
How is copper extracted from its sulfide ore? Explain the various steps supported by the chemical equation. Draw labeled diagram of the electrolytic refining of copper.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Copper sulfide is oxidized with a metal that is more reactive than the copper element. Smelting is also involved in this process. Arsenic and antimony are the impurities that are present during the refining.
Complete answer:
The sulfide ore i.e., copper pyrites after the concentration by froth flotation process is roasted in a reverberatory furnace when copper pyrites are converted into a mixture of \[FeS\]\[C{{u}_{2}}S\] and which, in turn, are partially oxidized.
\[2FeCu{{S}_{2}} + {{O}_{2}}\to C{{u}_{2}}S + 2FeS + S{{O}_{2}}\]
\[2FeS+3{{O}_{2}}\to 2FeO+2S{{O}_{2}}\]
\[2C{{u}_{2}}S + 3{{O}_{2}}\to 2C{{u}_{2}}O + 2S{{O}_{2}}\]
Since iron is more reactive than the copper, \[FeS\] is preferentially oxidized to \[FeO\] than \[C{{u}_{2}}S\] to \[C{{u}_{2}}O\]. If at all any \[C{{u}_{2}}O\] is formed, it combines with \[FeS\] and is changed back to \[C{{u}_{2}}S\].
\[C{{u}_{2}}O + FeS\to C{{u}_{2}}S + FeO\]
Thus, the roasted ore mainly contains \[C{{u}_{2}}S\] and along with unreacted \[FeS\]
The roasted ore is then mixed with silica (flux) and some powdered coke and heated strongly in a blast furnace. This process is called smelting. During smelting combines with silica to form fusible ferrous silicate slag.
\[FeO + Si{{O}_{2}}\to FeSi{{O}_{3}}\]
At the temperature of the furnace, the entire mass melts, and two layers of molten mass are formed. The slag being lighter makes the upper layer which can be withdrawn from the slag whole from time to time. The lower molten layer is called copper matte. It chiefly consists of \[C{{u}_{2}}S\] and some unchanged \[FeS\].
Recovery of copper from matte:
To obtain pure copper from matte, the molten matte is transferred to a besimmer converter which is a pear-shaped furnace made up of steel and lined inside with silica. It is mounted on a horizontal axel and can be tilted in any position. It is fitted with small pipes called tuyeres through which a blast of hot air and fine sand is admitted.
During the process of bessemerization, any sulfur, arsenic, and antimony still present as an impurity in matte escape as their respective volatile oxides are\[FeS\] is oxidized to\[FeO\] which combines with silica from \[FeSi{{O}_{3}}\] slag.
\[2FeS + 3{{O}_{2}}\to 2FeO + 2S{{O}_{2}}\]; \[FeO + Si{{O}_{2}}\to FeSi{{O}_{3}}(slag)\]
The slag thus melts and floats on the top of the molten mass and is removed. When the whole of iron has been removed as slag, some of the cuprous sulfides undergo oxidation to form a cuprous oxide which reacts with cuprous sulfide to form copper metal.
\[2C{{u}_{2}}S + 3{{O}_{2}}\to 2C{{u}_{2}}O+2S{{O}_{2}}\]; \[2C{{u}_{2}}O + C{{u}_{2}}S\to 6Cu + S{{O}_{2}}\]
The diagram of electrolytic refining is given below:
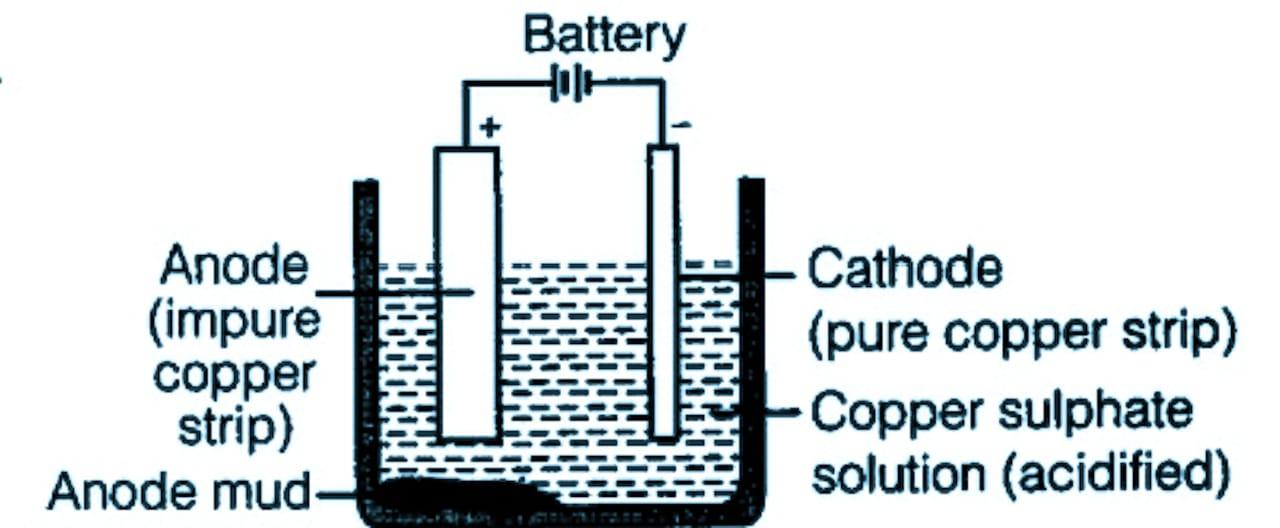
Note: There are two processes of converting copper sulfide to copper. The sulfide is converted to oxide then the oxide is converted into pure copper using coke as the reducing agent. The reducing agent is selected by observing the Ellingham diagram.
