
Consider the following compound:
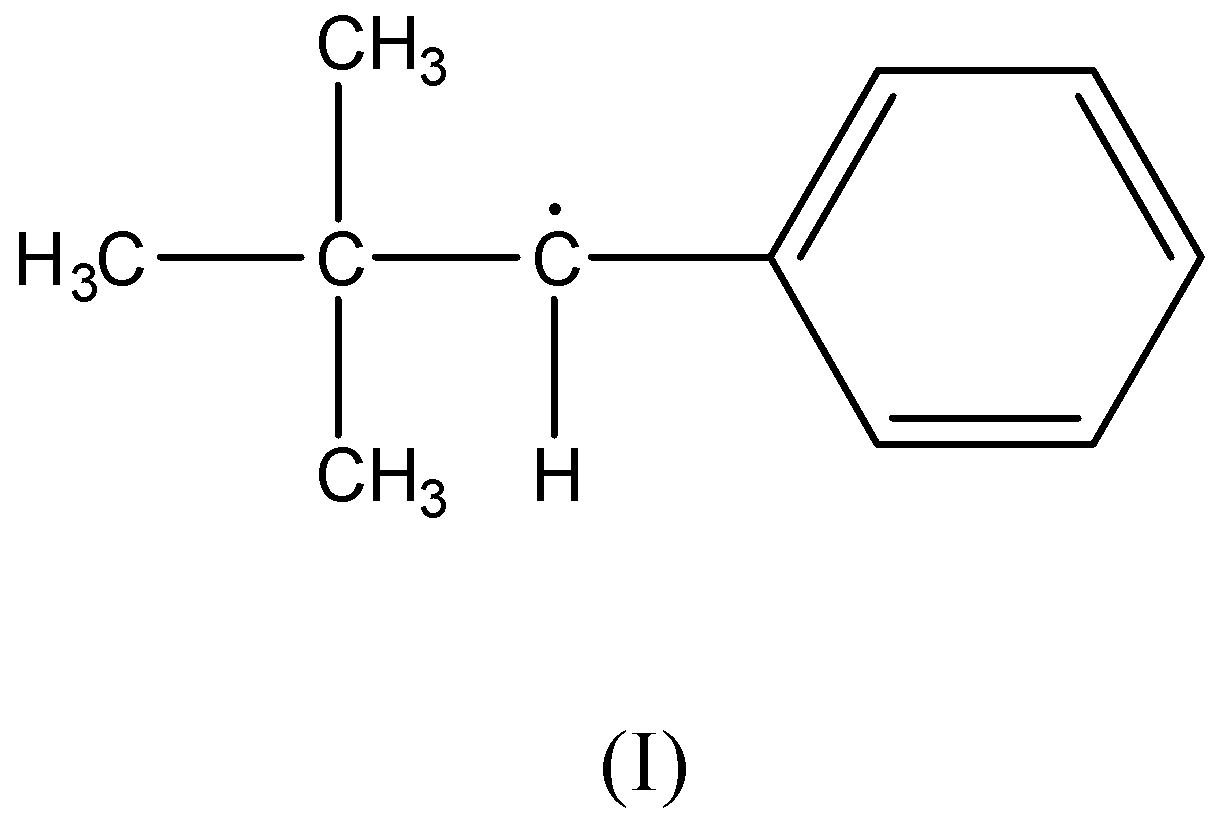
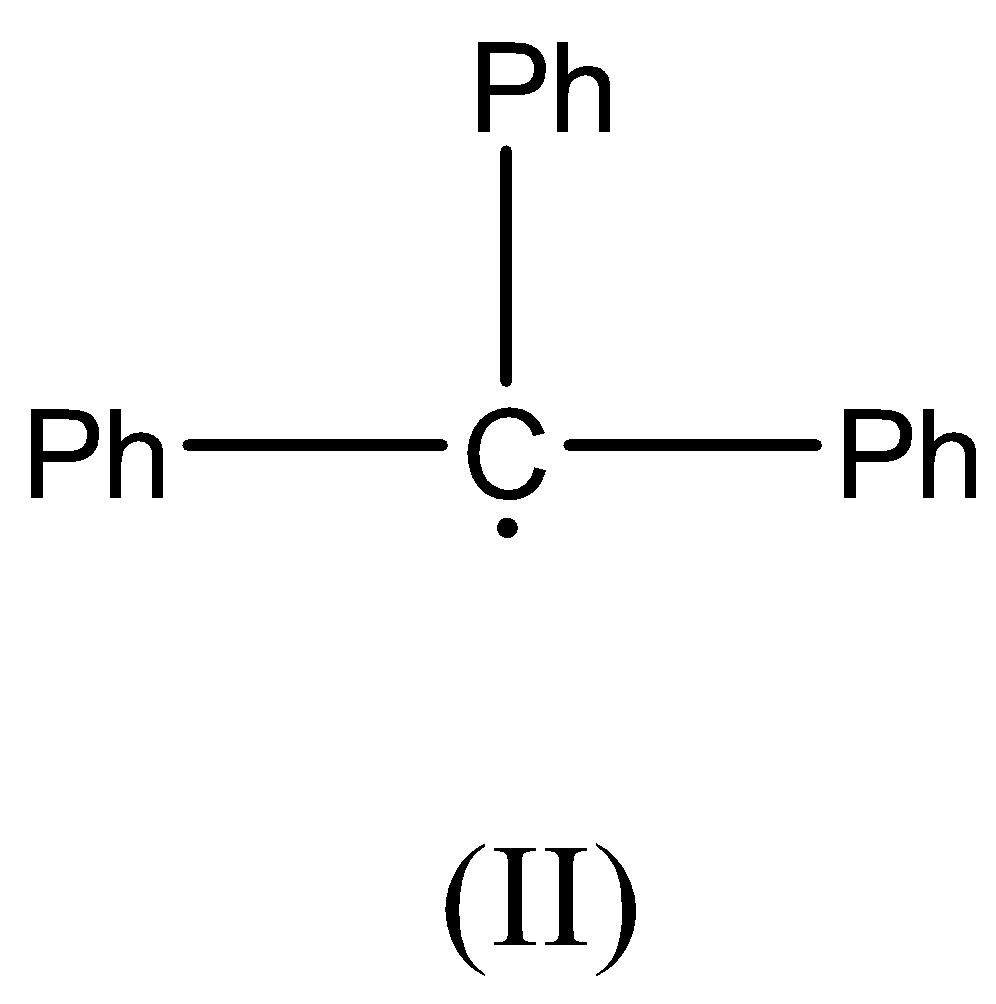
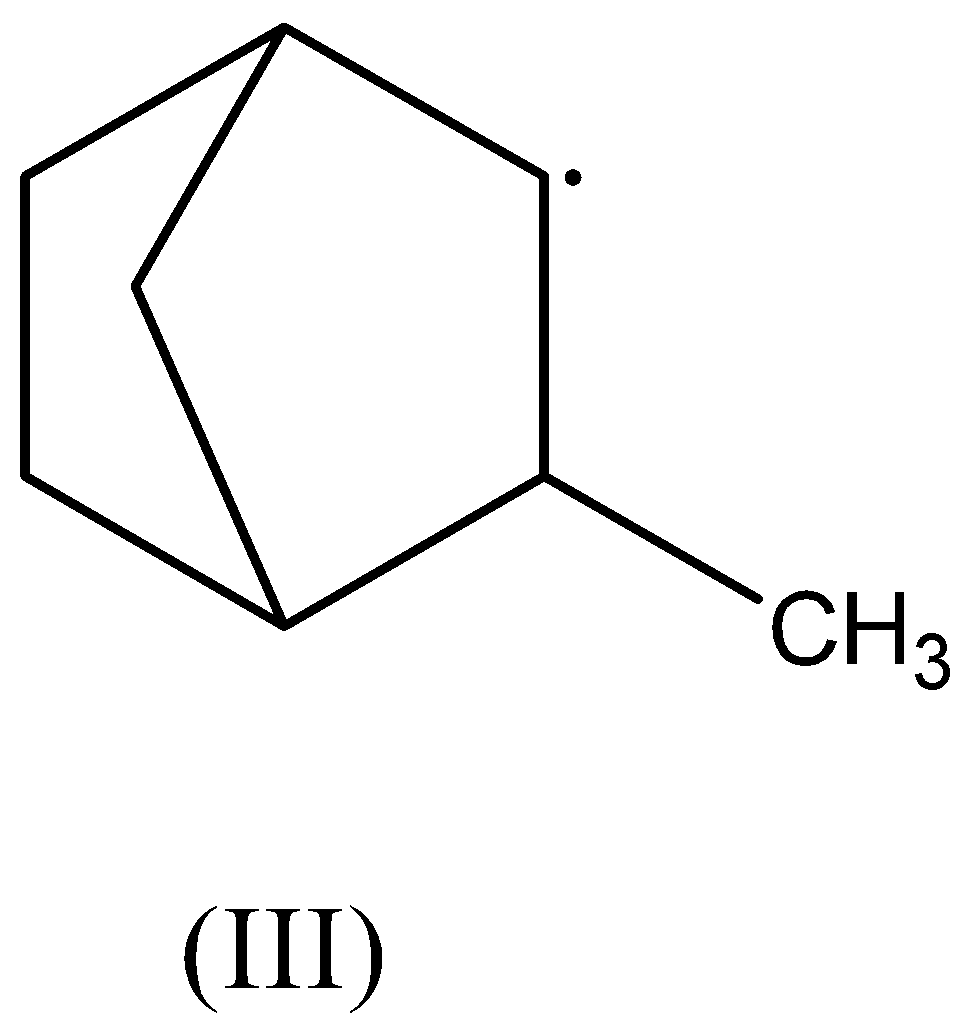
Hyperconjugation occurs in:
A.III only
B.I and III
C.I only
D.II only



Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that the hyperconjugation refers to delocalization of electrons with the participation of bonds of sigma character. Increased electron delocalization associated with hyperconjugation increases the stability of the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
In the compounds given above, all the three compounds have free radicals. We know that hyperconjugation can lead to a stabilized compound. We will identify the electron interaction taking place in each compound to find out which effect is enhancing the stability of the compound.
