
Consider a ‘beam expander’ which contains two converging lenses of focal lengths $40{\text{ cm}}$ and $100{\text{ cm}}$ having a common optical axis. A laser beam of diameter $2{\text{ mm}}$ is incident on the $40{\text{ cm}}$ focal length lens. Then what is the diameter (in mm) of the final beam?

Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: We are given a beam expander that consists of two converging lenses and we are required to find the diameter of the final beam through the second lens. We need to know the relation between focal length and the diameter of the objective lens and image lens in a beam expander to solve the problem.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw a diagram first to understand the given situation and to find the relation between the focal lengths of the two lenses and the diameter of the beam.
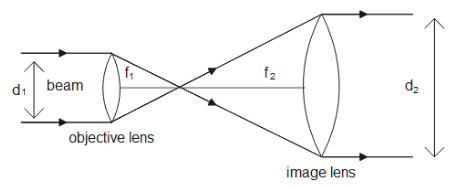
A beam expander consists of an objective lens and an imaging lens. As we can see, the ratio of the radius and focal length of the first lens will be equal to the ratio of the radius and focal length of the second lens. Therefore
$\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{f_1}}} = \dfrac{{{r_2}}}{{{f_2}}}$
Substituting the value we get,
$ \therefore {r_2} = 5{\text{ mm}}$
Therefore the diameter of the final beam will be $10{\text{ mm}}$.
Note: Beam expanders are used to increase the magnification of the image and obtain the erect image of an object. It also reduces the aberrations or defects caused by using a lens. Beam expanders increase the diameter of the collimated input beam to a larger collimated output beam and thus the value of the diameter of the final beam we obtained is more than the beam which was incident in the first lens. The first lens in the arrangement with a relatively shorter focal length is known as the objective lens and the lens after that with a greater focal length is called the imaging lens.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw a diagram first to understand the given situation and to find the relation between the focal lengths of the two lenses and the diameter of the beam.

A beam expander consists of an objective lens and an imaging lens. As we can see, the ratio of the radius and focal length of the first lens will be equal to the ratio of the radius and focal length of the second lens. Therefore
$\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{f_1}}} = \dfrac{{{r_2}}}{{{f_2}}}$
Substituting the value we get,
$ \therefore {r_2} = 5{\text{ mm}}$
Therefore the diameter of the final beam will be $10{\text{ mm}}$.
Note: Beam expanders are used to increase the magnification of the image and obtain the erect image of an object. It also reduces the aberrations or defects caused by using a lens. Beam expanders increase the diameter of the collimated input beam to a larger collimated output beam and thus the value of the diameter of the final beam we obtained is more than the beam which was incident in the first lens. The first lens in the arrangement with a relatively shorter focal length is known as the objective lens and the lens after that with a greater focal length is called the imaging lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




