
Choose the correct option for the following:
Assertion: $NBS$ is a reagent in allylic bromination.
Reason: Alkenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct. The reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct. The reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
(C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:We know that reagent used in a chemical reaction is a compound added to the system to cause a chemical reaction. A reagent is used in allylic bromination in which a hydrogen atom that is attached to a carbon atom adjacent to a double bond is replaced.
Complete step-by-step solution:We know that reagent used in a chemical reaction is a compound added to the system to cause a chemical reaction. The reagent causes the desired chemical reaction. Here the reagent used is $NBS$ . Its full name is $N - $ bromosuccinimide. It is a substitute for bromine as it gives a low concentration of $B{r_2}$ . It is used as a reagent in allylic bromination. Allylic bromination is the replacement of a hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom adjacent to a double bond. The reaction occurs in presence of light. An example of this reaction is as follow:
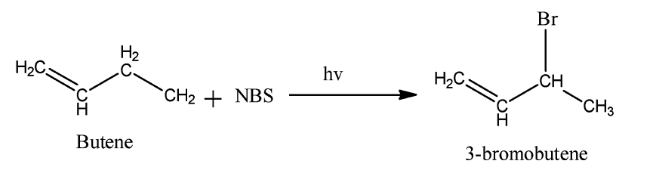
Thus, we see that the assertion is correct. Now alkenes are hydrocarbons in which there is at least one double bond between carbon-carbon atoms. Alkenes have molecular formula ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$ . Electrophiles are electron-deficient species. Due to the presence of $pi$ bond in alkenes, electrophiles attack alkenes and cause electrophilic addition reactions. An example of this reaction is when hydrogen bromide attacks ethane to form bromoethane.

Thus we see that the statement in reason is correct but it is not the correct explanation for the given assertion. As discussed $NBS$ gives a low concentration of $B{r_2}$ . Therefore it causes substitution reaction and prevents addition reaction.
Therefore, the correct option is $B$.
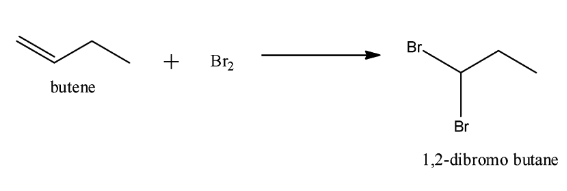
Note:It is important to know that a low concentration of bromine is needed to cause free radical halogenation reaction. We should not use $B{r_2}$ directly as it will simply add to the alkene. When $B{r_2}$ is added to butene instead of $NBS$ following reaction will occur
Complete step-by-step solution:We know that reagent used in a chemical reaction is a compound added to the system to cause a chemical reaction. The reagent causes the desired chemical reaction. Here the reagent used is $NBS$ . Its full name is $N - $ bromosuccinimide. It is a substitute for bromine as it gives a low concentration of $B{r_2}$ . It is used as a reagent in allylic bromination. Allylic bromination is the replacement of a hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom adjacent to a double bond. The reaction occurs in presence of light. An example of this reaction is as follow:

Thus, we see that the assertion is correct. Now alkenes are hydrocarbons in which there is at least one double bond between carbon-carbon atoms. Alkenes have molecular formula ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$ . Electrophiles are electron-deficient species. Due to the presence of $pi$ bond in alkenes, electrophiles attack alkenes and cause electrophilic addition reactions. An example of this reaction is when hydrogen bromide attacks ethane to form bromoethane.

Thus we see that the statement in reason is correct but it is not the correct explanation for the given assertion. As discussed $NBS$ gives a low concentration of $B{r_2}$ . Therefore it causes substitution reaction and prevents addition reaction.
Therefore, the correct option is $B$.
Note:It is important to know that a low concentration of bromine is needed to cause free radical halogenation reaction. We should not use $B{r_2}$ directly as it will simply add to the alkene. When $B{r_2}$ is added to butene instead of $NBS$ following reaction will occur

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