The main criterion for any ion to get stabilized by hyperconjugation is the presence of an adjacent alkyl group having at least one free hydrogen atom also called $\beta - $ hydrogen atom bonded to it.
Let us look at the first chemical structure,
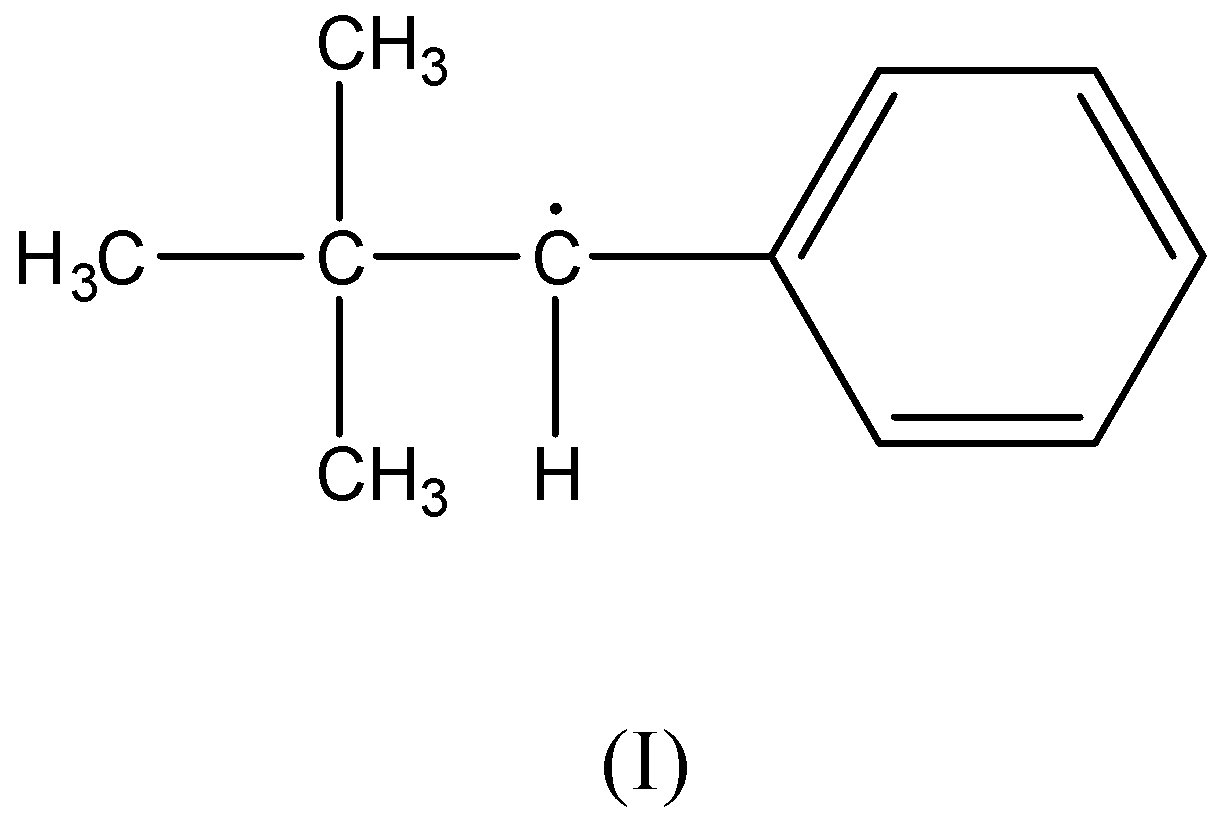
There is no $\beta - $ hydrogen atom present as the carbon radical is bonded to a phenyl ring and a tertiary-butyl group. Therefore, this compound is not stabilized by hyperconjugation.
