
Convex mirror has virtual focus or concave mirror has real focus.
a) True
b) False
Answer
534.6k+ views
Hint: First work is to make the diagram for observing rays, how and where they meet. Rays cannot go behind the mirror as on the backside, polishing will be there, so rays cannot penetrate through that shading part but in convex mirror case, rays seem to be meet in virtuality.
Complete answer:
A convex mirror has a focus behind the mirror, and a concave mirror has focus in front of the mirror. When parallel rays fall on the convex mirror, they meet at the focus behind the mirror; it seems like they meet virtually. In this case, a Virtual image will form. When parallel rays fall on the concave mirror, they meet at the focus in front of the mirror; they meet in reality. In this case, a Real or virtual image will be formed.
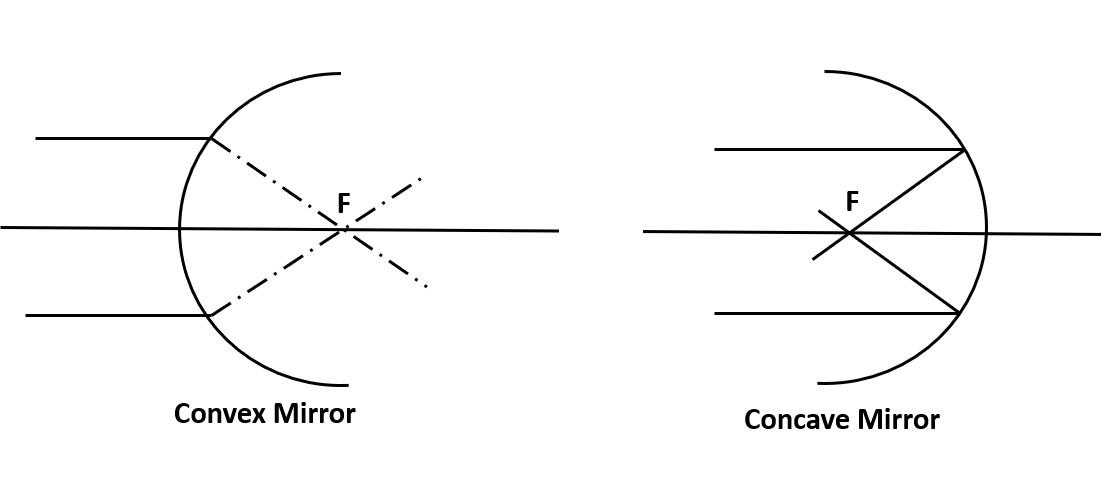
The reflective surface of the convex mirror is bent outwards. It produces a virtual image after reflecting from the mirror; the ray of light meets a specific point. The image produced is vertical and decreased in size concerning the object.
A concave mirror reflecting surface is bent inward to focus, i.e., away from the light source. When the curve bounces the light up to a particular area, they form an image.
It is true that a convex mirror has virtual focus or a concave mirror has real focus.
Option (a) is correct.
Additional Information:
The concave mirror can reflect images by two methods:
When the object is nearer to the mirror, the image produced will appear higher, and a virtual image is formed. When the object is distant from the mirror, the image formed will appear short, and an actual image is formed.
Note:
A convex mirror is also identified as a diverging mirror, as the light beam arising from the source will radiate and diverge. On the other hand, a concave mirror is a converging mirror; when a parallel light beam comes on the mirror, the mirror will radiate and converge.
Complete answer:
A convex mirror has a focus behind the mirror, and a concave mirror has focus in front of the mirror. When parallel rays fall on the convex mirror, they meet at the focus behind the mirror; it seems like they meet virtually. In this case, a Virtual image will form. When parallel rays fall on the concave mirror, they meet at the focus in front of the mirror; they meet in reality. In this case, a Real or virtual image will be formed.

The reflective surface of the convex mirror is bent outwards. It produces a virtual image after reflecting from the mirror; the ray of light meets a specific point. The image produced is vertical and decreased in size concerning the object.
A concave mirror reflecting surface is bent inward to focus, i.e., away from the light source. When the curve bounces the light up to a particular area, they form an image.
It is true that a convex mirror has virtual focus or a concave mirror has real focus.
Option (a) is correct.
Additional Information:
The concave mirror can reflect images by two methods:
When the object is nearer to the mirror, the image produced will appear higher, and a virtual image is formed. When the object is distant from the mirror, the image formed will appear short, and an actual image is formed.
Note:
A convex mirror is also identified as a diverging mirror, as the light beam arising from the source will radiate and diverge. On the other hand, a concave mirror is a converging mirror; when a parallel light beam comes on the mirror, the mirror will radiate and converge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




