Br }>I>{ OH> }{ OR> }{ NH }{ C(CH }_{ 3 })_{ 3 }{ >CH(CH }_{ 3 })_{ 2 }{ >CH }_{ 2 }{ CH }_{ 3 }{ >CH }_{ 3 }>H$
Positive inductive effect (+I): the electron releasing nature of a group of atoms is called positive inductive effect. It is denoted by +I.
The decreasing order of +I effect of some electron releasing groups is as follows:-
Tertiary methyl > secondary methyl > primary methyl > hydrogen.
The relative stability of the conjugate bases is responsible for the strength of their respective acids. In case of chloro acetic acid, due to —I effect of chlorine atom, the conjugate base of chloro acetic acid gets stability. On the other hand, in case of acetic acid, the stability of acetate anion that is the conjugate base of acetic acid becomes less stable due to+ I effect of methyl group. Hence chloro acetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.

This diagram shows inductive effects in both acetic acid and chloroacetic acid.

This diagram depicts that the conjugate base of chloroacetic acid is more stable than acetic acid.
Note: The strength of an acid depends on the extent of its ionization to give protons. The carboxylate anion is formed on deprotonation of carboxylic acids. The anion is stabilized by resonance (i.e. the charge spreads over both oxygen atoms) but can also be stabilized by the R group if this has -I effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




