
Complete following reactions.
1.
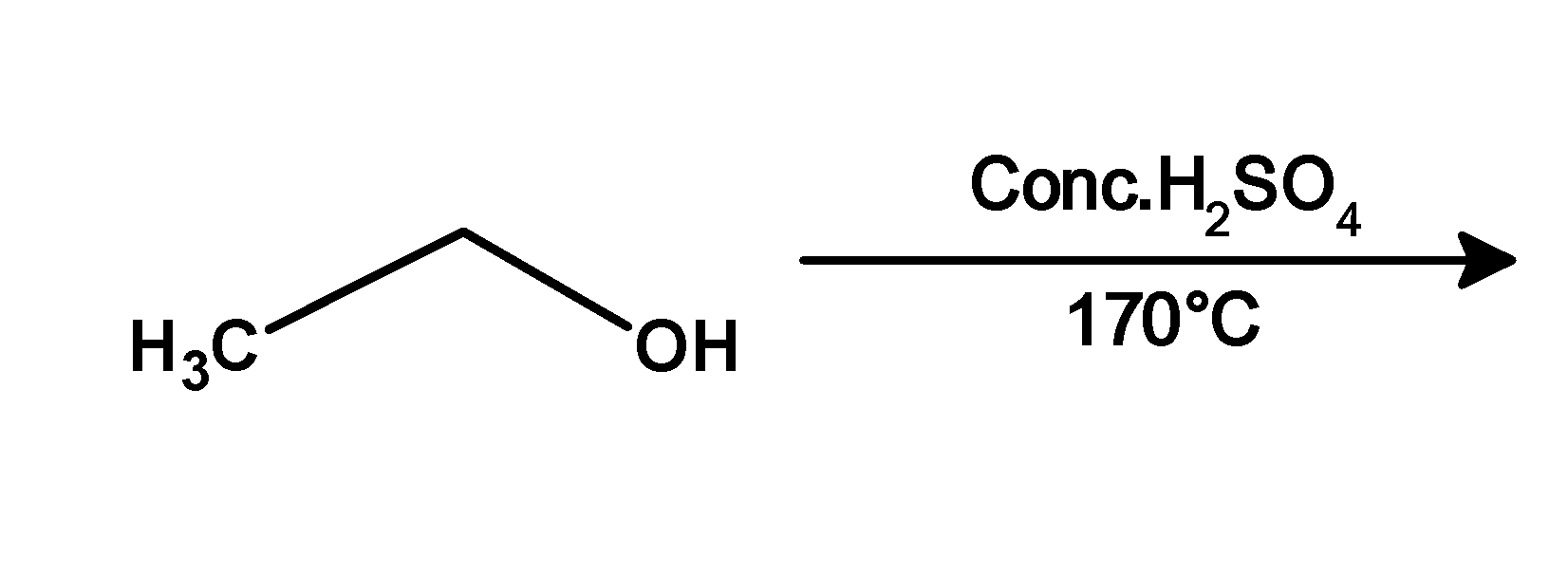
2.

3.

4.
