
Conversion of hexane into benzene involves the reaction of:
A. Hydration
B. Hydrolysis
C. Hydrogenation
D. Dehydrogenation
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: Hexane is a saturated alkane with 6 – carbon atom alkyl chain. The conversion of hexane into benzene involves it being converted into a cyclic structure and then the aromatic compound benzene. For a cyclic or ring structure, it is necessary to remove the hydrogen atoms to make it into a ring. Also aromatic compounds involve unsaturated (double) bonds.
Complete answer:
Hexane is a hydrocarbon and classified as an alkane with saturated single bonds having a chain of 6 carbon atoms with molecular formula, ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$. Now, we have to convert it into benzene that has a molecular formula${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. Clearly, as we can see there is removal of hydrogen atoms from hexane${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$to make it benzene ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. So, this will go through a process of removal of hydrogen called dehydrogenation.
The conversion will include treating the hexane molecule with the catalyst that is oxides of metals like vanadium oxide or chromium oxide. This will remove hydrogen atoms from hexane and form a cyclic structure called cyclohexane. The reaction is:
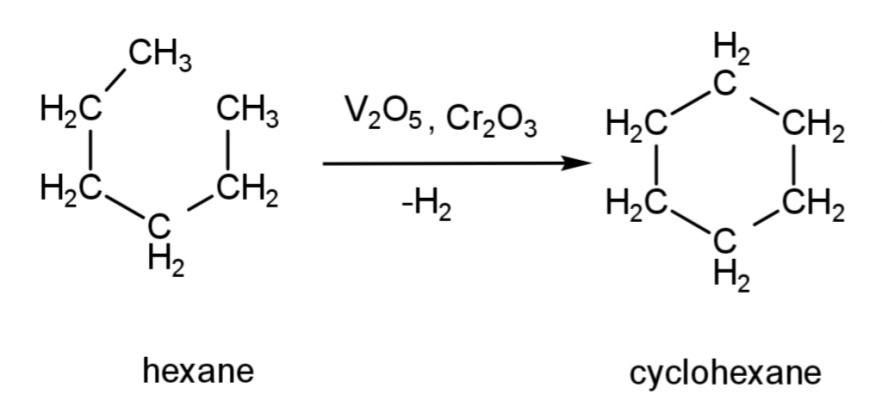
This cyclohexane at a very high temperature loses more hydrogen atoms (3 hydrogen molecules) and undergoes aromatization to form aromatic benzene. The reaction is:
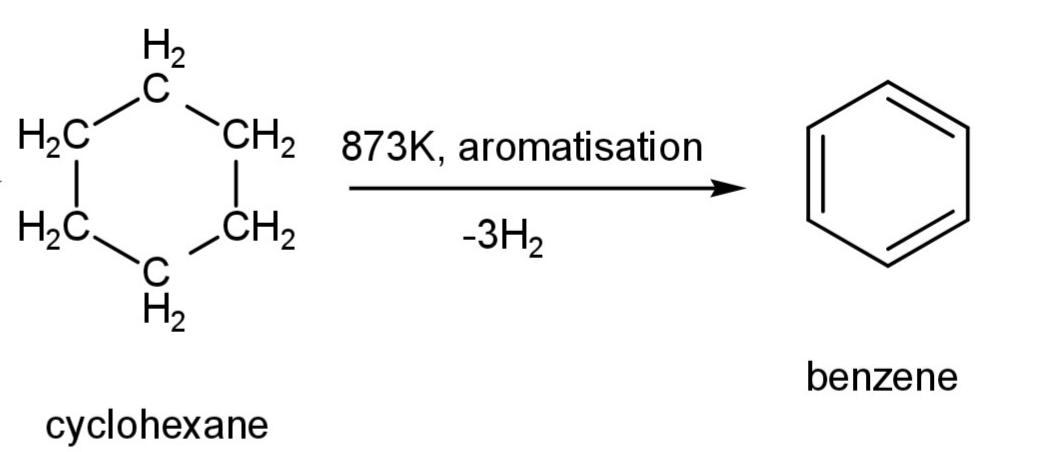
Hence, conversion of hexane into benzene involves the reaction of dehydrogenation, so option D is correct.
Note:
As dehydrogenation removes the hydrogen molecules, hydrogenation is the opposite of it as it is the reaction where an unsaturated compound (alkenes) adds hydrogen and converts to saturated compounds. Hydration is the addition of water molecules, and hydrolysis involves the cleavage of any compound in presence of water.
Complete answer:
Hexane is a hydrocarbon and classified as an alkane with saturated single bonds having a chain of 6 carbon atoms with molecular formula, ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$. Now, we have to convert it into benzene that has a molecular formula${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. Clearly, as we can see there is removal of hydrogen atoms from hexane${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}$to make it benzene ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. So, this will go through a process of removal of hydrogen called dehydrogenation.
The conversion will include treating the hexane molecule with the catalyst that is oxides of metals like vanadium oxide or chromium oxide. This will remove hydrogen atoms from hexane and form a cyclic structure called cyclohexane. The reaction is:

This cyclohexane at a very high temperature loses more hydrogen atoms (3 hydrogen molecules) and undergoes aromatization to form aromatic benzene. The reaction is:

Hence, conversion of hexane into benzene involves the reaction of dehydrogenation, so option D is correct.
Note:
As dehydrogenation removes the hydrogen molecules, hydrogenation is the opposite of it as it is the reaction where an unsaturated compound (alkenes) adds hydrogen and converts to saturated compounds. Hydration is the addition of water molecules, and hydrolysis involves the cleavage of any compound in presence of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




