
Cholecystokinin and secretin is secreted by
(a) Stomach
(b) Liver
(c) Duodenum
(d) Ileum
Answer
582.6k+ views
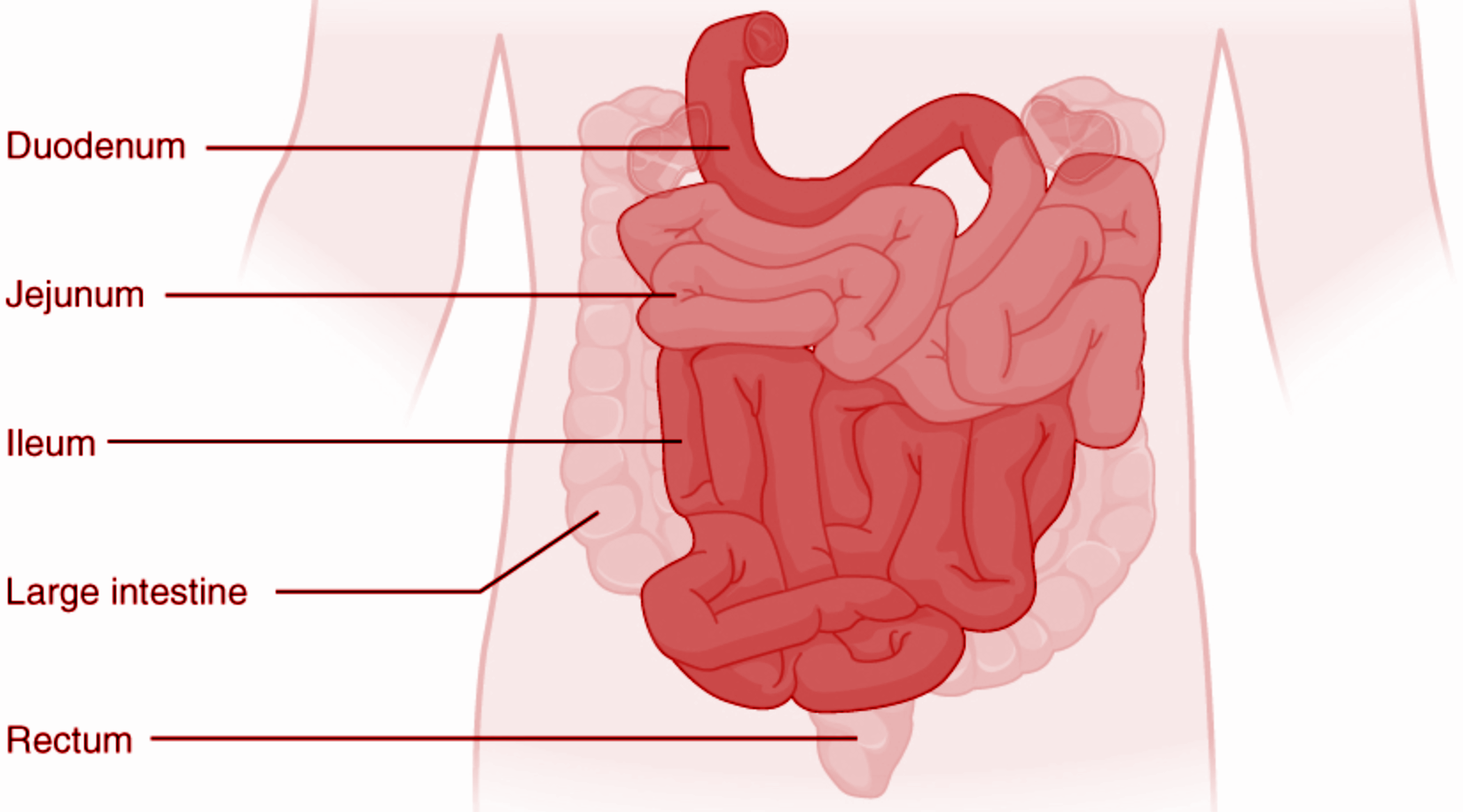
Hint: This forms the first portion of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. After foods mix with stomach acid, they move into this part.
Complete step by step answer:
Cholecystokinin is secreted from the duodenum of the body and causes contraction of gall bladder and secretion of the pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Secretin is secreted from the duodenum and stimulates the secretion of pancreatic juice but inhibits the secretion of gastric juices.
So, the correct answer is 'Duodenum'.
Additional Information: The food is finally digested in the small intestine of the alimentary canal because it has all the enzymes needed for the digestion of every type of food. The intestine has a bile enzyme for the emulsification (break down) of fats. It has pancreatic lipase and intestinal lipase enzyme, which help in the final digestion of fats. It has pancreatic amylase for the digestion of carbohydrates. It has trypsinogen, which breaks trypsin under influence of enterokinase enzyme. Trypsin enzyme helps in the digestion of proteins. It has Erepsin, which again helps in the digestion of protein.
The small intestine is the longest part (6 meters) of the alimentary canal. It is a tubular part occupying the central and lower part of the abdominal cavity.
The small intestine is divided into the following parts:
1. Duodenum: It is the widest, shortest, and most flexed part of the small intestine. It is C- shape and receives bile from the pancreas.
2. Jejunum: It is the middle part of the small intestine.
3. Ileum: It is the longest part of the small intestine. Its finally open in the caecum in the lower part of the abdominal cavity.
Note:
- Cholecystokinin is secreted by cells of the upper intestine. Its secretion is stimulated by the introduction of acid, amino acids, or fatty acids into the stomach or duodenum. Cholecystokinin stimulates the gallbladder to contract and to produce stored bile into the intestine.
- Secretin has mainly three functions: regulation of gastric acid, regulation of pancreatic bicarbonate, and osmoregulation. The major physiological actions of secretion are stimulation of pancreatic fluid and bicarbonate secretion. S cells in the small intestine emit secretion.
Complete step by step answer:
Cholecystokinin is secreted from the duodenum of the body and causes contraction of gall bladder and secretion of the pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Secretin is secreted from the duodenum and stimulates the secretion of pancreatic juice but inhibits the secretion of gastric juices.

So, the correct answer is 'Duodenum'.
Additional Information: The food is finally digested in the small intestine of the alimentary canal because it has all the enzymes needed for the digestion of every type of food. The intestine has a bile enzyme for the emulsification (break down) of fats. It has pancreatic lipase and intestinal lipase enzyme, which help in the final digestion of fats. It has pancreatic amylase for the digestion of carbohydrates. It has trypsinogen, which breaks trypsin under influence of enterokinase enzyme. Trypsin enzyme helps in the digestion of proteins. It has Erepsin, which again helps in the digestion of protein.
The small intestine is the longest part (6 meters) of the alimentary canal. It is a tubular part occupying the central and lower part of the abdominal cavity.
The small intestine is divided into the following parts:
1. Duodenum: It is the widest, shortest, and most flexed part of the small intestine. It is C- shape and receives bile from the pancreas.
2. Jejunum: It is the middle part of the small intestine.
3. Ileum: It is the longest part of the small intestine. Its finally open in the caecum in the lower part of the abdominal cavity.
Note:
- Cholecystokinin is secreted by cells of the upper intestine. Its secretion is stimulated by the introduction of acid, amino acids, or fatty acids into the stomach or duodenum. Cholecystokinin stimulates the gallbladder to contract and to produce stored bile into the intestine.
- Secretin has mainly three functions: regulation of gastric acid, regulation of pancreatic bicarbonate, and osmoregulation. The major physiological actions of secretion are stimulation of pancreatic fluid and bicarbonate secretion. S cells in the small intestine emit secretion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