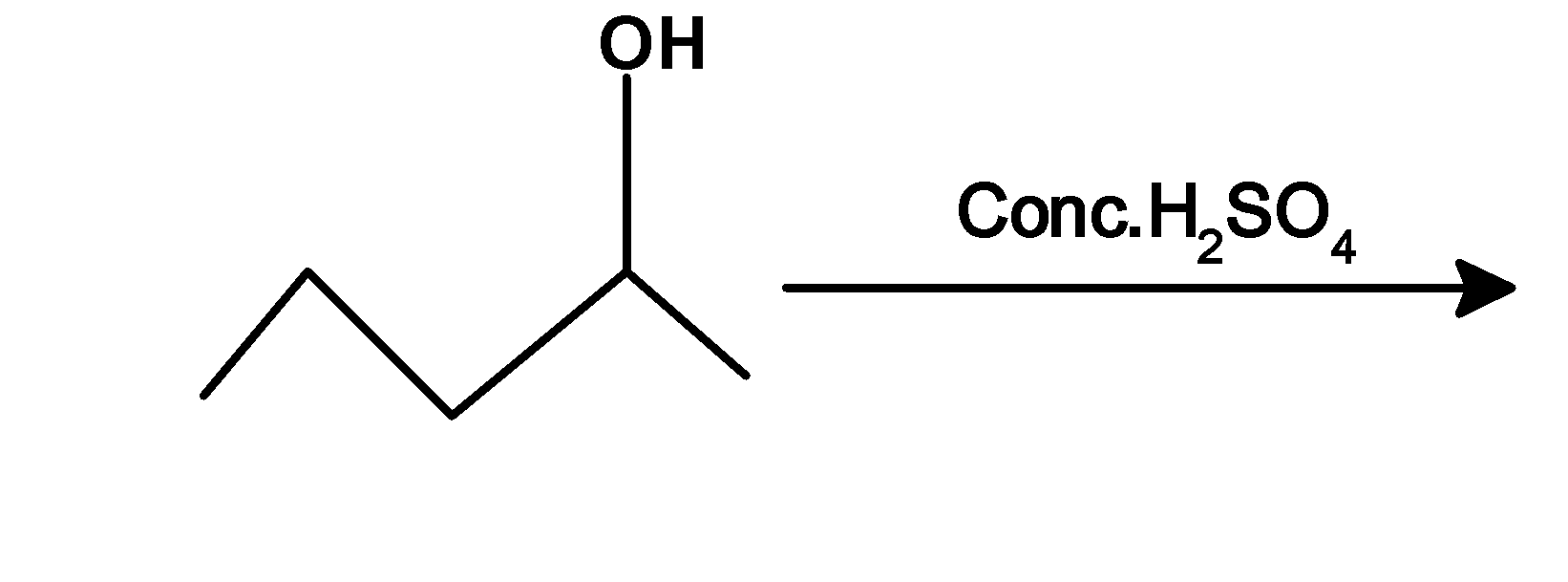
5.
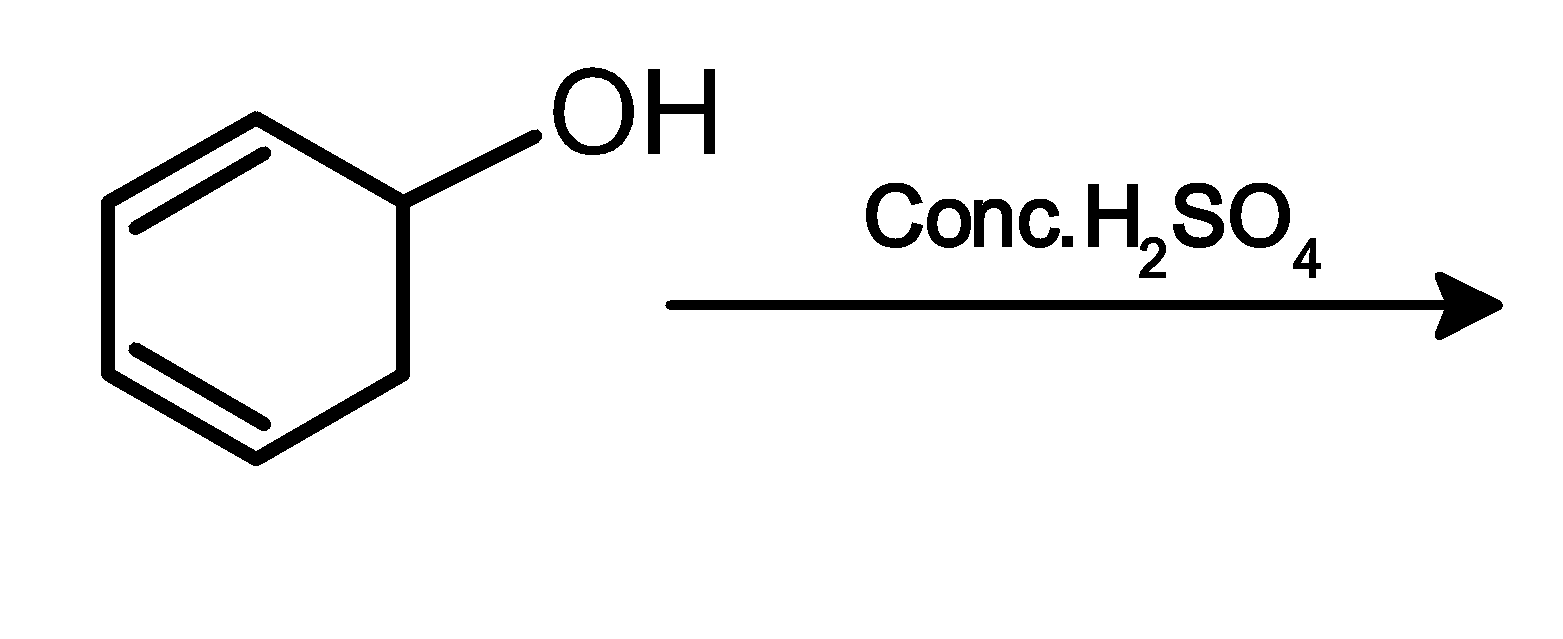
| 1. | 
|
| 2. | 
|
| 3. | 
|
| 4. | 
|
| 5. | 
|
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: When alcohols are heated with a protonic acid such as conc.$\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$ Or $\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$ at high temperatures they got dehydrated to form alkenes. The generation reaction of acidic dehydration of alcohols is as shown below,
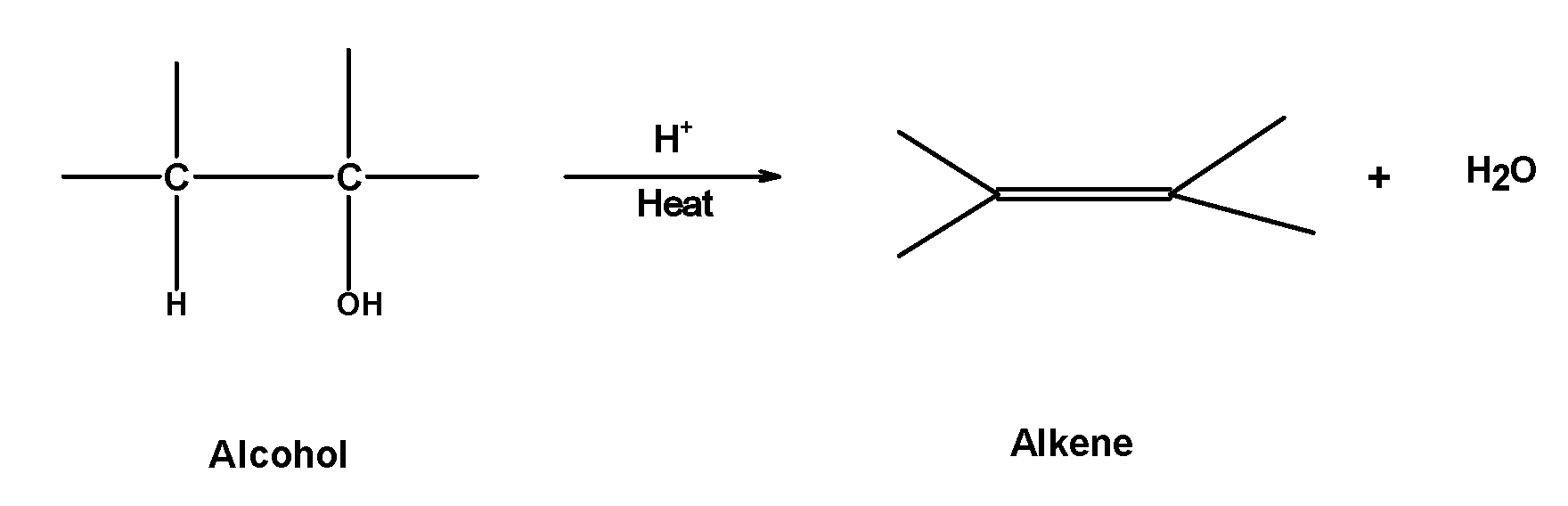
The product formation follows Saytzeff’s rule. According to this rule, the more highly substituted alkene is always the major product.
