
Chrysanthemum multiplies vegetatively by?
(a) Suckers
(b) Runners
(c) Stolons
(d) Rhizomes
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: Organisms multiply or reproduce their young ones by various modes. In sweet potatoes, reproduction occurs through vegetative propagation by the roots, here roots produce the shoots and buds which later develop into a new plant.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Vegetative propagation is a mode of asexual reproduction in parents where the cell divides to form a daughter cell by mitosis due to which the offsprings are genetically identical to the parent.
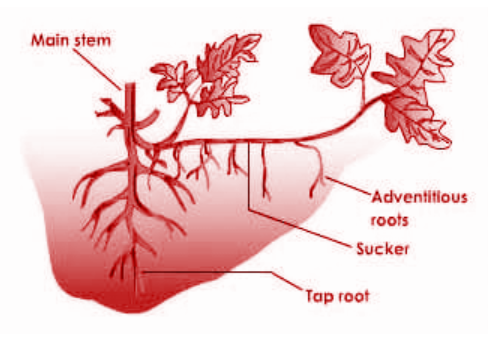
Vegetative propagation by sucker in chrysanthemum
In chrysanthemum, a lateral branch arising from the main stem close to the ground level travels underground for some distance. This branch is called a sucker.
It turns up at its end and produces adventitious roots in the ground and shoots above forming a new plant.

Additional Information:
1. A lateral branch runner arises from the base of the stem and runs along the surface of the soil. It develops different nodes and internodes. The runner produces roots below and leaves above the ground at each node, e.g., Oxalis, Fragaria, etc.
2. Stolons are lateral branches that arise from the stem above the soil for a certain distance. A new plant is produced when the tip touches the ground at the nodal region. As the plant grows the stolons grow horizontally outward for a varying distance in the soil. Ultimately their end emerges out of the ground and develops into a new plant e.g., Mentha, Rosaceae.
3. In rhizomes, the nodes have dry scale leaves with axillary buds. They have a specialized lateral growth pattern in which the apical meristem is terminated and make it different from the roots.
So, the correct answer is ‘suckers’
Notes:
1. The name “chrysanthemum” is derived from the Greek words chrysos (gold) and anthemon (flower). They are native to Asia and northeastern Europe.
2. There are 40 wild species of chrysanthemum and from these wild species thousands of varieties created via selective breeding.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Vegetative propagation is a mode of asexual reproduction in parents where the cell divides to form a daughter cell by mitosis due to which the offsprings are genetically identical to the parent.

Vegetative propagation by sucker in chrysanthemum
In chrysanthemum, a lateral branch arising from the main stem close to the ground level travels underground for some distance. This branch is called a sucker.
It turns up at its end and produces adventitious roots in the ground and shoots above forming a new plant.

Additional Information:
1. A lateral branch runner arises from the base of the stem and runs along the surface of the soil. It develops different nodes and internodes. The runner produces roots below and leaves above the ground at each node, e.g., Oxalis, Fragaria, etc.
2. Stolons are lateral branches that arise from the stem above the soil for a certain distance. A new plant is produced when the tip touches the ground at the nodal region. As the plant grows the stolons grow horizontally outward for a varying distance in the soil. Ultimately their end emerges out of the ground and develops into a new plant e.g., Mentha, Rosaceae.
3. In rhizomes, the nodes have dry scale leaves with axillary buds. They have a specialized lateral growth pattern in which the apical meristem is terminated and make it different from the roots.
So, the correct answer is ‘suckers’
Notes:
1. The name “chrysanthemum” is derived from the Greek words chrysos (gold) and anthemon (flower). They are native to Asia and northeastern Europe.
2. There are 40 wild species of chrysanthemum and from these wild species thousands of varieties created via selective breeding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




