
Compare bond dissociation energies of \[{H_a}\], \[{H_b}\], \[{H_c}\] and \[{H_d}\] in the given compound.
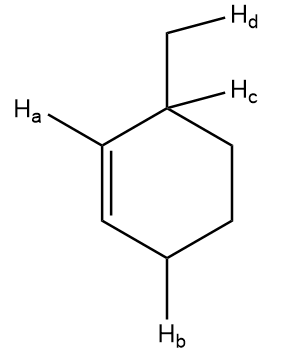

Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Bond dissociation energy: The amount of heat released in the homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond is termed as bond dissociation energy. In diatomic molecules, the value of bond dissociation energy is equal to the value of bond energy of the molecules. It can be used to compare the strength of chemical bonds.
Complete answer:
Free radical: When homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond takes place, electrons are distributed in such a manner that after breaking the bond, each atom has an unshared electron which is known as free radical.
Let us have a look on the free radicals formed on the homolytic cleavage of marked atoms:
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_a}\] is as follows:
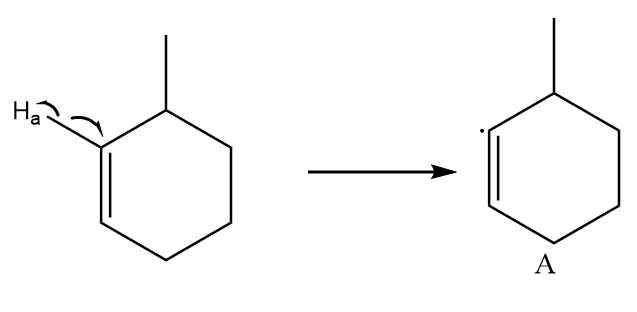
As the unshared electron is present on an electronegative atom i.e., \[s{p^2}\] hybridized atom. So, it is the least stable free radical.
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_b}\] is as follows:
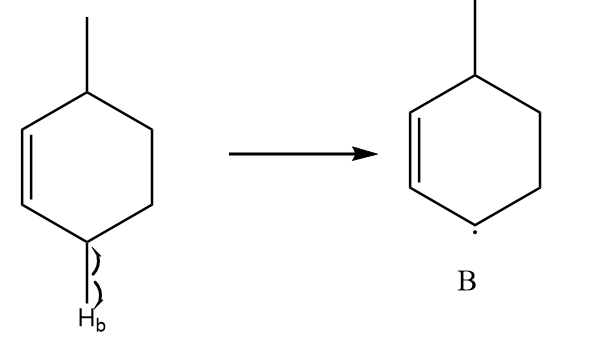
The free radical formed in structure B participates in resonance and there are a total three alpha hydrogens present in the structure. So, it is a relatively stable free radical than A.
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_c}\] is as follows:
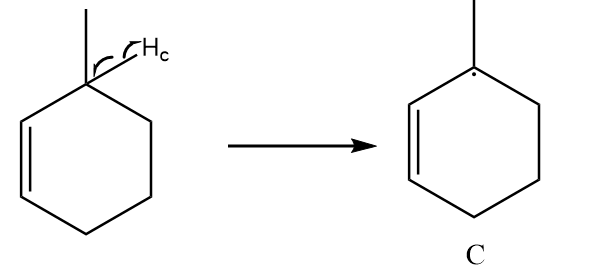
The free radical formed in structure C participates in resonance and there are a total five alpha hydrogens present in the structure. So, it is the most stable free radical.
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_d}\] is as follows:
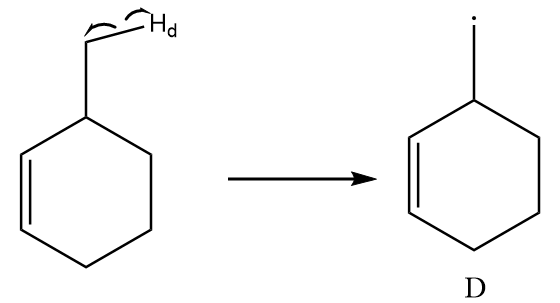
The free radical formed in structure D does not participate in resonance and there is only one alpha hydrogen present in the structure. So, it is a relatively less stable free radical than B and C.
Therefore, the order of stability of free radical formed is as follows:
\[C > B > D > A\]
As bond dissociation energy is inversely proportional to stability. Hence, the correct order for bond dissociation energy for given hydrogen atoms is as follows:
\[{H_c} < {H_b} < {H_d} < {H_a}\]
Note:
It is important to note that the more the stability of free radicals, the more easily the bond can be broken and therefore lesser will be the energy required to dissociate the bond. Hence, greater the stability of free radical, lesser will be its bond dissociation energy.
Complete answer:
Free radical: When homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond takes place, electrons are distributed in such a manner that after breaking the bond, each atom has an unshared electron which is known as free radical.
Let us have a look on the free radicals formed on the homolytic cleavage of marked atoms:
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_a}\] is as follows:

As the unshared electron is present on an electronegative atom i.e., \[s{p^2}\] hybridized atom. So, it is the least stable free radical.
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_b}\] is as follows:

The free radical formed in structure B participates in resonance and there are a total three alpha hydrogens present in the structure. So, it is a relatively stable free radical than A.
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_c}\] is as follows:

The free radical formed in structure C participates in resonance and there are a total five alpha hydrogens present in the structure. So, it is the most stable free radical.
Free radical formed on homolytic cleavage of \[C - {H_d}\] is as follows:

The free radical formed in structure D does not participate in resonance and there is only one alpha hydrogen present in the structure. So, it is a relatively less stable free radical than B and C.
Therefore, the order of stability of free radical formed is as follows:
\[C > B > D > A\]
As bond dissociation energy is inversely proportional to stability. Hence, the correct order for bond dissociation energy for given hydrogen atoms is as follows:
\[{H_c} < {H_b} < {H_d} < {H_a}\]
Note:
It is important to note that the more the stability of free radicals, the more easily the bond can be broken and therefore lesser will be the energy required to dissociate the bond. Hence, greater the stability of free radical, lesser will be its bond dissociation energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