Complete step by step answer:
Alcohols undergo an acidic dehydration reaction. Let's consider the following reaction,
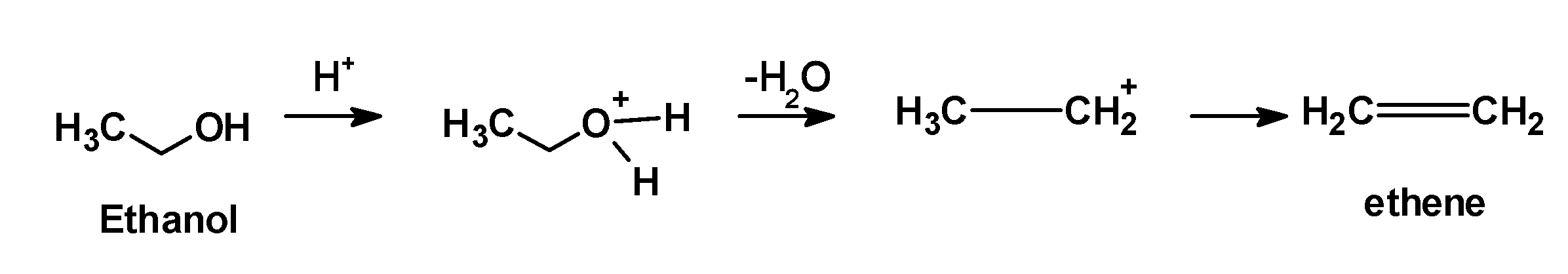
1) Ethanol when heated at the $\text{ 393 K }$ or $\text{ 17}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{C }$ undergoes the acidic dehydration reaction. It is dehydrated under the presence of acidic catalysts such as sulphuric acid. Ethanol protonated followed by the removal of water molecules. Ethanol dehydrated to form ethene.
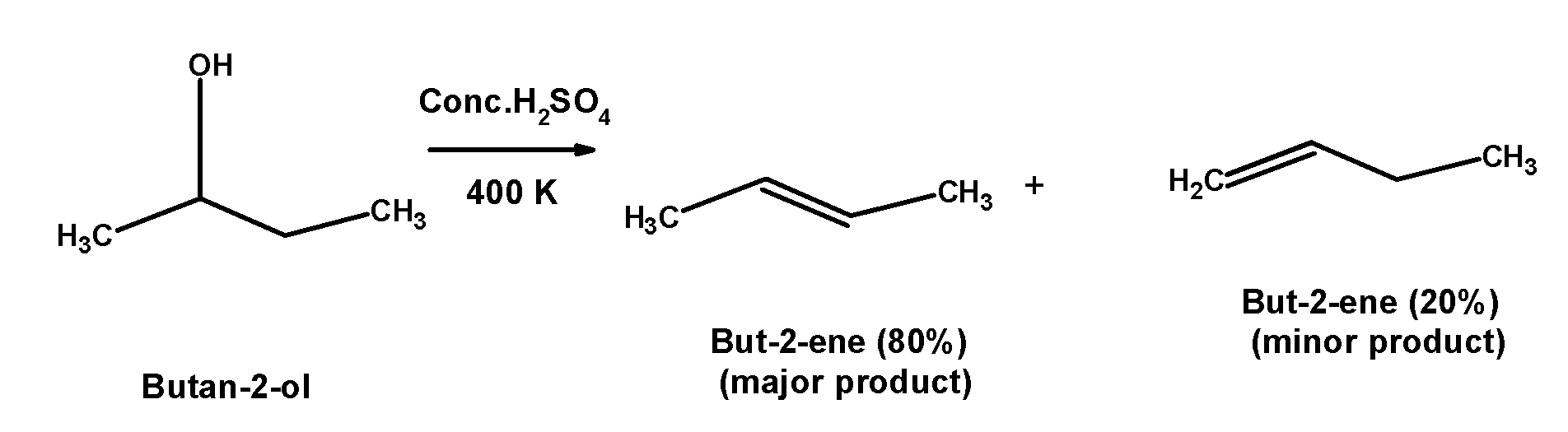
2) Butan-2-ol is a secondary alcohol. It is dehydrated under mild conditions. butan-2-ol abstracts a proton from the acid followed by the removal of hydronium ion at high-temperature $\text{ 400 K }$.the reaction of secondary alcohol with the sulphuric acid is as shown below,
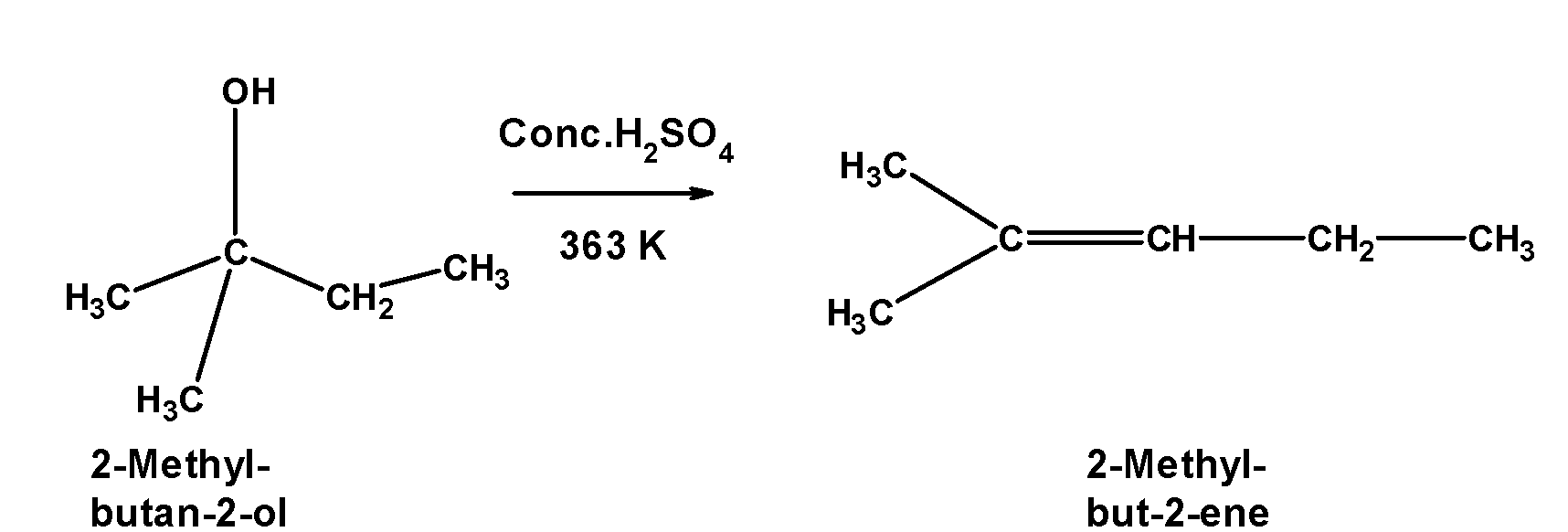
3) 2,2-dimethylpropan-2-ol$\text{ (}{{\text{3}}^{\text{o}}}\text{) }$ is a tertiary alcohol. It is dehydrated under mild conditions. 2,2-dimethylpropan-2-ol abstracts a proton from the acid followed by the removal of hydronium ion at high-temperature $\text{ 363 K }$.the reaction of tertiary alcohol with the sulphuric acid is as shown below,
