
(-CHO) group is:
(A) +ME and +IE group
(B) -ME and –IE group
(C) +ME and –IE group
(D) -ME and +IE group
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Due to presence of oxygen atom in the (-CHO) group it has the ability to attract electrons towards itself and attain negative charge, while the carbon chain to which it is attached will get a positive charge.
Complete step by step answer:
-First we will learn about the Mesomeric (MI) and Inductive (IE) effects.
-Mesomeric effect (MI): The mesomeric effect is basically the development of polarity between atoms of a system that undergoes conjugation by transfer of electrons or transfer of pi-bond electrons inside the structure itself. It can simply be described as movement of pi-electrons away from or towards the substituent group (or functional group) in a conjugated orbital system.
This mesomeric effect is of 2 types: +ME and –ME
(1)+ME: This occurs when the electrons or pi-electrons are transferred towards the conjugate system from the substituent group. This increases the electron density of the conjugate system and substituent attains positive charge. For this to happen the substituent should have either a lone pair of electrons or a negative charge and are known as electron donating groups.
For example: ($ - N{H_2}$), (-OH), (-COR), (-SH), etc.
(2)-ME: This occurs when the electrons or pi-electrons are transferred towards the substituent group from the conjugate system or the substituent attracts these electrons toward itself. This decreases the electron density of the conjugate system and substituent attains negative charge. For this to happen the substituent should have either a vacant orbital or a positive charge and are known as electron withdrawing groups.
For example: ($ - N{O_2}$), ($ - CON{H_2}$), (-CHO), (-COOH), (-CN), etc.
(-CHO) group being electron withdrawing due to presence of oxygen shows –ME.
-Inductive effect (IE): The phenomenon where a permanent dipole arises within a molecule due to unequal sharing of the bonding electrons inside the molecule is known as inductive effect. This occurs only in the sigma bonds. This occurs due to the presence of some electron withdrawing or electron donating species in the carbon chain.
This inductive effect is of 2 types: +IE and –IE
(1)+IE: This occurs when the chemical species has the ability to donate or release electrons towards the carbon chain and itself forms the positive side of the dipole.
For example: the R (alkyl) group.
(2)-IE: This occurs when an electronegative atom or group is introduced in the carbon chain. The electronegative group attracts electrons towards itself generating positive charge towards the chain and negative charge at itself.
For example: any halogen atom.
We know that (-CHO) group has the ability to attract electrons towards itself and thus it will show –IE.
-For an example let us see the delocalization of electrons in benzaldehyde (${C_6}{H_6} - CHO$):
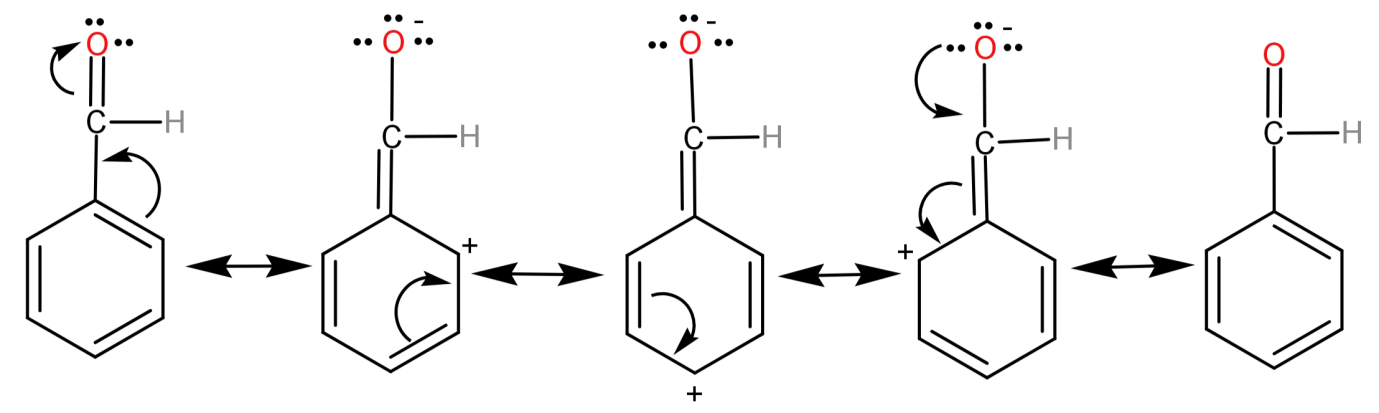
So, the correct answer will be: -ME and –IE group
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The presence of (-CHO) group or aldehydic group increases the acidic character of the compound because it is an electron withdrawing group. They have a characteristic odour (scent) and taste. Do not get confused between inductive effect and resonance effect. In the inductive effect there is unequal sharing of electrons but in resonance effect there is complete transfer of electrons giving complete positive and negative charge.
Complete step by step answer:
-First we will learn about the Mesomeric (MI) and Inductive (IE) effects.
-Mesomeric effect (MI): The mesomeric effect is basically the development of polarity between atoms of a system that undergoes conjugation by transfer of electrons or transfer of pi-bond electrons inside the structure itself. It can simply be described as movement of pi-electrons away from or towards the substituent group (or functional group) in a conjugated orbital system.
This mesomeric effect is of 2 types: +ME and –ME
(1)+ME: This occurs when the electrons or pi-electrons are transferred towards the conjugate system from the substituent group. This increases the electron density of the conjugate system and substituent attains positive charge. For this to happen the substituent should have either a lone pair of electrons or a negative charge and are known as electron donating groups.
For example: ($ - N{H_2}$), (-OH), (-COR), (-SH), etc.
(2)-ME: This occurs when the electrons or pi-electrons are transferred towards the substituent group from the conjugate system or the substituent attracts these electrons toward itself. This decreases the electron density of the conjugate system and substituent attains negative charge. For this to happen the substituent should have either a vacant orbital or a positive charge and are known as electron withdrawing groups.
For example: ($ - N{O_2}$), ($ - CON{H_2}$), (-CHO), (-COOH), (-CN), etc.
(-CHO) group being electron withdrawing due to presence of oxygen shows –ME.
-Inductive effect (IE): The phenomenon where a permanent dipole arises within a molecule due to unequal sharing of the bonding electrons inside the molecule is known as inductive effect. This occurs only in the sigma bonds. This occurs due to the presence of some electron withdrawing or electron donating species in the carbon chain.
This inductive effect is of 2 types: +IE and –IE
(1)+IE: This occurs when the chemical species has the ability to donate or release electrons towards the carbon chain and itself forms the positive side of the dipole.
For example: the R (alkyl) group.
(2)-IE: This occurs when an electronegative atom or group is introduced in the carbon chain. The electronegative group attracts electrons towards itself generating positive charge towards the chain and negative charge at itself.
For example: any halogen atom.
We know that (-CHO) group has the ability to attract electrons towards itself and thus it will show –IE.
-For an example let us see the delocalization of electrons in benzaldehyde (${C_6}{H_6} - CHO$):

So, the correct answer will be: -ME and –IE group
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The presence of (-CHO) group or aldehydic group increases the acidic character of the compound because it is an electron withdrawing group. They have a characteristic odour (scent) and taste. Do not get confused between inductive effect and resonance effect. In the inductive effect there is unequal sharing of electrons but in resonance effect there is complete transfer of electrons giving complete positive and negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




