
Convert the following
Acetic acid to Butan-2-one
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The acetic acid is first converted into ethanol by reduction and then this ethanol on oxidation gives ethyl aldehyde. This is converted to 2-ethyl 2-ethanol which on further oxidation gives us the desired product Butan-2-one.
Complete step by step solution:
The acetic acid can be converted into Butan-2-one through the following steps.
- In the first step acetic acid is treated with Lithium aluminum hydride ($LiAl{{H}_{4}}$) with dry ether and water and ethanol is formed. Lithium aluminum hydride acts as a reducing agent here and it is used along with dry ether. The reaction is shown below
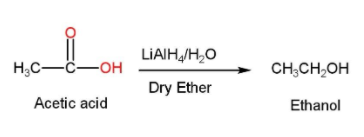
- In the next step, ethanol is treated with P.C.C and ethyl aldehyde (acetaldehyde or $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$) is formed. PCC is Pyridinium chlorochromate and is used in organic synthesis for the oxidation of alcohols to carbonyls. PCC is used because of its property of the selective oxidation of alcohols to carbonyls while many other reagents are less selective compared to PCC. Here the ethanol is oxidized into acetaldehyde and the reaction is shown below
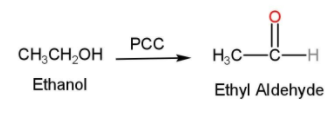
- In the next step, this ethyl aldehyde is treated with Grignard reagent with ether and water to form 2-ethyl 2-ethanol. Grignard reagent is generally formed by the interaction of an organic halide and magnesium usually in the presence of ether. They are generally used for the synthesis of alcohols from aldehydes and ketones. The reaction can be written as follows
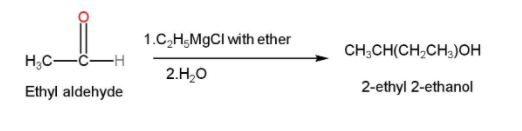
- The 2-ethyl 2-ethanol is then treated with acidified $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ or PCC for oxidation and our desired product Butan-2-one is formed. The reaction is shown below
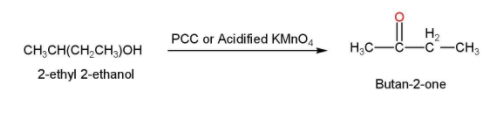
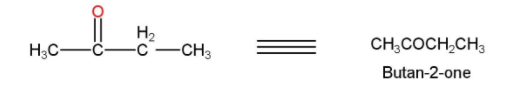
Thus, the acetic acid is converted into Butan-2-one.
Note: The usage of dry ether with lithium aluminum hydride has to be noted down. Since the hydride ion in lithium aluminum hydride is very basic, it reacts violently with water and for this reason it must be used in dry solvents like dry ether. This is the reason why we use dry ether with reagents like lithium aluminum hydride.
Complete step by step solution:
The acetic acid can be converted into Butan-2-one through the following steps.
- In the first step acetic acid is treated with Lithium aluminum hydride ($LiAl{{H}_{4}}$) with dry ether and water and ethanol is formed. Lithium aluminum hydride acts as a reducing agent here and it is used along with dry ether. The reaction is shown below

- In the next step, ethanol is treated with P.C.C and ethyl aldehyde (acetaldehyde or $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$) is formed. PCC is Pyridinium chlorochromate and is used in organic synthesis for the oxidation of alcohols to carbonyls. PCC is used because of its property of the selective oxidation of alcohols to carbonyls while many other reagents are less selective compared to PCC. Here the ethanol is oxidized into acetaldehyde and the reaction is shown below

- In the next step, this ethyl aldehyde is treated with Grignard reagent with ether and water to form 2-ethyl 2-ethanol. Grignard reagent is generally formed by the interaction of an organic halide and magnesium usually in the presence of ether. They are generally used for the synthesis of alcohols from aldehydes and ketones. The reaction can be written as follows

- The 2-ethyl 2-ethanol is then treated with acidified $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ or PCC for oxidation and our desired product Butan-2-one is formed. The reaction is shown below


Thus, the acetic acid is converted into Butan-2-one.
Note: The usage of dry ether with lithium aluminum hydride has to be noted down. Since the hydride ion in lithium aluminum hydride is very basic, it reacts violently with water and for this reason it must be used in dry solvents like dry ether. This is the reason why we use dry ether with reagents like lithium aluminum hydride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




