
Compound heated with soda lime to obtain ${C_2}{H_6}$ in the laboratory is:
A. $C{H_3}C{H_2}COOH$
B. $C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$
C. $C{H_3}C{H_2}COC{H_3}$
D. $C{H_3}C{H_2}COONa$
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: We must understand the formation of hydrocarbons by the decarboxylation of carboxylic acid salts by heating them with soda lime. In the decarboxylation reaction, the removal of $ - COOH$ (or) $ - COONa$ takes place and it is replaced by a hydrogen atom.
Complete step by step answer: Let’s start by discussing what is carboxylic acid? Carboxylic acids are organic aids which has the form of $RCOOH,$ here R can be a hydrogen atom (or) alkyl group (hydrocarbon atom).The general structure of carboxylic acid is,
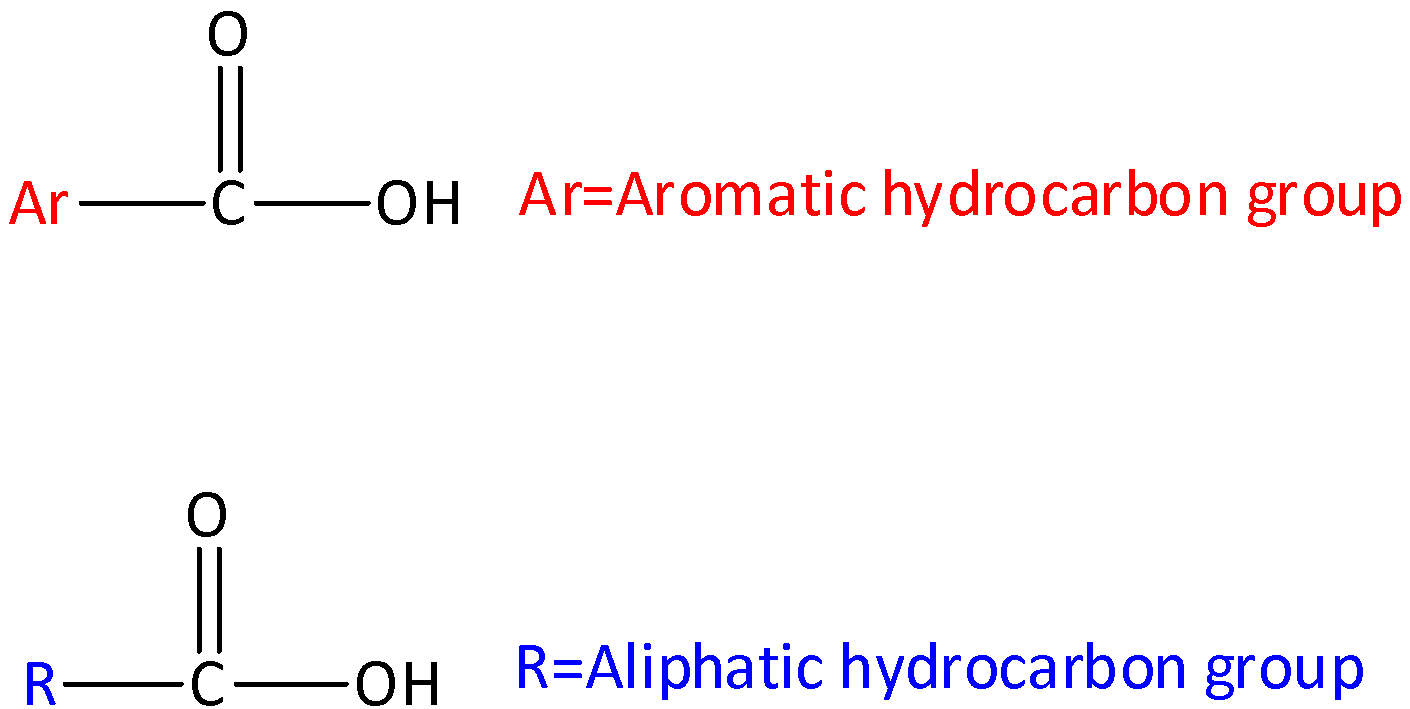
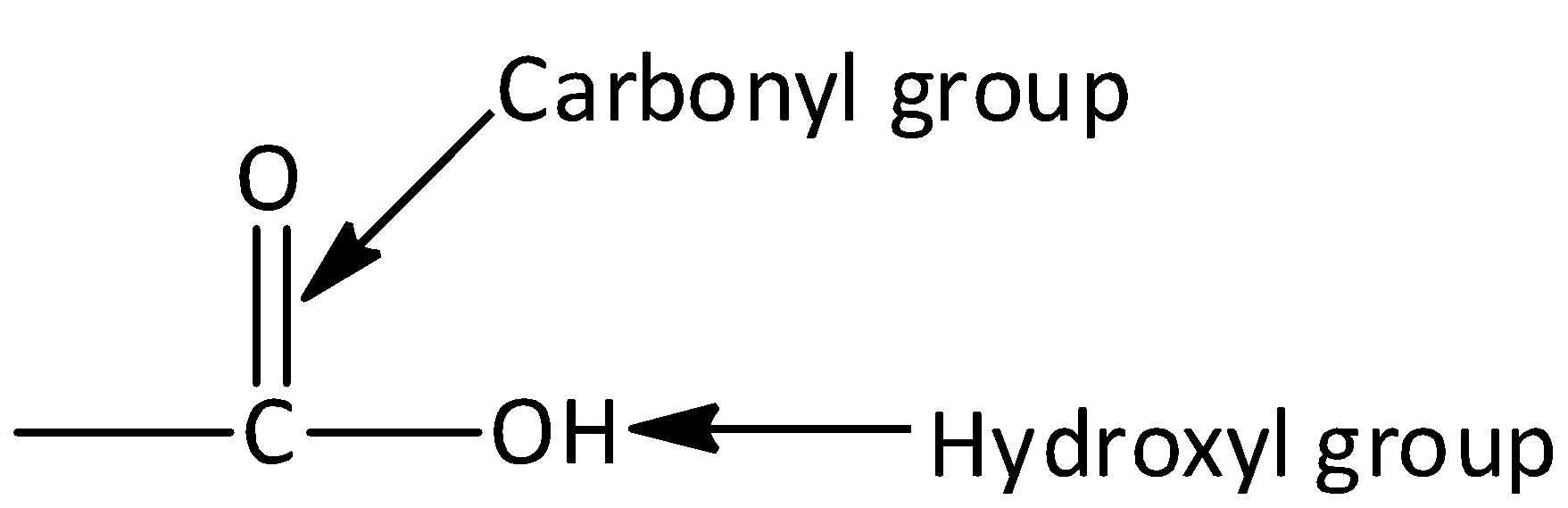
Carboxylic acid consists of two polar functional groups namely the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group. The carbonyl group and hydroxyl group are collectively called carboxyl groups.
Now coming back, we have to identify the reactant that produces ethane gas on reacting with soda lime. Soda lime is a mixture of sodium hydroxide, calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide. It appears as white granules
We know that $C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$ is an aldehyde and therefore, it can be eliminated. And $C{H_3}C{H_2}COC{H_3}$ is a ketone, it can also be opted out.
Now we have the remaining two options that is $C{H_3}C{H_2}COOH$ and $C{H_3}C{H_2}COONa.$
Let us now understand decarboxylation. The elimination of carbon dioxide from a molecule is called decarboxylation. Sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acid in the presence of soda lime undergo decarboxylation. The products formed are an alkane and sodium carbonate. The solid sodium salt of carboxylic acid is reacted with soda lime, to form the gas. The general reaction is,
$R - COONa + NaOH\xrightarrow{{CaO}}RH + N{a_2}C{O_3}$
Therefore, sodium propanoate will be a compound that would react with soda lime to give ethane gas in the laboratory.
$C{H_3}C{H_2}COONa\, + \,\,\,NaOH\xrightarrow{{CaO}}{C_2}{H_6}\,\, + \,\,\,\,N{a_2}C{O_3} \\
Sodium\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Soda\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Ethane\,\,\,\,\,Sodium \\
propanoate\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,lime\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Carbonate$