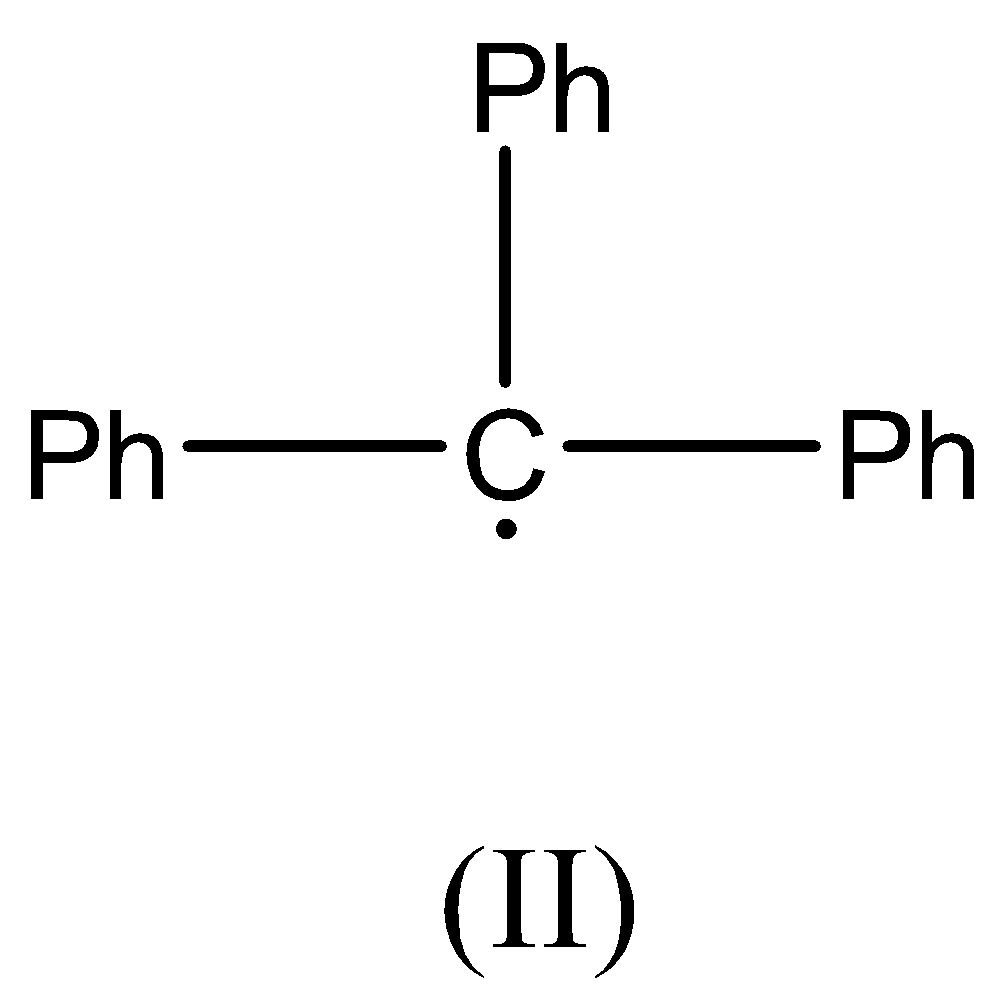
Now we can discuss the second compound, there is no $\beta - $ hydrogen atom present as the carbon radical is bonded to three Phenyl rings. This radical is resonance stabilized.
