
Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme β - galactosidase a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above?
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Recombinant and non-recombinant can also be distinguished by colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. Here, the recombinant DNA is inserted into the sequence encoding the β-galactosidase enzyme, which inactivates the enzyme. Thus, bacterial colonies that have inserted plasmids do not exhibit colour, whereas colonies that do not have plasmid exhibit blue colour.
Complete answer:
Recombinant selection is a complex process because two different antibiotic dishes must be used at the same time due to antibiotic inactivation. Thus, alternative markers can be developed to distinguish between recombinant and non-recombinant based on their ability to reproduce colon in the presence of a colour developer.
The recombinant DNA is now included in the coding sequence for the β-galactosidase enzyme, resulting in an enzyme inactivation known as insert inactivation. If there are no bacterial inserts in the plasmid, blue colonies are formed if there is a chromogenic substrate. The presence of the insert causes β-galactosidase inactivation, so the colonies are not stained. These colonies are characterized as recombinant colonies.
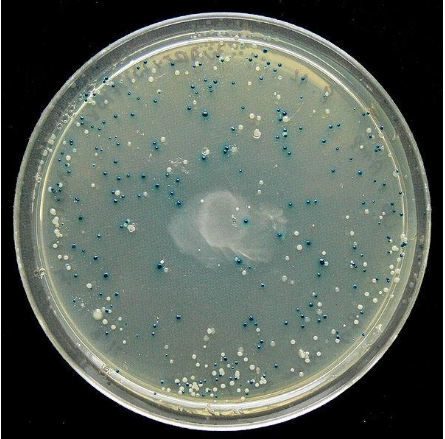
The blue and white screen is a screening technique that enables the fast and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria in vector-based molecular cloning experiments.
Note: Limitation of blue white screening: The blue and white technology is just a screening process. This is not a method of choice. The vector lacZ gene sometimes does not work and does not produce β-galactosidase. The resulting colonies do not recombine, but appear white. Small sequences of foreign DNA can also be inserted into the MCS to change the reading frame of the lacZ gene. This leads to the formation of false positive white colonies. Small inserts in the lacZ reading frame can form cloudy sky-blue colonies because β-galactosidase is only partially inactive.
Complete answer:
Recombinant selection is a complex process because two different antibiotic dishes must be used at the same time due to antibiotic inactivation. Thus, alternative markers can be developed to distinguish between recombinant and non-recombinant based on their ability to reproduce colon in the presence of a colour developer.
The recombinant DNA is now included in the coding sequence for the β-galactosidase enzyme, resulting in an enzyme inactivation known as insert inactivation. If there are no bacterial inserts in the plasmid, blue colonies are formed if there is a chromogenic substrate. The presence of the insert causes β-galactosidase inactivation, so the colonies are not stained. These colonies are characterized as recombinant colonies.

The blue and white screen is a screening technique that enables the fast and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria in vector-based molecular cloning experiments.
Note: Limitation of blue white screening: The blue and white technology is just a screening process. This is not a method of choice. The vector lacZ gene sometimes does not work and does not produce β-galactosidase. The resulting colonies do not recombine, but appear white. Small sequences of foreign DNA can also be inserted into the MCS to change the reading frame of the lacZ gene. This leads to the formation of false positive white colonies. Small inserts in the lacZ reading frame can form cloudy sky-blue colonies because β-galactosidase is only partially inactive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