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note: We must know that the decarboxylation is also known as Duma reaction. The product alkane formed will have one carbon less than parent carboxylic acid. Aromatic carboxylic acid also undergoes this reaction.
Complete step by step answer: Let’s start by discussing what is carboxylic acid? Carboxylic acids are organic aids which has the form of $RCOOH,$ here R can be a hydrogen atom (or) alkyl group (hydrocarbon atom).The general structure of carboxylic acid is,

Carboxylic acid consists of two polar functional groups namely the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group. The carbonyl group and hydroxyl group are collectively called carboxyl groups.

Now coming back, we have to identify the reactant that produces ethane gas on reacting with soda lime. Soda lime is a mixture of sodium hydroxide, calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide. It appears as white granules
We know that $C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$ is an aldehyde and therefore, it can be eliminated. And $C{H_3}C{H_2}COC{H_3}$ is a ketone, it can also be opted out.
Now we have the remaining two options that is $C{H_3}C{H_2}COOH$ and $C{H_3}C{H_2}COONa.$
Let us now understand decarboxylation. The elimination of carbon dioxide from a molecule is called decarboxylation. Sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acid in the presence of soda lime undergo decarboxylation. The products formed are an alkane and sodium carbonate. The solid sodium salt of carboxylic acid is reacted with soda lime, to form the gas. The general reaction is,
$R - COONa + NaOH\xrightarrow{{CaO}}RH + N{a_2}C{O_3}$
Therefore, sodium propanoate will be a compound that would react with soda lime to give ethane gas in the laboratory.
$C{H_3}C{H_2}COONa\, + \,\,\,NaOH\xrightarrow{{CaO}}{C_2}{H_6}\,\, + \,\,\,\,N{a_2}C{O_3} \\
Sodium\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Soda\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Ethane\,\,\,\,\,Sodium \\
propanoate\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,lime\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Carbonate$
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note: We must know that the decarboxylation is also known as Duma reaction. The product alkane formed will have one carbon less than parent carboxylic acid. Aromatic carboxylic acid also undergoes this reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




