
How do you convert phenol to picric acid? Explain the equation.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Phenol is a molecule in which a –OH group is attached to the benzene ring.
- Picric acid contains three nitro groups in the ortho and para positions of phenol.
Complete step by step answer:
So in the question we are asked to convert phenol to picric acid. For that we should have some basic idea about the structure of the compounds and about the resonance structures and various effects the functional group may possess like +R effect etc.
Here let’s first see the structure of phenol and picric acid.
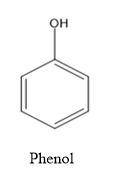
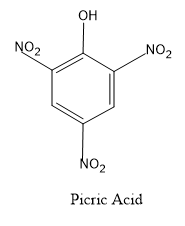
- So by comparing the two structures,we can say that the ortho and para positions of the phenol molecule are getting nitrated i.e. the addition of nitro groups.
- Ortho position is the carbon position next to the carbon which is directly attached to the functional group and para position is the carbon position exactly opposite to the carbon to which the functional group is attached to.
- And we know that the nitro group is a strong electrophile and the phenol is undergoing electrophilic substitution.
- To undergo electrophilic substitution the phenol should possess high nucleophilic nature,this is explained by the resonance effect.
As phenol is an aromatic system it has resonance and the –OH group attached to the benzene ring is an electron donating group and possesses the +R effect and they will be ortho, para directing.
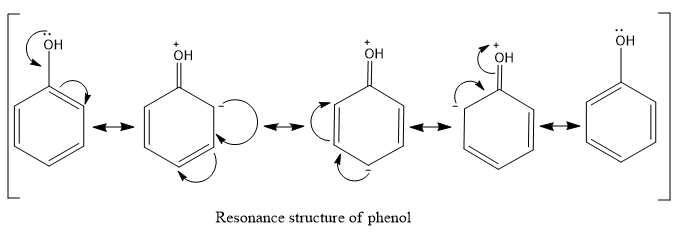
- From the resonance structure of the phenol,we can say that the aggregation of the negative charge is in the ortho and para positions ,so the nitro group will attack these positions during the electrophilic substitution reaction.
- Now let's write the preparation of picric acid from phenol.
When phenol is treated with hot conc.nitric acid in the presence of conc.sulphuric acid yellow coloured picric acid is produced.
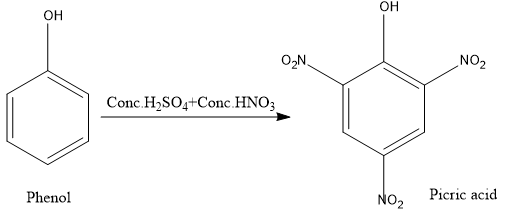
Note: The mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid in the ratio 1 : 1 is called the nitrating mixture.
- Here phenol is undergoing nitration reaction with 3 moles of conc.nitric acid.
- The IUPAC name of picric acid is 2,4,6-trinitrophenol.
- Picric acid contains three nitro groups in the ortho and para positions of phenol.
Complete step by step answer:
So in the question we are asked to convert phenol to picric acid. For that we should have some basic idea about the structure of the compounds and about the resonance structures and various effects the functional group may possess like +R effect etc.
Here let’s first see the structure of phenol and picric acid.


- So by comparing the two structures,we can say that the ortho and para positions of the phenol molecule are getting nitrated i.e. the addition of nitro groups.
- Ortho position is the carbon position next to the carbon which is directly attached to the functional group and para position is the carbon position exactly opposite to the carbon to which the functional group is attached to.
- And we know that the nitro group is a strong electrophile and the phenol is undergoing electrophilic substitution.
- To undergo electrophilic substitution the phenol should possess high nucleophilic nature,this is explained by the resonance effect.
As phenol is an aromatic system it has resonance and the –OH group attached to the benzene ring is an electron donating group and possesses the +R effect and they will be ortho, para directing.

- From the resonance structure of the phenol,we can say that the aggregation of the negative charge is in the ortho and para positions ,so the nitro group will attack these positions during the electrophilic substitution reaction.
- Now let's write the preparation of picric acid from phenol.
When phenol is treated with hot conc.nitric acid in the presence of conc.sulphuric acid yellow coloured picric acid is produced.

Note: The mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid in the ratio 1 : 1 is called the nitrating mixture.
- Here phenol is undergoing nitration reaction with 3 moles of conc.nitric acid.
- The IUPAC name of picric acid is 2,4,6-trinitrophenol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