Complete answer:
The sulfide ore i.e., copper pyrites after the concentration by froth flotation process is roasted in a reverberatory furnace when copper pyrites are converted into a mixture of \[FeS\]\[C{{u}_{2}}S\] and which, in turn, are partially oxidized.
\[2FeCu{{S}_{2}} + {{O}_{2}}\to C{{u}_{2}}S + 2FeS + S{{O}_{2}}\]
\[2FeS+3{{O}_{2}}\to 2FeO+2S{{O}_{2}}\]
\[2C{{u}_{2}}S + 3{{O}_{2}}\to 2C{{u}_{2}}O + 2S{{O}_{2}}\]
Since iron is more reactive than the copper, \[FeS\] is preferentially oxidized to \[FeO\] than \[C{{u}_{2}}S\] to \[C{{u}_{2}}O\]. If at all any \[C{{u}_{2}}O\] is formed, it combines with \[FeS\] and is changed back to \[C{{u}_{2}}S\].
\[C{{u}_{2}}O + FeS\to C{{u}_{2}}S + FeO\]
Thus, the roasted ore mainly contains \[C{{u}_{2}}S\] and along with unreacted \[FeS\]
The roasted ore is then mixed with silica (flux) and some powdered coke and heated strongly in a blast furnace. This process is called smelting. During smelting combines with silica to form fusible ferrous silicate slag.
\[FeO + Si{{O}_{2}}\to FeSi{{O}_{3}}\]
At the temperature of the furnace, the entire mass melts, and two layers of molten mass are formed. The slag being lighter makes the upper layer which can be withdrawn from the slag whole from time to time. The lower molten layer is called copper matte. It chiefly consists of \[C{{u}_{2}}S\] and some unchanged \[FeS\].
Recovery of copper from matte:
To obtain pure copper from matte, the molten matte is transferred to a besimmer converter which is a pear-shaped furnace made up of steel and lined inside with silica. It is mounted on a horizontal axel and can be tilted in any position. It is fitted with small pipes called tuyeres through which a blast of hot air and fine sand is admitted.
During the process of bessemerization, any sulfur, arsenic, and antimony still present as an impurity in matte escape as their respective volatile oxides are\[FeS\] is oxidized to\[FeO\] which combines with silica from \[FeSi{{O}_{3}}\] slag.
\[2FeS + 3{{O}_{2}}\to 2FeO + 2S{{O}_{2}}\]; \[FeO + Si{{O}_{2}}\to FeSi{{O}_{3}}(slag)\]
The slag thus melts and floats on the top of the molten mass and is removed. When the whole of iron has been removed as slag, some of the cuprous sulfides undergo oxidation to form a cuprous oxide which reacts with cuprous sulfide to form copper metal.
\[2C{{u}_{2}}S + 3{{O}_{2}}\to 2C{{u}_{2}}O+2S{{O}_{2}}\]; \[2C{{u}_{2}}O + C{{u}_{2}}S\to 6Cu + S{{O}_{2}}\]
The diagram of electrolytic refining is given below:

Note: There are two processes of converting copper sulfide to copper. The sulfide is converted to oxide then the oxide is converted into pure copper using coke as the reducing agent. The reducing agent is selected by observing the Ellingham diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




