
complete the reaction:
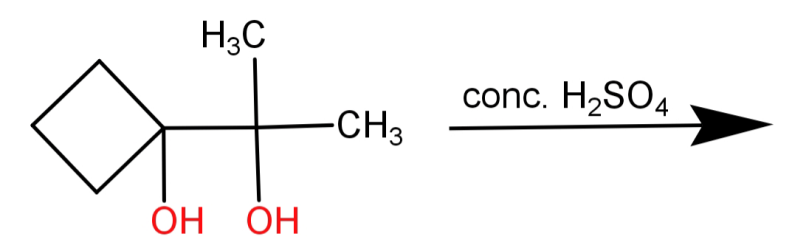

Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: This is a Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement. Here the acid leads to protonation of the hydroxyl group, then removal of water leads to formation of carbocation. Now 1,2-rearrangement occurs leading to formation of a ketone compound.
Complete step by step answer:
-The reaction shown in the question is Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement. This is a method by which 1,2-diols into carbonyl compounds which contain a carbon oxygen double bond. This happens because 1,2-rearrangement takes place under acidic conditions.
A compound which contains 2 hydroxyl groups (-OH) groups, each being attached to a vicinal carbon atom is known as Pinacol.
Pinacolone is the ketone to which the Pinacol is converted after 1,2-rearrangement under acidic conditions.
Hence the reaction is named as Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement.
A basic representation of this reaction can be written as:
${(C{H_3})_2}(OH)C - C(OH){(C{H_3})_2}\xrightarrow{{{H^ + }acid}}{(C{H_3})_3}COC{H_3} + {H_2}O$
-During this reaction the hydroxyl group of the Pinacol is protonated by the acid. Then water is removed which leaves behind a carbocation which is tertiary and hence stable. So, the alkyl group from the adjacent carbon migrates to the carbocation centre which is known as 1,2-rearrangement. Now the oxygen atom which was bonded to the carbon atom via double bond is deprotonated, which gives rise to the Pinacolone.
The reaction will thus proceed as:
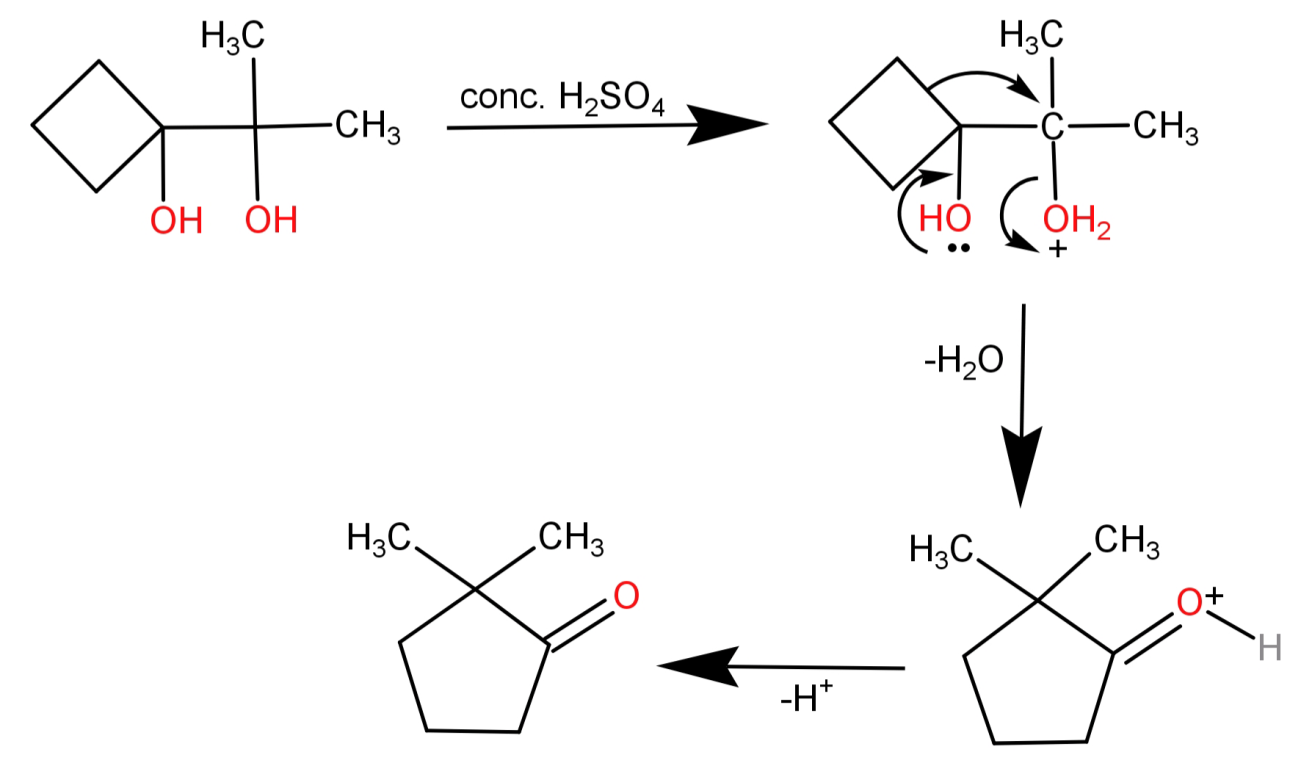
Note: The Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement is regioselective in nature, which means that only the more stable carbocation yields a major product. Also the rearrangement occurs because of the relative stability of the resulting oxonium ion.
Complete step by step answer:
-The reaction shown in the question is Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement. This is a method by which 1,2-diols into carbonyl compounds which contain a carbon oxygen double bond. This happens because 1,2-rearrangement takes place under acidic conditions.
A compound which contains 2 hydroxyl groups (-OH) groups, each being attached to a vicinal carbon atom is known as Pinacol.
Pinacolone is the ketone to which the Pinacol is converted after 1,2-rearrangement under acidic conditions.
Hence the reaction is named as Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement.
A basic representation of this reaction can be written as:
${(C{H_3})_2}(OH)C - C(OH){(C{H_3})_2}\xrightarrow{{{H^ + }acid}}{(C{H_3})_3}COC{H_3} + {H_2}O$
-During this reaction the hydroxyl group of the Pinacol is protonated by the acid. Then water is removed which leaves behind a carbocation which is tertiary and hence stable. So, the alkyl group from the adjacent carbon migrates to the carbocation centre which is known as 1,2-rearrangement. Now the oxygen atom which was bonded to the carbon atom via double bond is deprotonated, which gives rise to the Pinacolone.
The reaction will thus proceed as:

Note: The Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement is regioselective in nature, which means that only the more stable carbocation yields a major product. Also the rearrangement occurs because of the relative stability of the resulting oxonium ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