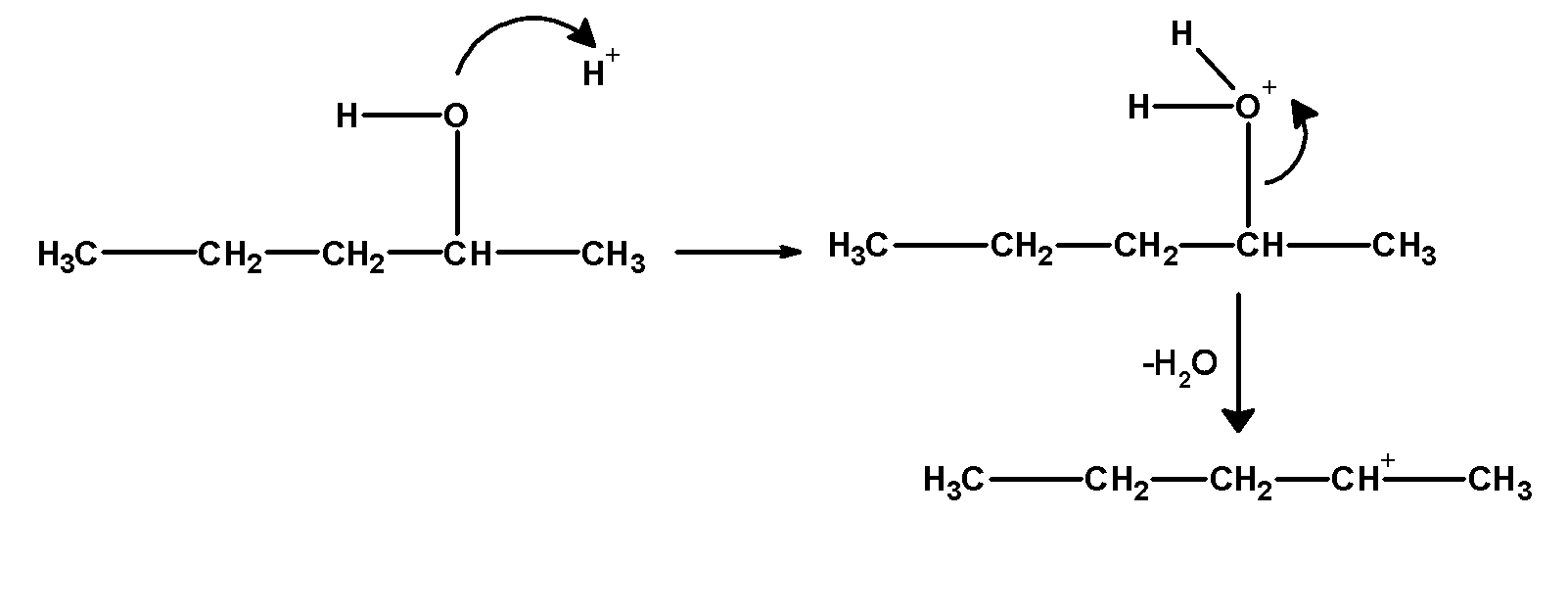
4) Alcohol undergoes acidic dehydration in presence. Alcohol is first protonated by the acid. Deprotonation of butanol is carried out in two stages.
First stage: in this step alcohol abstracts a proton from sulphuric acid. In the next step positive ions lose water molecules and form a carbocation. These steps are as shown below,
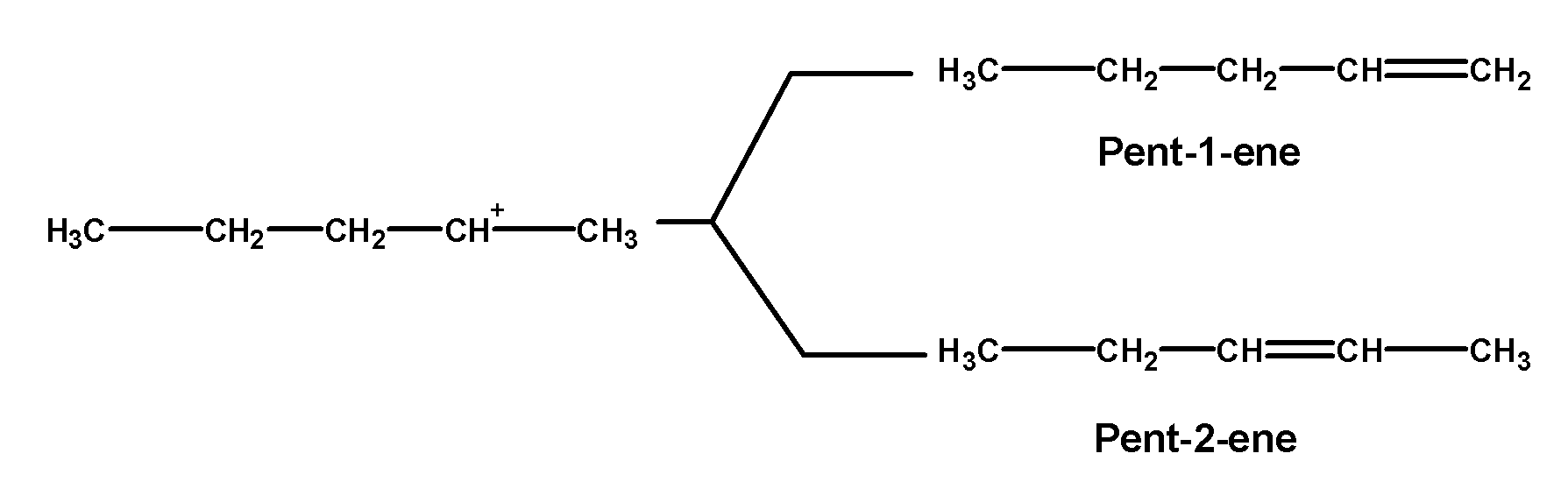
In the third step, the hydrogen atom is removed from the carbon which is next to the positively charged carbon atom to form a double-bonded compound. Hydrogen can be removed through the two pathways. These carbon atoms are located on either side of the carbon-bearing a positive charge. Thus obtained products would be pent-1-ene or pent-2-ene. The products are obtained by following Saytzeff’s rule.
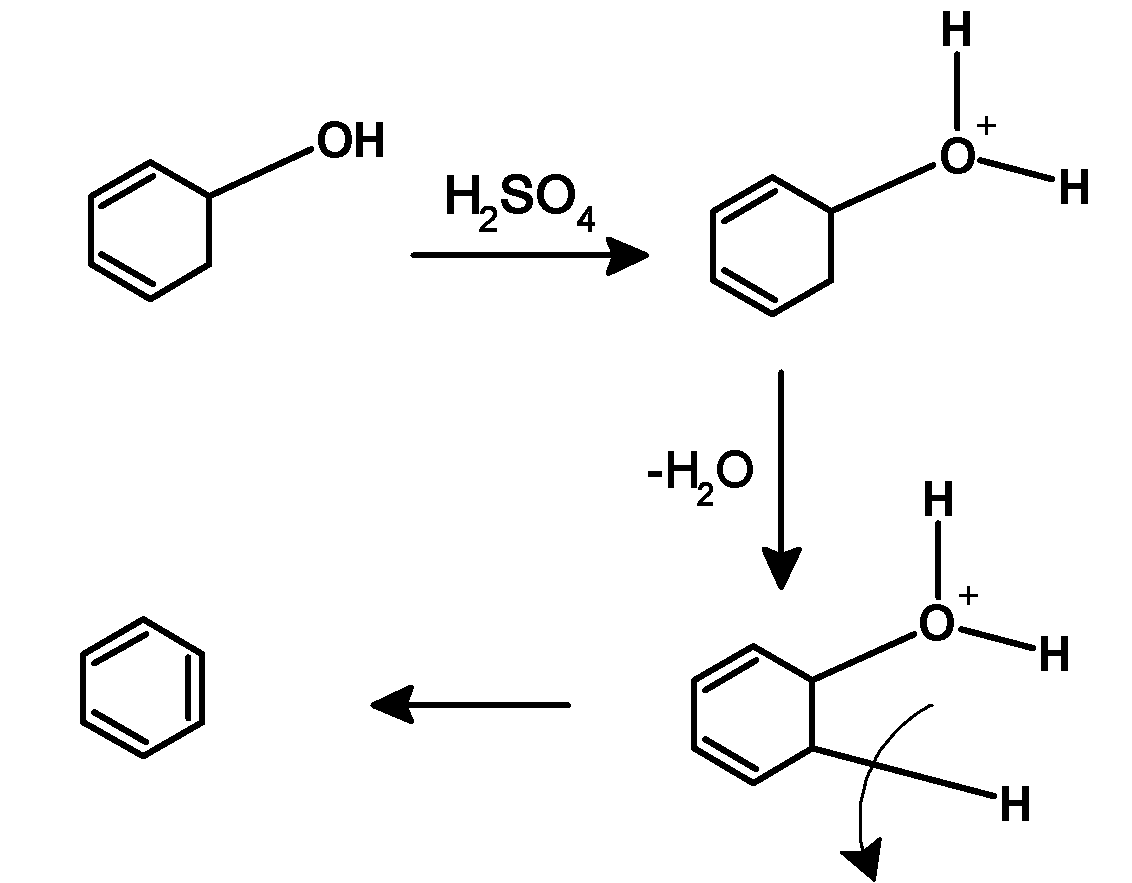
