
How to convert propan-2-ol to propan-1-ol?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: Firstly it could be Convert the propan-2-ol to propanone by using potassium dichromate and then convert propanone to propan by using Wolff kishner reaction and finally it can be converted to propan-1-ol.
Complete step by step answer:
1 Propan-2-ol to propanone
On controlled oxidation, alcohols give aldehyde or ketones. Primary alcohols on controlled oxidation give aldehydes and secondary alcohols on controlled oxidation give ketones
The common oxidizing agent used for alcohols to produce ketones or aldehydes is acidified potassium dichromate
Now, therefore oxidation of propan-2-ol with its oxidizing agent potassium dichromate will give its resultant ketone which is propanone.
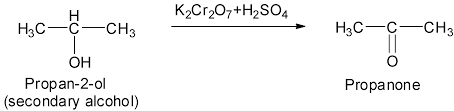
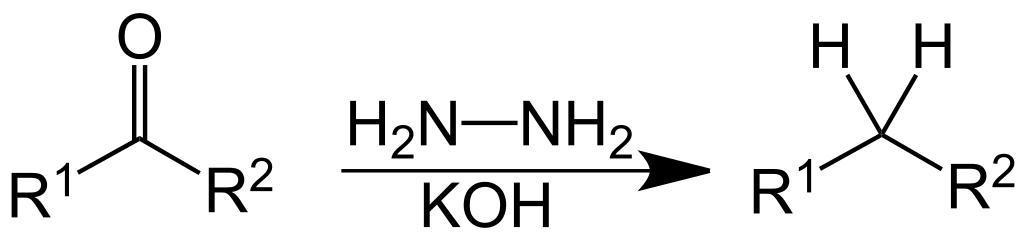
2 Propanone to propane-
Propanone Is converted to propane by the help of . Wollf kishner reduction- Wolff Kishner reduction mechanism begins with the formation of a hydrazone anion which then releases the nitrogen atom to form a carbanion. This carbanion then reacts with the water in the system to give a hydrocarbon. Typically, diethylene glycol is used as a solvent for this method.
This reduction is an organic reaction as aldehydes and ketones are reduced to alkanes. Some carbonyl compounds are stable in strongly basic conditions
The Clemmensen reduction is a reaction that is used to reduce aldehydes or ketones to alkanes using hydrochloric acid and zinc amalgam. Now, converting propanone to propane by wolff kishner reduction
3 Propane to Propanol
Propane Can be converted into propanol by following these steps:
It is treated with bromine gas (or any halogen in presence of UV light) which converts it into 2- bromo propane .
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_3} + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}CH\left( {Br} \right)C{H_3}\]
2- bromopropane is treated with alcoholic KOH which converts it into propene.
\[C{H_3}CH\left( {Br} \right)C{H_3} + KOH\left( {alc} \right) \to C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\]
Propene is treated with H-Br in presence of peroxide which converts it into 1- bromopropane
\[C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + H - Br\to C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br\]
1- bromopropane is treated with aqueous \[KOH\] which converts it into (propanol).
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br+ KOH\left( {aq} \right) \to C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\]
Note: Clemmensen reduction is a naming reaction in which reduction of ketones to alkanes using zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid. This reaction is named after Erik Christian Clemmensen, a Danish chemist.
Complete step by step answer:
1 Propan-2-ol to propanone
On controlled oxidation, alcohols give aldehyde or ketones. Primary alcohols on controlled oxidation give aldehydes and secondary alcohols on controlled oxidation give ketones
The common oxidizing agent used for alcohols to produce ketones or aldehydes is acidified potassium dichromate
Now, therefore oxidation of propan-2-ol with its oxidizing agent potassium dichromate will give its resultant ketone which is propanone.
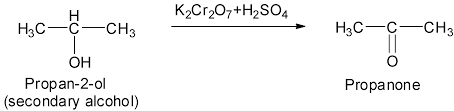
2 Propanone to propane-
Propanone Is converted to propane by the help of . Wollf kishner reduction- Wolff Kishner reduction mechanism begins with the formation of a hydrazone anion which then releases the nitrogen atom to form a carbanion. This carbanion then reacts with the water in the system to give a hydrocarbon. Typically, diethylene glycol is used as a solvent for this method.
This reduction is an organic reaction as aldehydes and ketones are reduced to alkanes. Some carbonyl compounds are stable in strongly basic conditions
The Clemmensen reduction is a reaction that is used to reduce aldehydes or ketones to alkanes using hydrochloric acid and zinc amalgam. Now, converting propanone to propane by wolff kishner reduction

3 Propane to Propanol
Propane Can be converted into propanol by following these steps:
It is treated with bromine gas (or any halogen in presence of UV light) which converts it into 2- bromo propane .
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_3} + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}CH\left( {Br} \right)C{H_3}\]
2- bromopropane is treated with alcoholic KOH which converts it into propene.
\[C{H_3}CH\left( {Br} \right)C{H_3} + KOH\left( {alc} \right) \to C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\]
Propene is treated with H-Br in presence of peroxide which converts it into 1- bromopropane
\[C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + H - Br\to C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br\]
1- bromopropane is treated with aqueous \[KOH\] which converts it into (propanol).
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br+ KOH\left( {aq} \right) \to C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\]
Note: Clemmensen reduction is a naming reaction in which reduction of ketones to alkanes using zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid. This reaction is named after Erik Christian Clemmensen, a Danish chemist.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




