
Compare a human eye with a photographic camera.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The eye is a sensory organ that helps in sensory transduction, transmission, integration, and response when light focuses on the lens. It is a type of photoreceptor with electromagnetic stimuli found in rods and cones of the retina.
Complete answer:
The lens of both the camera and the human eye focus on an image that is real and inverted and the incoming light gets focused on the retina in humans and on sensor chips in the camera.
Both eye and camera can control the amount of light that enters, in the eye, it is controlled by iris, and in-camera it is controlled by an adjustment in an aperture.
Both eye and camera can focus on a single object and both can focus on the large scape.
Both eye and camera have a limited scope but it is possible to change the scope of the camera by adjusting focal length but eye scope is fixed.
The lens of both eye and camera is convex but in the eye it is biconvex, and both allow the light of different shades.
Additional Information: In humans, the conjunctiva, cornea, aqueous humor, lens, and vitreous humor refract the light rays which focus on the retina. Maximum refraction caused by the cornea which produces images on the retina which is inverted and reversed. Accommodation causes the focus of light rays on the retina by altering the shape of the lens. Bright light causes contraction of the iris by which the pupil becomes smaller and causes less light to enter whereas dim light causes the size of the pupil to increase to allow a high amount of light to enter. The potential difference causes the generation of an action potential in the ganglion cell through bipolar neuron which transmits by optic nerves to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe of the brain.
Note: The vision of a cat is much better than a human because cats have a high concentration of rod receptors. The cat can see the fine object and they can also see in the dark. Eagle has the best vision, they can see a long distance. The main difference between human vision and other mammals' vision is a color receptor, only humans can see different color shades.
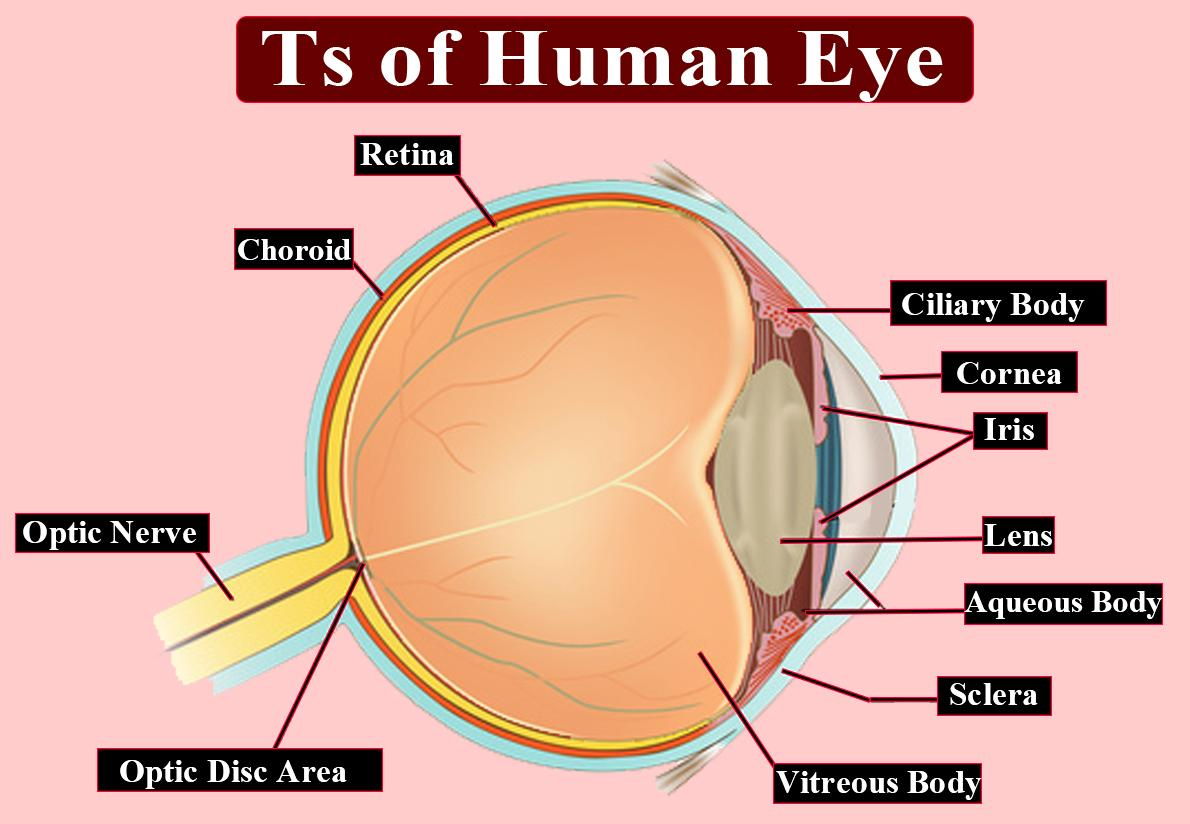
Complete answer:
The lens of both the camera and the human eye focus on an image that is real and inverted and the incoming light gets focused on the retina in humans and on sensor chips in the camera.
Both eye and camera can control the amount of light that enters, in the eye, it is controlled by iris, and in-camera it is controlled by an adjustment in an aperture.
Both eye and camera can focus on a single object and both can focus on the large scape.
Both eye and camera have a limited scope but it is possible to change the scope of the camera by adjusting focal length but eye scope is fixed.
The lens of both eye and camera is convex but in the eye it is biconvex, and both allow the light of different shades.
Additional Information: In humans, the conjunctiva, cornea, aqueous humor, lens, and vitreous humor refract the light rays which focus on the retina. Maximum refraction caused by the cornea which produces images on the retina which is inverted and reversed. Accommodation causes the focus of light rays on the retina by altering the shape of the lens. Bright light causes contraction of the iris by which the pupil becomes smaller and causes less light to enter whereas dim light causes the size of the pupil to increase to allow a high amount of light to enter. The potential difference causes the generation of an action potential in the ganglion cell through bipolar neuron which transmits by optic nerves to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe of the brain.
Note: The vision of a cat is much better than a human because cats have a high concentration of rod receptors. The cat can see the fine object and they can also see in the dark. Eagle has the best vision, they can see a long distance. The main difference between human vision and other mammals' vision is a color receptor, only humans can see different color shades.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