5) Cyclohexadienol undergoes acidic dehydration. Here acid catalyst attacks on the oxygen atom followed by the loss of water molecules to form a carbocation. Carbon atoms neighbouring the positive charge carbon atom lose its hydrogen followed by the formation of the double bond. The acidic dehydration results in benzene. As follows,
Note: The reaction between alcohol and the conc.sulphuric acid depends upon the conditions. In excess of alcohol, ethers are obtained. Dehydration of alcohol involves the formation of intermediates carbocation which are always prone to rearrangement, therefore, the alkenes formed are always those obtained from rearranged carbocation.

The product formation follows Saytzeff’s rule. According to this rule, the more highly substituted alkene is always the major product.
Complete step by step answer:
Alcohols undergo an acidic dehydration reaction. Let's consider the following reaction,
1) Ethanol when heated at the $\text{ 393 K }$ or $\text{ 17}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{C }$ undergoes the acidic dehydration reaction. It is dehydrated under the presence of acidic catalysts such as sulphuric acid. Ethanol protonated followed by the removal of water molecules. Ethanol dehydrated to form ethene.

2) Butan-2-ol is a secondary alcohol. It is dehydrated under mild conditions. butan-2-ol abstracts a proton from the acid followed by the removal of hydronium ion at high-temperature $\text{ 400 K }$.the reaction of secondary alcohol with the sulphuric acid is as shown below,

3) 2,2-dimethylpropan-2-ol$\text{ (}{{\text{3}}^{\text{o}}}\text{) }$ is a tertiary alcohol. It is dehydrated under mild conditions. 2,2-dimethylpropan-2-ol abstracts a proton from the acid followed by the removal of hydronium ion at high-temperature $\text{ 363 K }$.the reaction of tertiary alcohol with the sulphuric acid is as shown below,

4) Alcohol undergoes acidic dehydration in presence. Alcohol is first protonated by the acid. Deprotonation of butanol is carried out in two stages.
First stage: in this step alcohol abstracts a proton from sulphuric acid. In the next step positive ions lose water molecules and form a carbocation. These steps are as shown below,

In the third step, the hydrogen atom is removed from the carbon which is next to the positively charged carbon atom to form a double-bonded compound. Hydrogen can be removed through the two pathways. These carbon atoms are located on either side of the carbon-bearing a positive charge. Thus obtained products would be pent-1-ene or pent-2-ene. The products are obtained by following Saytzeff’s rule.

5) Cyclohexadienol undergoes acidic dehydration. Here acid catalyst attacks on the oxygen atom followed by the loss of water molecules to form a carbocation. Carbon atoms neighbouring the positive charge carbon atom lose its hydrogen followed by the formation of the double bond. The acidic dehydration results in benzene. As follows,

Note: The reaction between alcohol and the conc.sulphuric acid depends upon the conditions. In excess of alcohol, ethers are obtained. Dehydration of alcohol involves the formation of intermediates carbocation which are always prone to rearrangement, therefore, the alkenes formed are always those obtained from rearranged carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