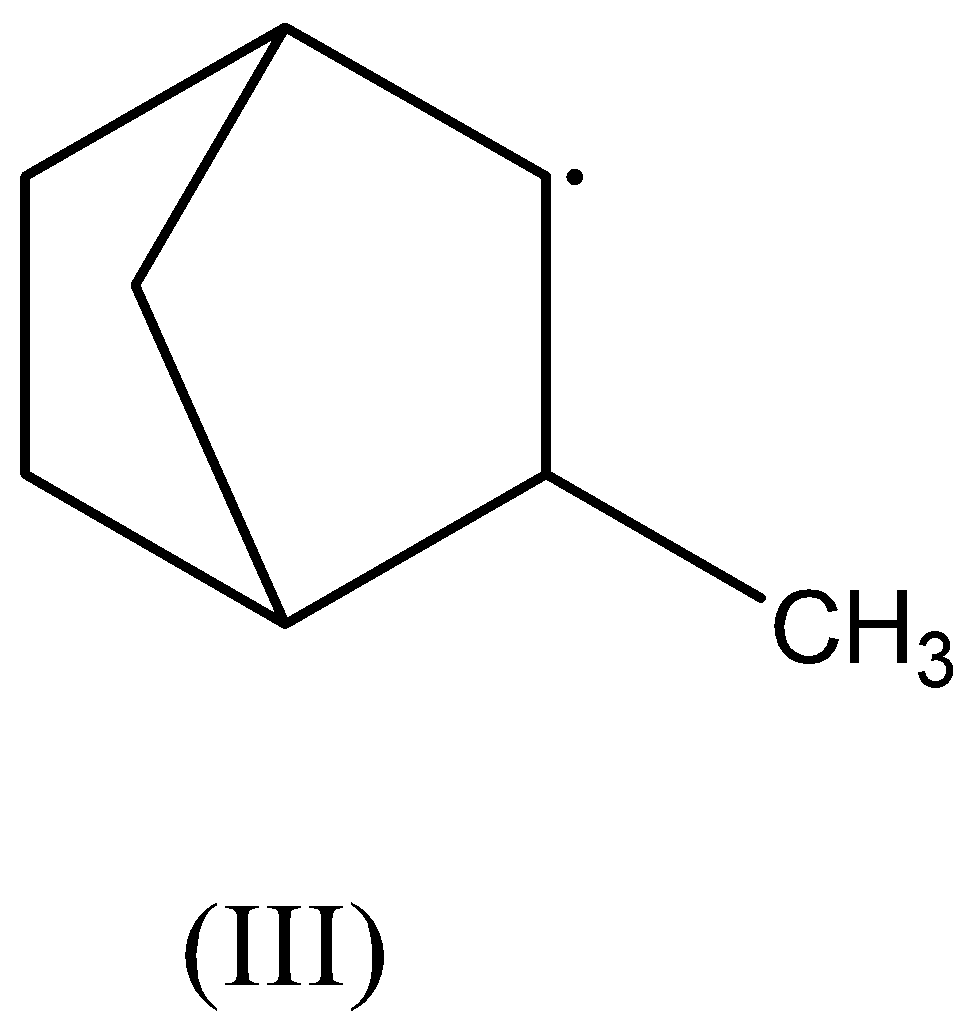
In the third compound, there are two $\beta - $ hydrogen atoms present. Thus, this radical is stabilized by hyperconjugation.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option A.
Note:
We need to remember that the hyperconjugation effect is a stabilizing interaction of free radical which is possible only in the presence of $\beta - $ hydrogen atom present in the structure. It can stabilize carbocation and free radical intermediates only. In the presence of phenyl groups, the stability is established by resonance. Hyperconjugation affects various properties such as bond length, dipole moments, heat of formation of molecules, stability of carbocations, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
In the compounds given above, all the three compounds have free radicals. We know that hyperconjugation can lead to a stabilized compound. We will identify the electron interaction taking place in each compound to find out which effect is enhancing the stability of the compound.
The main criterion for any ion to get stabilized by hyperconjugation is the presence of an adjacent alkyl group having at least one free hydrogen atom also called $\beta - $ hydrogen atom bonded to it.
Let us look at the first chemical structure,

There is no $\beta - $ hydrogen atom present as the carbon radical is bonded to a phenyl ring and a tertiary-butyl group. Therefore, this compound is not stabilized by hyperconjugation.

Now we can discuss the second compound, there is no $\beta - $ hydrogen atom present as the carbon radical is bonded to three Phenyl rings. This radical is resonance stabilized.

In the third compound, there are two $\beta - $ hydrogen atoms present. Thus, this radical is stabilized by hyperconjugation.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option A.
Note:
We need to remember that the hyperconjugation effect is a stabilizing interaction of free radical which is possible only in the presence of $\beta - $ hydrogen atom present in the structure. It can stabilize carbocation and free radical intermediates only. In the presence of phenyl groups, the stability is established by resonance. Hyperconjugation affects various properties such as bond length, dipole moments, heat of formation of molecules, stability of carbocations, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




