
Chloromethane on treatment with excess ammonia yields mainly:
A.N, N-dimethylmethanamine
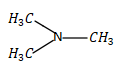
B.N-methylmethanamine (\[{H_3}C - NH - C{H_3}\])
C.Methanamine (${H_3}C - N{H_2}$)
D.Mixture containing all of these in equal proportion

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: It is known that chlorine is a better leaving group and ammonia and amines are good nucleophiles so chloromethane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reactions in the presence of ammonia. Also it is given that ammonia is in excess so ammonia can only react with one equivalent of chloromethane.
Complete step by step solution:
The reaction given in the question is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (${S_N}2$). We know that $Cl$ is a good leaving group and ammonia due to the lone pair on nitrogen is a good nucleophile. So, now ammonia will attack on the carbon attached to chlorine which will have a partial positive charge due to the higher electronegativity of the chlorine atom attached to it. Ammonia will attack from the back side of the $Cl$, removing $Cl$ from chloromethane, forming a $C - N$ bond as shown in the diagram, this is the transition state in which the bond breaking and bond formation takes place at the same time. The chlorine removed will be then attacking on $H$ of the ammonia and forms $HCl$ as a by-product. But since ammonia is in excess it should be noted that we do not have more chloromethane to react with this excessive ammonia and the only product that will be formed will be methanamine.
Additional information:
${S_N}2$ reactions is a type of bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the rate of the reaction depends upon the concentration of both the reactants. In these reactions there is an inversion of the initial configuration and the reaction proceeds without the formation of intermediate. These are also known as concerted reactions in which bond breaking and bond formation takes place at the same time.
Note: The other options could have been possible if chloromethane would have been in similar amount of ammonia because the nitrogen in methanamine can further attack on the chloromethane following ${S_N}2$ mechanism, but since ammonia is in excess this possibility is nullified.
Complete step by step solution:
The reaction given in the question is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (${S_N}2$). We know that $Cl$ is a good leaving group and ammonia due to the lone pair on nitrogen is a good nucleophile. So, now ammonia will attack on the carbon attached to chlorine which will have a partial positive charge due to the higher electronegativity of the chlorine atom attached to it. Ammonia will attack from the back side of the $Cl$, removing $Cl$ from chloromethane, forming a $C - N$ bond as shown in the diagram, this is the transition state in which the bond breaking and bond formation takes place at the same time. The chlorine removed will be then attacking on $H$ of the ammonia and forms $HCl$ as a by-product. But since ammonia is in excess it should be noted that we do not have more chloromethane to react with this excessive ammonia and the only product that will be formed will be methanamine.
Additional information:
${S_N}2$ reactions is a type of bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the rate of the reaction depends upon the concentration of both the reactants. In these reactions there is an inversion of the initial configuration and the reaction proceeds without the formation of intermediate. These are also known as concerted reactions in which bond breaking and bond formation takes place at the same time.
Note: The other options could have been possible if chloromethane would have been in similar amount of ammonia because the nitrogen in methanamine can further attack on the chloromethane following ${S_N}2$ mechanism, but since ammonia is in excess this possibility is nullified.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




